The establishment of British rule over India was not a smooth one. The disruption brought about in our society and economy by British rule produced discontentment and resistance at every stage. These dis-locations resulted in Civil Rebellions (Non-tribal).
Get the list of Non-Tribal Movements for the IAS Exam.
| Aspirants can cover the topics mentioned in the UPSC Syllabus of the history subject by following the below-mentioned links: |
Introduction to Non-Tribal Movements in India
In the initial century of British rule, these Civil Rebellions were mostly led by deposed Rajas or Zamindars or landed military magnates (E.g. Palaegars in South India). The major cause was changes brought about by the British in the economy, land revenue system and administration.
The Civil rebellions began as soon as British rule was established in Bihar and Bengal (e.g. Sanyasi rebellion in Bengal). These revolts were local and isolated from each other and led by local leaders. These revolts were ruthlessly suppressed by the British with the full might of the state machinery. The suppression of these revolts was a major reason as to why the Revolt of 1857 did not spread to South India and most of Eastern and Western India.
Below is a list of some of these Non-tribal or Civil rebellions in the form of Infographics for easy understanding and quick revision for IAS Exam preparation.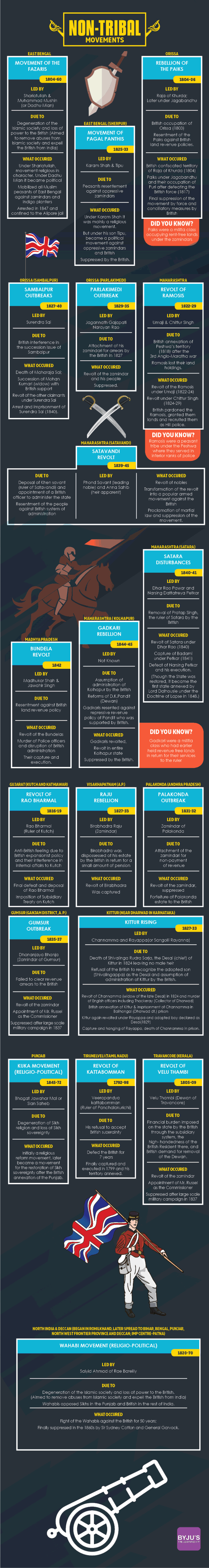
Some Important History Articles:
| Difference Between the Non-Cooperation Movement and Civil Disobedience Movement | Difference Between Moderates and Extremists |
| Peasant Movements in India | Social and Religious Reforms in India |
Comments