CNA 5th April 2021:- Download PDF Here
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS 1 Related B. GS 2 Related POLITY AND GOVERNANCE 1. ₹25,586 crore paid out under loan scheme C. GS 3 Related DISASTER MANAGEMENT 1. Over 41 dead in Indonesia flash floods DEFENCE 1. Another batch of Rafale jets to fly in by mid-May D. GS 4 Related E. Editorials GOVERNANCE 1. A good start 2. The Kerala Model at the crossroads INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS 1. A walk-back SOCIAL ISSUES 1. A road map for tolerance F. Prelims Facts 1. NASA’s chopper dropped on Mars’ surface G. Tidbits 1. Philippines accuses China of plans to occupy more areas 2. PSU banks may have to take ₹2,000 crore hit 3. Gender Disparity Deepens H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS 1 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
B. GS 2 Related
Category: POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. ₹25,586 crore paid out under loan scheme
Context:
Banks have sanctioned more than ₹25,000 crore to over 1.14 lakh accounts under the Stand-Up India Scheme.
Stand Up India Scheme:
- The Stand-Up India scheme was launched by the government to promote entrepreneurship among women, Scheduled Castes (SC) & Scheduled Tribes (ST).
- The scheme was launched on 5th April 2016.
- As per the scheme, bank loans between ₹10 lakh and ₹1 crore are routed to at least one SC or ST borrower, and at least one woman borrower, by each branch of the scheduled commercial banks.
Details:
- Official data suggest that women-led enterprises have dominated the sanctions so far under the scheme.
- The scheme has now been extended till 2025.
Read more on Stand-up India Scheme.
C. GS 3 Related
1. Over 41 dead in Indonesia flash floods
Context:
According to Indonesia’s disaster relief agency, landslips and flash floods from torrential rain in eastern Indonesia has killed at least 41 people and displaced thousands.
What are Flash Floods?
- A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions.
- It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, tropical storm, or meltwater from ice or snow flowing over ice sheets or snowfields.
- Flash floods may also occur after the collapse of a natural ice or debris dam, or a human structure such as a man-made dam.
- Flash Floods are highly localized events of short duration with a very high peak and usually have less than six hours between the occurrence of the rainfall and peak flood.
Concerns:
- Flash floods induce severe impacts in both the built and the natural environment. Especially within urban areas, the effects of flash floods can be catastrophic and show extensive diversity, ranging from damages in buildings and infrastructure to impacts on vegetation, human lives and livestock.
- There is a general lack of flash flood warning capabilities and capacities of the nations across the world.
- In 2020, India launched Flash Flood Guidance services for South Asian countries — India, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Nepal and Sri Lanka — to issue impact-based forecasting of floods, which are very sudden and of short duration, at watershed and also city level.
- The Flash Flood Guidance is a robust system designed to provide the necessary products in real-time to support the development of warnings for flash floods about 6- 12 hours in advance at the watershed level with a resolution of 4kmx4km for the Flash Flood prone South Asian countries.
- The guidance for flash floods in the form of threats (6 hours in advance) and risks (24 hours in advance) will be provided by the Regional Centre to the National Meteorological and Hydrological Services, National and State Disaster Management Authorities and all other stakeholders for taking necessary mitigation measures to reduce the loss of life and property.
1. Another batch of Rafale jets to fly in by mid-May
Context:
India will receive another 8 to 9 Rafale jets from France by mid-May 2021 completing the first squadron of the fighters in the Indian Air Force (IAF).
Read more on Rafale Fighter Jets.
Also read 15th October 2019 Comprehensive News Analysis.
D. GS 4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
1. A good start
Context:
- The recent notification of the National Policy for Rare Diseases, 2021.
Background:
Rare diseases:
- Rare diseases are broadly defined as diseases that infrequently occur in a population, and three markers are used — the total number of people with the disease, its prevalence, and the availability/non-availability of treatment options. WHO defines a rare disease as having a frequency of less than 6.5-10 per 10,000 people.
- As per an estimate, there are 7,000 known rare diseases with an estimated 300 million patients in the world; 70 million are in India.
- Rare Diseases include inherited cancers, autoimmune disorders, congenital malformations, Hirschsprung’s disease, Gaucher disease, cystic fibrosis, muscular dystrophies and Lysosomal Storage Disorders (LSDs).
