According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been renumbered as Chapter 3.
Introduction to Coal and Petroleum
Energy
Energy can be extracted from natural resources in many forms, and it can be transferred from one body to another in the form of heat or work.
To know more about Energy, visit here.
Types of Energy
Some different types of energies are:
- Mechanical energy
- Chemical energy
- Thermal energy
- Nuclear energy
- Solar energy
- Wind energy
- Sound energy
- Electrical energy
To know more about “Different Types of Energy”, visit here.
Energy Conversion from One Form to Another
- Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another.
- For example, In a microphone, sound energy is converted into electrical energy.
Natural Resources
Natural resources are the resources that are provided by the earth. Two types of natural resources are as follows.
- Inexhaustible/Renewable natural resources are present in unlimited quantity in nature, for example, Sunlight and Wind.
- Exhaustible/Non-Renewable natural resources are present in limited quantity in nature. For example, Coal and Petroleum.
To know more about Natural Resources, visit here.
Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are the exhaustible resources that are formed from the decomposition of dead organic matter, for example, Coal and Natural gas.
For more information on History of Fuel, watch the below video

To know more about Fossil Fuels, visit here.
Energy Stored in Fossil Fuels
Energy stored in fossil fuels are derived from decayed animals and plants that have existed for millions of years.
Energy Utilisation from Fossil Fuels
- 40% of energy is used by the industries
- 24% of energy is used by the Transportation sector
- 6% of energy is used by farms
- 30% of energy is used for domestic and other purposes.
Coal Formation
Coal
Coal is a black-coloured fossil fuel which is extracted from the ground and is used as a fuel for different purposes.
Peat
Peat is a dark fibrous fuel composed of partly decomposed plant matter. It is the first stage in the formation of coal.
Formation of Coal
Under high pressure and temperature, the dead vegetation gets converted into coal. This process is called carbonisation.
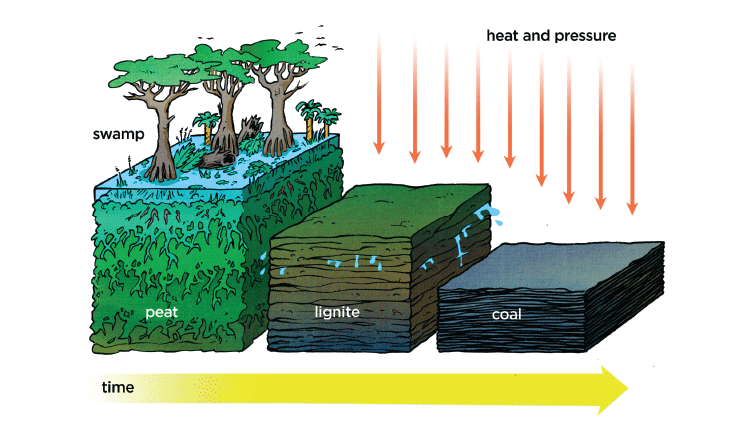
For more information on How Coal is Formed? watch the below video

To know more about Formation of Coal, visit here.
Types of Coal
Types of Coal
The four types of coals are as follows.
- Anthracite
- Bituminous
- Sub-bituminous
- Lignite
Destructive Distillation of Coal
Destructive distillation of coal is the process of heating coal in the absence of air. By-products formed in this process are coke, coal tar, ammonia, and coal gas.
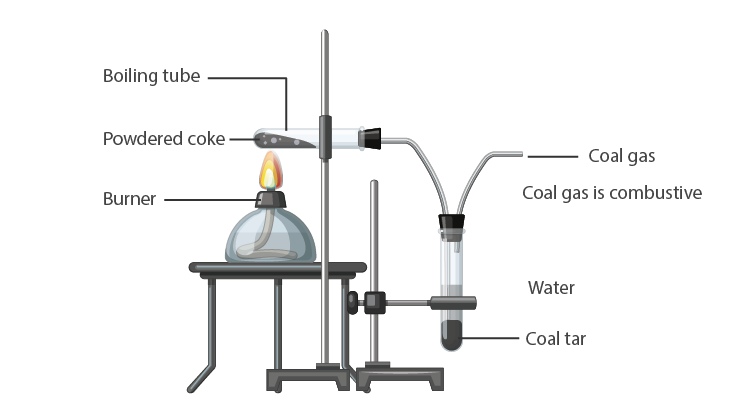
For more information on Destructive Distillation of Coal, watch the below video

