The National Highways Authority of India or NHAI is the nodal agency of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways in India. Students preparing for the IAS Exam must be aware of this topic and can expect questions in UPSC Prelims as well as USPC Mains.
The National Highways Authority of India can be associated with GS Paper III under Indian Economy (Transportation). Since ‘Indian Economy’ is an important part of General Studies paper-3 in the UPSC Syllabus, aspirants must know about the topic.
Aspirants can go through the following links to prepare for the upcoming UPSC exam even better:
| Major National Highways in India | Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) |
| Sagarmala Project – Sagarmala Seaplane Services | Bharatmala Pariyojana |
| Atal Tunnel | New Financing Model for Highway Projects |
National Highways Authority of India or NHAI
- National Highways Authority of India was formed under the NHAI Act in 1988.
- It is an autonomous organization that looks after the management of the complete network of National Highways in the country.
- Headquarters of the NHAI – New Delhi.
- It operates under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
- NHAI signed an MoU with the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the North East Centre For Technology Application and Research (NECTAR) in 2016 that allowed the use of spatial technology for highways monitoring.
- It has been entrusted with the National Highways Development Project, which along with other minor projects, has vested in it 50329 km of National Highways for development, maintenance and management.
- As of July, 2021, the total length of National Highways (including expressways) in the country is 1,32,499 km. While Highways/Expressways constitute only about 1.7% of the length of all roads, they carry about 40% of the road traffic.
- Mandate:
- NHAI is mandated to implement the National Highways Development Project (NHDP) which is India’s largest-ever Highways Project in a phased manner and accordingly government of India has launched many initiatives to strengthen the National Highways.
- Considering the high road traffic in Highways, and increasing passenger and freight traffic, it becomes essential to improve the road network in the country.
Functions of NHAI
- Developing, maintaining and managing National Highways (NH) across the country.
- Collecting fees/tolls on NH, regulating and controlling the plying of vehicles on NH for proper management.
- Developing and providing consultancy and construction services on a national and international level. Also, conducting research activities that help develop, maintain and manage highways or other facilities thereat.
- Advising the Central government on issues related to NH.
- Formulating and implementing schemes for NH development.
- Constructing offices and residential buildings for NHAI employees.
- Providing facilities and amenities to NH users necessary for the smooth flow of traffic on such highways.
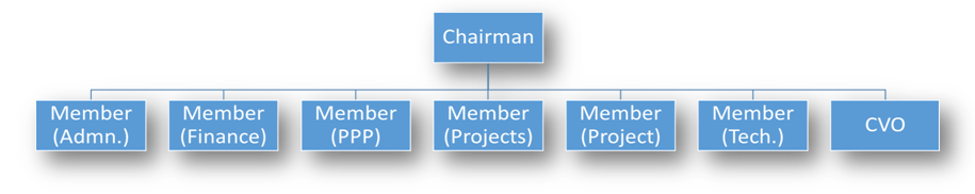
Organisational Structure of NHAI
The Authority consists of a full-time Chairman, and not more than five full-time Members and four part-time Members who are appointed by the Central Government.
The below figure shows the present organisational structure of NHAI:
Green Highways Policy – 2015
- The policy aims to promote greening of highway corridors with the participation of the community, farmers, private sector, NGOs, and government institutions.
- The policy envisages a strong monitoring mechanism in place by using ISRO’s Bhuvan and GAGAN satellite systems.
- Every planted tree will be counted and auditing will be done.
- The project aims to make India pollution-free, curtail the number of road accidents and provide dignified employment to local people and communities.
Features of Green Highways Policy
- Development of eco-friendly NH corridors across India and promoting greening is a major concern of this project.
- It also includes the participation of farmers, government institutions including the Forest Department and the private sector.
- Objectives:
- Reducing the impact of Air Pollution and Dust by planting trees and shrubs along the NH.
- The trees also act as a natural sink for air pollutants and arrest soil erosion at the embankment slopes.
NHAI:- Download PDF Here
Related Links:

Comments