NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 – Free PDF Download
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry are useful for students as they help them in scoring high marks in the examination. These NCERT Solutions contain detailed step-by-step explanations of all the problems that come under the Chapter 4 Practical Geometry of the Class 8 NCERT Textbook. By understanding the concepts used in NCERT Solutions for Class 8, students will be able to clear all their doubts related to Practical Geometry. These solutions are prepared by subject matter experts at BYJU’S, describing the complete method of solving problems.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 – Practical Geometry
Access Answers of Maths NCERT Class 8 Chapter 4 – Practical Geometry
Exercise 4.1 Page: 60
1. Construct the following quadrilaterals.
(i) Quadrilateral ABCD AB = 4.5 cm
BC = 5.5 cm
CD = 4 cm AD = 6 cm AC = 7 cm
Solution:
 The rough sketch of the quadrilateral ABCD can be drawn as follows.
The rough sketch of the quadrilateral ABCD can be drawn as follows.
(1) ∆ABC can be constructed by using the given measurements as follows.

(2) Vertex D is 6 cm away from vertex A. Therefore, while taking A as the centre, draw an arc of radius 6 cm.

(3) Taking C as the centre, draw an arc of radius 4 cm, cutting the previous arc at point D. Joint D to A and C.

ABCD is the required quadrilateral.
(ii) Quadrilateral JUMP JU = 3.5 cm
UM = 4 cm MP = 5 cm PJ = 4.5 cm PU = 6.5 cm
Solution:
The rough sketch of the quadrilateral JUMP can be drawn as follows.
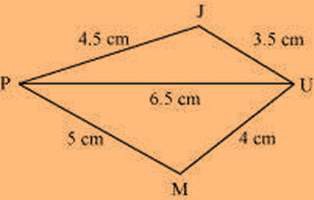
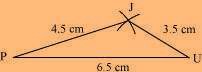
(1) ∆ JUP can be constructed by using the given measurements as follows.
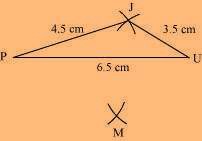
(2) Vertex M is 5 cm away from vertex P and 4 cm away from vertex U. Taking P and U as centres, draw arcs of radii 5 cm and 4 cm, respectively. Let the point of intersection be M.
(3) Join M to P and U.
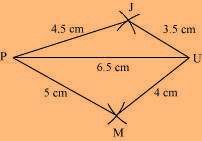
JUMP is the required quadrilateral.
(iii) Parallelogram MORE
OR = 6 cm
Solution:
RE = 4.5 cm
EO = 7.5
We know that opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length, and also, these are parallel to each other.
i.e., ME = OR, MO = ER
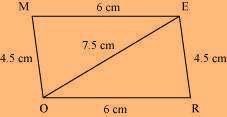 The rough sketch of the parallelogram MORE can be drawn as follows.
The rough sketch of the parallelogram MORE can be drawn as follows.
(1) ∆ EOR can be constructed by using the given measurements as follows.
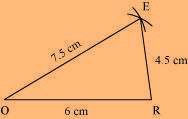
(2) Vertex M is 4.5 cm away from vertex O and 6 cm away from vertex E. Therefore, while taking O and E as centres, draw arcs of 4.5 cm radius and 6 cm radius, respectively. These will intersect each other at point M.
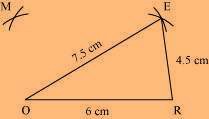
(3) Join M to O and E.
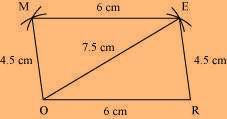
MORE is the required parallelogram.
(iv) Rhombus BEST
BE = 4.5 cm
ET = 6 cm
Solution:
We know that all sides of a rhombus are of the same measure. Hence, BE = ES = ST = TB