Coal Tar
Coal tar is a black thick liquid with an unpleasant smell and is used as a starting material for manufacturing various substances.
Coal Gas
Coal gas is a fuel produced during the destructive distillation of coal. It is used as a fuel in many industries.
Ammonia Liquor
Ammonia liquor or ammonium hydroxide is one of the by-products formed during the destructive distillation of coal. It is used to make fertilizers.
Coke
Coke is a black-coloured substance and pure form of carbon used for manufacturing steel and extraction of metals.
Extraction of Oil
Oil Wells and Reservoirs
- An oil well is used to bring the oil or other hydrocarbons to the surface. It is a long hole created into the earth.
- An oil reservoir is an underground lake of oil composed of hydrocarbons.
Extraction of Oils
Extraction of oil is the process by which usable oil is extracted from the earth’s surface location.
Determining the Characteristics of Oil Reservoirs
Characteristics of oil reservoirs are:
- Devices like geophones are used to determine the presence of oil in rocks by identifying the reflected sound waves.
- Exploratory wells are used to extract oil samples.
Primary Production of Oil
The natural flow of oil is called the primary production of the oil. It can persist for days or years.
Secondary Recovery Process
The secondary process can be carried out by the process of:
- Water flooding
- Injecting chemicals into the reservoir.
- Injecting carbon dioxide into the reservoir.
- Microbially enhanced oil recovery
Fractional Distillation
Crude Oil
Crude oil is a type of fossil fuel, which is an unrefined petroleum product composed of hydrocarbons.
For more information on How Crude Oil is Processed? watch the below Video

Boiling Point and Vaporisation
- The boiling point is the temperature when the pressure exerted by surroundings on liquid & pressure of the liquid becomes equal.
- Vaporisation is the process of changing the state from liquid to gas.
Oil Refining or Fractional Distillation
Oil refining or fractional distillation is the process of separating liquids with different boiling points at different temperatures using fractional columns.
Uses of Products Obtained in Fractional Distillation
Products and their uses:
- LPG: Fuel for home and industry
- Petrol and diesel: Motor and aviation fuel
- Kerosene: Fuel for stoves and lamps
- Lubricating oil: Lubrication
- Bitumen: Used to make paints
- Paraffin wax: Used to make ointments, candles
To know more about Fractional Distillation, visit here.
Shortage of Petroleum and Tips for Its Conservation
- Petroleum should be carefully used to avoid its shortage.
- PCRA proposed some methods to save petrol and diesel, like driving vehicles at constant speed.
Natural Gas
Hazards and Estimates of Fossil Fuels
Hazards caused due to excessive use of fossil fuels:
- Air pollution
- Global warming
Estimates of fossil fuel:
- Coal may persist for another century and petroleum for another 40 years.
For more information on Effect of Burning Fuels on the Environment, watch the below video

Natural Gas
Natural gas is a colourless, odourless fossil fuel which is transported through pipes from one place to another.
To know more about Natural Gas, visit here.
CNG and Its Advantages
Natural gas stored under high pressure is known as CNG.
The advantages of CNG are are follows.
- It’s a Cleaner fuel
- It’s less polluting
- It can be used directly for burning.
Occurrences of Natural Gas in India
Natural gas is found in parts of Tripura, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Tamilnadu, and Andhra Pradesh.
| Also Access |
| NCERT Solutions for class 8 Science Chapter 5 |
| NCERT Exemplar for class 8 Science Chapter 5 |
Learn more about coal and petroleum and other related topics, including NCERT class 8 Science notes, at BYJU’S.
Also, Read
| Fossil Fuels: Coal and Petroleum | Formation of Fossil Fuels |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
What is fossil fuel?
Fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed underground from the remains of dead plants and animals that humans extract and burn to release energy for use.
What are the types of fossil fuels?
The types of fossil fuels are Petroleum, Coal, Natural gas and Orimulsion
What are the uses of fractional distillation?
The uses of fractional distillation are that it enables component separation into different phases and purification of organic compounds
Comments