Read the daily PIB update and stay up-to-date on current affairs for the UPSC exam.
February 12th, 2020 PIB:- Download PDF Here
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. MoU between India and Iceland 2. Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement between India and Sri Lanka 3. School Health Ambassador Initiative 4. BIMSTEC Disaster Management Exercise – 2020 5. Conference on Combating Drug Trafficking 6. New Delhi International Arbitration Centre (NDIAC) 7. Arbitration Council of India (ACI) 8. Index of Industrial Production (IIP) 9. Consumer Price Index (CPI)
1. MoU between India and Iceland
Context:
Cabinet approves MoU between India and Iceland in the field of Sustainable Fisheries Development.
Details:
- The MoU was signed in September 2019.
- The salient features of the MoU are:
- Creation of facilities for exchange of scientists and technical experts and their proper placement, especially in areas of estimating Total Allowable Catches in offshore and deep-sea areas.
- Provision of training to fisheries professionals from key fisheries institutions in the various management aspects on areas of modern fisheries management and fish processing.
- Exchange of scientific literature research findings and other information.
- Exchange of experts/expertise to study the prospects of fishing.
- Processing and marketing of products from high seas fisheries for entrepreneurship development.
- Also read: Blue Revolution – Neel Kranti Mission.
2. Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement between India and Sri Lanka
Context:
The Union Cabinet has approved the signing and ratification of the Protocol amending the Agreement between India and Sri Lanka for the avoidance of double taxation and the prevention of fiscal evasion with respect to taxes on income.
Details:
- The existing Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) between India and Sri entered into force in October 2013.
- India and Sri Lanka are members of the Inclusive Framework and as such are required to implement the minimum standards under G-20 OECD BEPS Action Reports in respect of their DTAAs with Inclusive Framework countries.
- India is a signatory to the Multilateral Convention to Implement Tax Treaty Related Measures to Prevent Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (MLI).
- Sri Lanka is, however, not a signatory to the MLI. Therefore, amendment of the India-Sri Lanka DTAA bilaterally is required to update the Preamble and also to insert Principal Purpose Test (PPT) provisions to meet the minimum standards on treaty abuse under Action 6 of G-20 OECD Base Erosion & Profit Shifting (BEPS) Project.
About the OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework on BEPS:
- The Inclusive Framework on BEPS brings together over 135 countries and around the globe to collaborate on the implementation of the OECD/G20 Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) Package.
- Base erosion and profit shifting (BEPS) refers to tax planning strategies used by multinational enterprises that exploit gaps and mismatches in tax rules to avoid paying tax.
- They exploit gaps and mismatches in tax rules to artificially shift profits to low or no-tax locations where there is little or no economic activity.
- Although some of these gap-exploiting schemes used by the multinational corporations are illegal, most of them are not.
- However, this undermines the fairness and integrity of tax systems because businesses that operate across borders can use BEPS to gain a competitive advantage over enterprises that operate at a domestic level.
- Under this framework, countries collaborate to put an end to tax avoidance strategies that exploit gaps and mismatches in tax rules to avoid paying tax.
- Working together in the OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework on BEPS, the member countries are implementing 15 Actions to tackle tax avoidance, improve the coherence of international tax rules and ensure a more transparent tax environment.
About the Multilateral Convention to Implement Tax Treaty Related Measures to Prevent Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (MLI):
- The Multilateral Convention/MLI is an outcome of the OECD/G20 Project to tackle BEPS.
- India ratified the MLI in 2017 and it entered into force for India in 2019.
- Its provisions will have an effect on India’s DTAAs from FY 2020-21 onwards.
- The MLI offers concrete solutions for governments to close the gaps in existing international tax rules by transposing results from the OECD/G20 BEPS Project into bilateral tax treaties worldwide.
- The MLI modifies the application of thousands of bilateral tax treaties concluded to eliminate double taxation.
- It also implements agreed minimum standards to counter treaty abuse and to improve dispute resolution mechanisms while providing flexibility to accommodate specific tax treaty policies.
To know more about the OECD, click on the linked article.
3. School Health Ambassador Initiative
Context:
Union ministers release curriculum for School Health Ambassador Initiative under Ayushman Bharat.
Details:
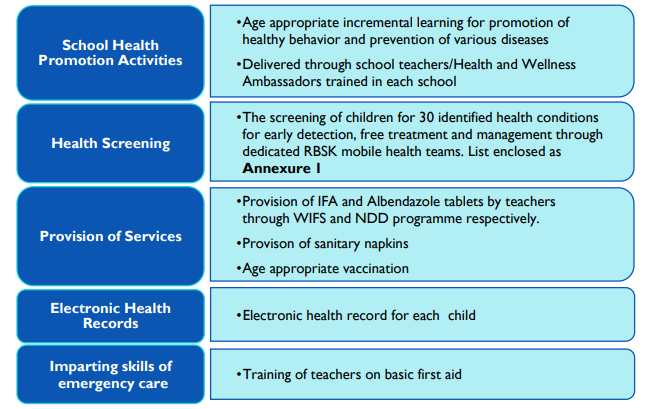
- Under this initiative, two teachers in every school will be made health and wellness ambassadors to spread awareness about health issues.
- These ambassadors will be supported by class monitors as Health and Wellness Messengers.
- Initially, the programme, under the Ayushman Bharat Mission, will be started in 200 districts.
- The first phase of implementation will be in all public upper primary, secondary, and senior secondary schools of aspirational districts.
- In this new initiative, health promotion and prevention activities programmes have been added in addition to on-going health screening programs through Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram (RBSK) teams and provision of services (IFA, Albendazole and sanitary napkins).
- The ambassadors are appointed under the aegis of the School Health Programme of the Central Government.