Significance:
- The National Policy on Rare Diseases is a good step forward based on the following aspects.
Principle of inclusion:
- The National Policy for Rare Diseases 2021 is pegged on the principle of inclusion of every single citizen.
- It is binding on a welfare state to secure the wellbeing of every single citizen, particularly those unable to help themselves, irrespective of whether they constitute a critical mass or not.
Financial support:
- The policy offers financial support for the one-time treatment of up to Rs. 20 lakh and also introduces a crowdfunding mechanism.
- Up until now, it was mainly patient support groups that used to work towards drumming up funding assistance for the treatment of rare diseases.
Early detection:
- The policy provides for early detection. Early detection is critical for management of the rare diseases.
Concerns:
- As per the Policy, diseases such as LSD for which definitive treatment is available, but costs are prohibitive, have been categorised lower and hence would qualify for lower support from the government.
- No funding has been allocated for the immediate and lifelong treatment needs, for therapies already approved by the Drugs Controller General of India.
Way forward:
Fund support:
- The Centre can set aside a substantial corpus to fund life-saving treatments, even as it rolls out the policy. Fund support from the government is vital for the continual treatment of those with rare diseases.
- The central government can extend the cost-sharing agreements that it has worked out with Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka, with other States too, which will help it reduce its costs by half.
Medical efforts:
- There is a need to support the development of and commercialisation of drugs for treatment, and improve funding for research on rare diseases.
2. The Kerala Model at the crossroads
Context:
- The article evaluates the Kerala Model of economic development.
Background:
Kerala Model of economic development:
- The ‘Kerala Model’ is based on the redistributive principle of growth where there is a marked emphasis on development over growth. The state interventions which rely on widespread participation of people are aimed at improving the people’s material conditions of living.
Concerns:
- Some economists have argued that the slow-growing State would not have the money to continue financing its welfare programmes.
- Economic stagnation in the 1970s and 1980s led many observers to predict the collapse of the Kerala model.
Counter arguments:
Significant economic growth:
- As against the popular misconception that Kerala has not had much economic growth, the author argues that Kerala has witnessed observable growth.
- The author points out a significant growth in agricultural incomes, services sector, secondary sector (which includes manufacturing, construction, etc.). While Kerala’s per capita income was almost 10% lower than the all-India figure in 1989-90, it was 65% higher than the all-India figure in 2019-20.
Social development:
- All along, Kerala’s education and health indicators have continued to improve, and its social security programmes have continued to expand.
- Kerala has registered impressive achievements in human development in the area of health and education.
Investments in infrastructure:
- There have been major investments by the state in infrastructure development.
- Apart from schools and hospitals, KIIFB funding is being used to build economic infrastructure such as roads, bridges, industrial parks, the massive public sector Internet project K-FON, or the Kerala Fibre Optic Network, and TransGrid 2.0 — a project to improve the power transmission network in the State.
Kerala Infrastructure Investment Fund Board (KIIFB):
- Kerala has been investing in infrastructure development through the Kerala Infrastructure Investment Fund Board (KIIFB). The KIIFB has been a major funding arm of the Kerala government.
- The KIIFB raised funds from the financial market and made them available to the government to finance infrastructure projects. Repayment of the loans is ensured by the government legally committing to pay a portion of its revenue from the motor vehicle tax and the petroleum cess to the KIIFB every year.
Better prepared:
- The real risks to the state’s economy are likely to be associated with shocks to the economy — such as natural disasters (floods), pandemic-induced worldwide recession, job losses in the West Asian countries where a lot of Keralites work, or contractionary fiscal policy by the central government — which could adversely impact economic growth.
- Even then, Kerala will be better prepared to face the eventualities as it has better infrastructure, and a better-educated, more highly skilled and healthier workforce.
Conclusion:
- The role of planning and social oversight in the economic development of the State holds significance and it needs to expand further.
Category: INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
1. A walk-back
This issue has been dealt with in the following article:
CNA dated April 4, 2021: Reversing a ban.
Category: SOCIAL ISSUES
Context:
- March 21 marks the International Day for the Elimination of Racial Discrimination.
Background:
Forms of racism:
- Current forms of racism and discrimination are complex and often covert.