The rough sketch of the rhombus BEST can be drawn as follows.
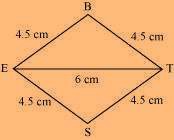
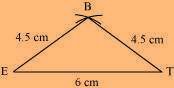 (1) ∆ BET can be constructed by using the given measurements as follows.
(1) ∆ BET can be constructed by using the given measurements as follows.
(2) Vertex S is 4.5 cm away from vertex E and also from vertex T. Therefore, while taking E and T as centres, draw arcs of 4.5 cm radius, which will intersect each other at point S.
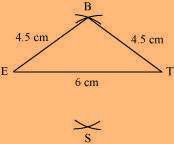
(3) Join S to E and T.
NCERT Solution For Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Image
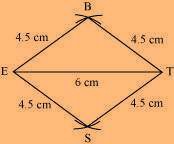
BEST is the required rhombus.
Exercise 4.2 Page: 62
1. Construct the following quadrilaterals.
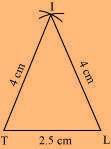
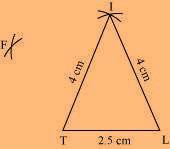
(i) Quadrilateral LIFT LI = 4 cm
IF = 3 cm TL = 2.5 cm LF = 4.5 cm
IT = 4 cm
Solution:
A rough sketch of the quadrilateral LIFT can be drawn as follows.
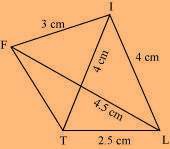
(1) ∆ ITL can be constructed by using the given measurements as follows.
(2) Vertex F is 4.5 cm away from vertex L and 3 cm away from vertex I. ∴ while taking L and I as centres, draw arcs of 4.5 cm radius and 3 cm radius, respectively, which will intersect each other at point F.
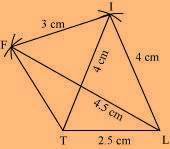 (3) Join F to T and F to I.
(3) Join F to T and F to I.
LIFT is the required quadrilateral.
(ii) Quadrilateral GOLD OL = 7.5 cm
GL = 6 cm GD = 6 cm LD = 5 cm OD = 10 cm
Solution:
The rough sketch of the quadrilateral GOLD can be drawn as follows.
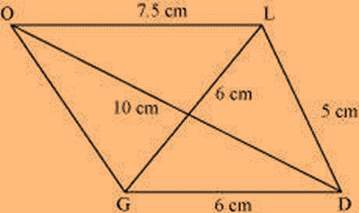
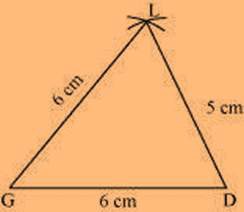
(1) ∆ GDL can be constructed by using the given measurements as follows.
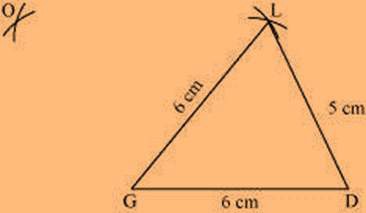
(2) Vertex O is 10 cm away from vertex D and 7.5 cm away from vertex L. Therefore, while taking D and L as centres, draw arcs of 10 cm radius and 7.5 cm radius, respectively. These will intersect each other at point O.
(3) Join O to G and L.
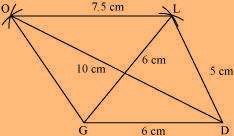
GOLD is the required quadrilateral.
(iii) Rhombus BEND
BN = 5.6 cm
DE = 6.5 cm
Solution:
We know that the diagonals of a rhombus always bisect each other at 90º.
Let us assume that these are intersecting each other at point O in this rhombus. Hence, EO = OD = 3.25 cm
The rough sketch of the rhombus BEND can be drawn as follows.
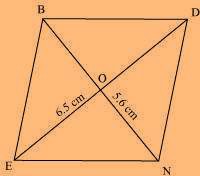
(1) Draw a line segment BN of 5.6 cm, and also draw its perpendicular bisector. Let it intersect the line segment BN at point O.
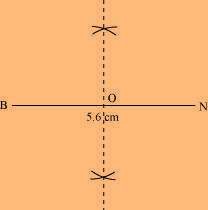
(2) Taking O as the centre, draw arcs of 3.25 cm radius to intersect the perpendicular bisector at points D and E.
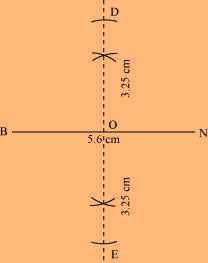
(3) Join points D and E to points B and N.
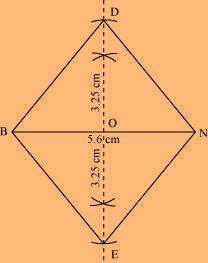
BEND is the required quadrilateral.
Exercise 4.3 Page: 64
1. Construct the following quadrilaterals.
(i) Quadrilateral MORE MO = 6 cm
OR = 4.5 cm
∠M = 60°
∠O = 105°
∠R = 105°
Solution:
Rough Figure:

 (1) Draw a line segment MO of 6 cm and an angle of 105º at point O. As vertex R is 4.5 cm away from the vertex O, cut a line segment OR of 4.5 cm from this ray.
(1) Draw a line segment MO of 6 cm and an angle of 105º at point O. As vertex R is 4.5 cm away from the vertex O, cut a line segment OR of 4.5 cm from this ray.
(2) Again, draw an angle of 105º at point R.

(3) Draw an angle of 60º at point M. Let this ray meet the previously drawn ray from R at point E.

MORE is the required quadrilateral.
(ii) Quadrilateral PLAN PL = 4 cm
LA = 6.5 cm
∠P = 90°
∠A = 110°
∠N = 85°
Solution:
The sum of the angles of a quadrilateral is 360°. In quadrilateral PLAN,
∠P + ∠L + ∠A + ∠N = 360° 90° + ∠L + 110° + 85° = 360°
285° + ∠L = 360°
∠L = 360° − 285° = 75°
Rough Figure:

(1) Draw a line segment PL of 4 cm and draw an angle of 75º at point L. As vertex A is 6.5 cm away from vertex L, cut a line segment LA of 6.5 cm from this ray.

(2) Again, draw an angle of 110º at point A.

(3) Draw an angle of 90º at point P. This ray will meet the previously drawn ray from A at point N.

PLAN is the required quadrilateral.
(iii) Parallelogram HEAR HE = 5 cm
EA = 6 cm
∠R = 85°
Solution:
Rough Figure:

(1) Draw a line segment HE of 5 cm and an angle of 85º at point E. As vertex A is 6 cm away from vertex E, cut a line segment EA of 6 cm from this ray.

(2) Vertex R is 6 cm and 5 cm away from vertex H and A, respectively. By taking radii as 6 cm and 5 cm, draw arcs from points H and A, respectively. These will intersect each other at point R.

(3) Join R to H and A.

HEAR is the required quadrilateral.
(iv) Rectangle OKAY
OK = 7 cm KA = 5 cm
Solution:
Rough Figure:

(1) Draw a line segment OK of 7 cm and an angle of 90º at point K. As vertex A is 5 cm away from vertex K, cut a line segment KA of 5 cm from this ray.

(2) Vertex Y is 5 cm and 7 cm away from vertex O and A, respectively. By taking
radii as 5 cm and 7 cm, draw arcs from points O and A, respectively. These will intersect each other at point Y.

(3) Join Y to A and O.

OKAY is the required quadrilateral.
Exercise 4.4 Page: 67
1. Construct the following quadrilaterals,
(i) Quadrilateral DEAR DE = 4 cm
EA = 5 cm AR
= 4.5 cm
∠E = 60°
∠A = 90°
Solution:
Rough Figure:

(1) Draw a line segment DE of 4 cm and an angle of 60º at point E. As vertex A is 5 cm away from vertex E, cut a line segment EA of 5 cm from this ray.

(2) Again, draw an angle of 90º at point A. As vertex R is 4.5 cm away from vertex A, cut a line segment RA of 4.5 cm from this ray.

 (3) Join D to R.
(3) Join D to R.
DEAR is the required quadrilateral.
(ii) Quadrilateral TRUE TR = 3.5 cm
RU = 3 cm UE = 4 cm
∠R = 75°
∠U = 120°
Solution:
Rough Figure:

(1) Draw a line segment RU of 3 cm and an angle of 120º at point U. As vertex E is 4 cm away from vertex U, cut a line segment UE of 4 cm from this ray.