- Objectives of the School Health Programme:
- To provide age-appropriate information about health and nutrition to the children in schools.
- To promote healthy behaviours among the children that they will inculcate for life.
- To detect and treat diseases early in children and adolescents including identification of malnourished and anaemic children with appropriate referrals to PHCs and hospitals.
- To promote the use of safe drinking water in schools.
- To promote safe menstrual hygiene practices by girls.
- To promote yoga and meditation through Health & Wellness Ambassadors.
- To encourage research on health, wellness and nutrition for children.
- Services under the School Health Programme are shown in the image below:
To know more about the Rashtriya Bal Swasthya Karyakram (RBSK), check PIB dated Sep 11, 2017.
4. BIMSTEC Disaster Management Exercise – 2020
Context:
The Minister of State for Home Affairs inaugurated the Field Training Exercise of the 2nd BIMSTEC Disaster Management Exercise on flood rescue at the Ramachandi Beach, Puri (Odisha).
About the BIMSTEC Disaster Management Exercise:
- This exercise will help in sharing best practices and expertise, consolidating the disaster response, coordination and cooperation among BIMSTEC countries during disasters.
- The first such exercise was held in 2017.
- The exercise is hosted by the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF).
- The theme of this year’s exercise is “A cultural heritage site that suffers severe damage in the earthquake and flooding or storm.”
- Five member countries namely, India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Myanmar and Nepal are participating in this three-day-long exercise.
- Two other member countries Bhutan and Thailand are not participating in the exercise this year.
- The purpose of the exercise is to test the existing emergency procedures for notification, preparedness and emergency response during a major natural disaster.
5. Conference on Combating Drug Trafficking
Context:
The Union Home Minister will inaugurate the ‘Conference on Combating Drug Trafficking’ for BIMSTEC Partner Nations in New Delhi.
Details:
- The Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) is organizing the conference.
- It is believed that this platform will provide the opportunity to all the member nations to deliberate on the increased threats posed by drug trafficking and the collective steps that are required to negate the threats by learning from the best practices adopted by member countries.
- Delegations from each BIMSTEC nation have been invited to participate in the conference.
- Further, various Central and State drug law enforcement agencies and other stakeholders have also been invited.
- Asian countries are increasingly being affected by drug trafficking and BIMSTEC, being the key link between South Asian and South East Asian Nations is one of the most effective platforms to tackle this global threat.
- Drug trafficking through the sea is a major security challenge faced by countries. Combating this necessitates collaborative efforts at sea, including further strengthening of effective coordination in operations and information sharing amongst partner nations.
- Recent events such as the seizing of Methamphetamine by the NCB suggest that the Bay of Bengal region is impregnated with the drug trafficking menace.
About the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB):
- NCB is the apex agency for exercising powers and functions of the Central Government under the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act.
- It is also the nodal agency for matters pertaining to drug law enforcement in India.
- It coordinates the actions taken by various agencies of Central and State Governments related to drug law enforcement in the country and matters pertaining to drug abuse.
- Further, NCB is also the nodal agency of the Government of India at the international level in all matters pertaining to narcotic drugs & psychotropic substances.
6. New Delhi International Arbitration Centre (NDIAC)
Context:
Draft New Delhi International Arbitration Centre (NDIAC) Rules issued for public consultation.
Details:
For more on the NDIAC, check PIB dated Feb 28, 2019 under the heading ‘New Delhi International Arbitration Centre (NDIAC)’.
7. Arbitration Council of India (ACI)
Context:
Draft Arbitration Council of India (ACI) Rules issued for public consultation.
Details:
- The Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996, was amended by the Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Act, 2015 in order to make arbitration process user-friendly, cost-effective and ensure speedy disposal and neutrality of arbitrators.
- To give a boost to institutional arbitration vis-a-vis ad hoc arbitration and to remove some practical difficulties in applicability of the Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Act, 2015, the Government has recently amended the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 by the Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Act, 2019.
- The 2019 amendment act establishes an independent body namely, the Arbitration Council of India (ACI) for the purpose of grading of arbitral institutions and accreditation of arbitrators, etc.
- ACI Composition:
- ACI will be headed by a Chairperson, who has been a Judge of the Supreme Court or a Chief Justice or Judge of a High Court or an eminent person, having special knowledge and experience in the conduct or administration of arbitration, to be appointed by the Central Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of India.
- Besides, it will also have two Full-time Members from amongst eminent arbitration practitioners and academicians.
- In addition, one representative of a recognized body of commerce and industry shall be nominated on a rotational basis as a Part-time Member.
- The Secretary, Department of Legal Affairs, Ministry of Law & Justice; Secretary, Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Finance and Chief Executive Officer, ACI will be ex-officio Members.
8. Index of Industrial Production (IIP)
Context:
The Quick Estimates of Index of Industrial Production (IIP) with base 2011-12 for the month of December 2019 stands at 133.5, which is 0.3 percent lower as compared to the level in the month of December 2018.
To know more about the Index of Industrial Production (IIP), click on the linked article.
Context:
The National Statistical Office (NSO) is releasing CPI (Rural, Urban, Combined) on Base 2012=100 for the month of January 2020.
Details:
All India inflation rates based on the provisional CPI for January 2020 are given in the table below:
| Rural | Urban | Combined |
| 7.73 | 7.39 | 7.59 |
To know more about the Consumer Price Index (CPI), click on the linked article.
February 12th, 2020 PIB:- Download PDF Here
Related Links:
| UPSC 2020 | UPSC Current Affairs |
| Monthly Magazine for UPSC Current Affairs | UPSC Current Affairs Quiz |
| Government Exams | UPSC Prelims Exam |
Read more PIB articles here.

Comments