- The anonymity of the Internet has allowed racist stereotypes and inaccurate information to spread online. At the onset of the pandemic, traffic to hate sites and specific posts against Asians grew by 200% in the U.S. In India and in Sri Lanka, social media groups and messaging platforms were used to call for social and economic boycotts of religious minorities, amid false information accusing them of spreading the virus.
- Structural forms of discrimination, including micro-aggressions and everyday indignities, remain widespread.
- The use of new technologies and artificial intelligence in security has raised the spectre of ‘techno-racism’.
Consequences of racism:
- Racial discrimination, beyond being a breach of human rights, has harmful effects on human health and well-being, and risks wider disruptions to social cohesion.
- Prejudiced attitudes and discriminatory acts, whether subtle or overt, aggravate existing inequalities in societies.
- A study published by The Lancet drew attention to the social dimension of the COVID-19 pandemic and the greater vulnerability of ethnic minorities, who have been disproportionately affected.
- The World Health Organization has cautioned on the dangers of profiling and stigmatising communities that can lead to fear and the subsequent concealment of cases and delays in detection.
- Racial discrimination deepens and fuels inequality in our societies.
UNESCO’s role in anti-racism movement:
- UNESCO has been playing a critical role in the anti-racism movement through its actions against racism through education, the sciences, culture, and communication. It has been promoting intercultural dialogue and learning.
- UNESCO’s headquarters in Paris recently hosted a Global Forum against Racism and Discrimination. The Forum gathered policymakers, academics, and partners to initiate a new multi-stakeholder partnership on anti-racism.
Way forward:
- The new manifestations of racism and discrimination call for renewed commitments to mobilise for equality.
- Racism will not be overcome with mere professions of good faith but must be combatted with anti-racist action.
- There is a need for a multisectoral effort to tackle the root causes of racism through anti-racist laws, policies and programmes.
- A global culture of tolerance, equality and anti-discrimination needs to be cultivated. There is the need to eradicate harmful stereotypes and foster tolerance.
Quote:
- Former UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan: “Our mission is to confront ignorance with knowledge, bigotry with tolerance, and isolation with the outstretched hand of generosity. Racism can, will, and must be defeated.”
F. Prelims Facts
1. NASA’s chopper dropped on Mars’ surface
What’s in News?
NASA’s Ingenuity mini-helicopter has been dropped on the surface of Mars in preparation for its first flight.
- Ingenuity, nicknamed Ginny, is a robotic rotorcraft that is planned to be used to test the technology to scout targets of interest on Mars, and help plan the best driving route for future Mars rovers.
- Ingenuity had been feeding off the Perseverance’s power system but will now have to use its own battery to run a vital heater to protect its electrical components.
- Ingenuity will be attempting to fly in an atmosphere that is one percent the density of Earth’s, which makes achieving lift harder — but will be assisted by gravity that is one-third of Earth’s.
Read more on NASA’s Perseverance Rover.
G. Tidbits
1. Philippines accuses China of plans to occupy more areas
What’s in News?
The Philippines’ Defence Secretary said that China was looking to occupy more areas in the South China Sea, citing the continued presence of Chinese vessels that it believes are manned by militias in disputed parts of the strategic waterway.
Read more on this issue covered in 22nd March 2021 Comprehensive News Analysis.
2. PSU banks may have to take ₹2,000 crore hit
What’s in News?
The public sector banks may have to bear a burden of ₹1,800 crore-₹2,000 crore arising out of a recent Supreme Court judgment on the waiver of compound interest on all loan accounts which opted for a moratorium during March-August 2020.
- The judgment covers loans above ₹2 crore as loans below this got blanket interest on interest waiver in November 2020.
- The compound interest support scheme for loan moratorium cost the government ₹5,500 crore during 2020-21 and the scheme covered all borrowers, including the prompt ones who did not opt for the moratorium.
- Also, the RBI had announced a moratorium on payment of instalments of term loans falling due between March 1 and May 31, 2020. It was later extended to August 31, 2020.
- Banks would provide compound interest waiver for the period a borrower had availed the moratorium.