(2) Next, draw an angle of 75º at point R. As vertex T is 3.5 cm away from vertex R, cut a line segment RT of 3.5 cm from this ray.

(3) Join T to E.

TRUE is the required quadrilateral.
Exercise 4.5 Page: 68
Draw the following:
1. The square READ with RE = 5.1 cm
Solution:
All the sides of a square are of the same measure, and also, all the interior angles of a square are 90º measure. Therefore, the given square READ can be drawn as follows.
 Rough Figure:
Rough Figure:
(1) Draw a line segment RE of 5.1 cm and an angle of 90º at points R and E.

(2) As vertex A and D are 5.1 cm away from vertex E and R, respectively, cut line segments EA and RD, each of 5.1 cm from these rays.

(3) Join D to A.

READ is the required square.
2. A rhombus whose diagonals are 5.2 cm and 6.4 cm long. Solution:
In a rhombus, diagonals bisect each other at 90º. ∴, the given rhombus ABCD can be drawn as follows.
 Rough Figure:
Rough Figure:
(1) Draw a line segment AC of 5.2 cm and draw its perpendicular bisector. Let it intersect the line segment AC at point O.

(2) Draw arcs of 6.4/2 = 3.2 on both sides of this perpendicular bisector. Let the arcs intersect the perpendicular bisector at points B and D.

(3) Join points B and D with points A and C.

ABCD is the required rhombus.
3. A rectangle with adjacent sides of length 5 cm and 4 cm. Solution:
Opposite sides of a rectangle have lengths of the same measure, and also, all the interior angles of a rectangle are 90º measure. The given rectangle ABCD may be drawn as follows.
Rough figure:

(1) Draw a line segment AB of 5 cm and an angle of 90º at points A and B.

(2) As vertex C and D are 4 cm away from vertex B and A, respectively, cut line segments AD and BC, each of 4 cm, from these rays.

(3) Join D to C.

ABCD is the required rectangle.
4. A parallelogram OKAY where OK = 5.5 cm and KA = 4.2 cm. Solution:
Opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal and parallel to each other. The given parallelogram OKAY can be drawn as follows.
Rough Figure:

(1) Draw a line segment OK of 5.5 cm and a ray at point K at a convenient angle.

(2) Draw a ray at point O parallel to the ray at K. As the vertices A and Y are 4.2 cm away from the vertices K and O, respectively, cut line segments KA and OY, each of 4.2 cm, from these rays.

(3) Join Y to A.

OKAY is the required rectangle.
| Also Access |
| NCERT Exemplar for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 |
| CBSE Notes for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 |
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 – Practical Geometry Summary
The major concepts covered in Chapter 4 – Practical Geometry include 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Constructing a Quadrilateral 4.2.1 When the lengths of four sides and a diagonal are given 4.2.2 When two diagonals and three sides are given 4.2.3 When two adjacent sides and three angles are known 4.2.4 When three sides and two included angles are given 4.3 Some special cases.
Exercise 4.1 Solutions 1 Question
Exercise 4.2 Solutions 1 Question
Exercise 4.3 Solutions 1 Question
Exercise 4.4 Solutions 1 Question
Exercise 4.5 Solutions 4 Questions
Chapter 4 of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths discusses the following:
- Five measurements can determine a quadrilateral uniquely.
- A quadrilateral can be constructed uniquely if the lengths of its four sides and a diagonal are given.
- A quadrilateral can be constructed uniquely if its two diagonals and three sides are known.
- A quadrilateral can be constructed uniquely if its two adjacent sides and three angles are known.
- A quadrilateral can be constructed uniquely if its three sides and two included angles are given.
Learning the chapter Practical Geometry enables the students to:
- Construction of Quadrilaterals:
- Given four sides and one diagonal
- Three sides and two diagonals
- Three sides and two included angles
- Two adjacent sides and three angles
Disclaimer:
Dropped Topics – 4.1 Introduction, 4.2 Construction of quadrilateral and 4.3 Some special cases.


























Byju’s link is very helpful for write science and maths notes thank you