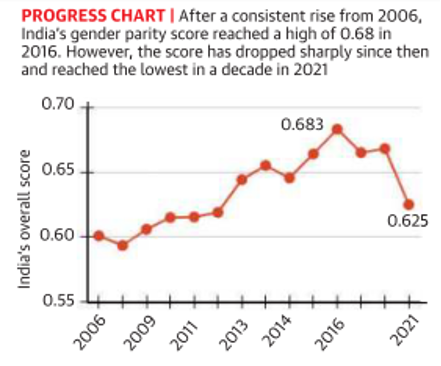
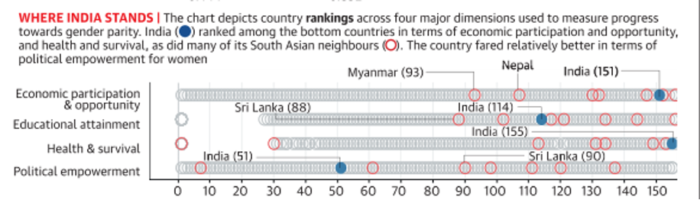
- India fell 28 spots to the 140th position in the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Report 2021.
- India’s score is at 0.625, implying that India has achieved 62.5% gender parity.
- Among the dimensions considered, India had its lowest ranking in terms of health and survival.
H. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions
Q1. Consider the following statements with respect to Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi (RAN):
- The scheme provides financial assistance to poor patients living below poverty line and suffering from life-threatening diseases relating to heart, kidney, liver, etc. for their treatment at government hospitals.
- Financial assistance to such patients is provided only through the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mechanism and no other means.
- It is a central sector scheme.
Which of the given statement/s is/are INCORRECT?
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: a
Explanation:
- The scheme provides financial assistance to poor patients living below poverty line and suffering from life-threatening diseases relating to heart, kidney, liver, etc. for their treatment at government hospitals.
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- The financial assistance to such patients is released in the form of a ‘one-time grant’, which is released to the Medical Superintendent of the Hospital in which the treatment has been/is being received.
Q2. The Global Gender Gap Report is published by:
- World Economic Forum
- Welthungerhilfe and Concern Worldwide
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
- International Monetary Fund
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: a
Explanation:
Global Gender Gap Report is published by the World Economic Forum.
Q3. Consider the following statements with respect to Stand-Up India Scheme:
- People belonging to the scheduled caste or scheduled tribe or women are eligible to avail loans under the scheme.
- Under the scheme, an amount ranging from Rs 10 lakhs to Rs.1 crore is provided as a loan, inclusive of working capital for setting up a new enterprise.
- Loans under the scheme are available for only greenfield projects.
Which of the given statement/s is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- 1 only
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation:
- Stand up India scheme was launched in April 2016, encouraging people from the scheduled caste and scheduled tribes and women across the country to become entrepreneurs by loaning them a sum of money to start a business.
- Under the scheme, an amount ranging from Rs 10 lakhs to Rs.1 crore is provided as a loan, inclusive of working capital for setting up a new enterprise.
- Loans under the scheme are available for only greenfield projects. Greenfield signifies, in this context, the first time venture of the beneficiary in the manufacturing or services or trading sector.
- People belonging to the scheduled caste or scheduled tribe or women are eligible to avail loans under the scheme.
Q4. Consider the following statements with respect to Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT):
- It is a statutory authority functioning under the Central Board of Revenue Act, 1963.
- All its members except for the chairman are selected from the Indian Revenue Service (IRS).
- It is administered by the Department of Revenue under the Ministry of Finance.
Which of the given statement/s is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
CHECK ANSWERS:-
Answer: c
Explanation:
- The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) is the authority vested with the responsibility of the administration of laws related to direct taxes through the Department of Income Tax.
- It is a statutory authority functioning under the Central Board of Revenue Act, 1963.
- All its members including the chairman are selected from the Indian Revenue Service (IRS).
- It is administered by the Department of Revenue under the Ministry of Finance.
I. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
- The National Policy on Rare Diseases, 2021, though a good start, falls short of the expectations. Comment. (10 marks, 150 words) (GS Paper 2/Governance)
- Current forms of racism and discrimination are complex and often covert. Elucidate. Also suggest necessary measures to combat these new manifestations of racism and discrimination. (10 marks, 150 words) (GS paper 1/Social issues)
Read the previous CNA here.
CNA 5th April 2021:- Download PDF Here
Comments