Phytohormones are chemical compounds present in very low concentrations in plants. They regulate plant development, growth, longevity and reproductive processes. Here, let’s look at the structure and functions of different phytohormones like auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene and abscisic acid.
Download Complete Chapter Notes of Plant growth and Development
Download Now
Table of Content
- Functions of Plant Hormones
- Auxin Hormone
- Gibberellins Hormone
- Cytokinins Hormone
- Abscisic Acid Function
- Ethylene Plant Hormone
What is Plant Hormones?
Plants need sunlight, water, oxygen, minerals for their growth and development. These are external factors. Apart from these, there are some intrinsic factors that regulate the growth and development of plants. These are called plant hormones or “Phytohormones”.
Don’t miss: NEET Answer Key
- Plant hormones are chemical compounds present in very low concentration in plants. They are derivatives of indole (auxins), terpenes (Gibberellins), adenine (Cytokinins), carotenoids (Abscisic acid) and gases (Ethylene).
- These hormones are produced in almost all parts of the plant and are transmitted to various parts of the plant.
- They may act synergistically or individually. Roles of different hormones can be complementary or antagonistic.
- Hormones play an important role in the processes like vernalisation, phototropism, seed germination, dormancy etc. along with extrinsic factors.
- Synthetic plant hormones are exogenously applied for controlled crop production
Charles Darwin first observed the phototropism in the coleoptiles of canary grass and F.W. Went first isolated auxin from the coleoptiles of oat seedlings.
What are the main functions of plant hormones?
Plant hormones control all the growth and development activities like cell division, enlargement, flowering, seed formation, dormancy and abscission.
Based on their action, plant hormones are categorised into two categories:
- Plant Growth Promoters
- Plant Growth Inhibitors
Also Check: All Hormones and Their Functions
Auxin Hormone
Auxin means “to grow”. They are widely used in agricultural and horticultural practices. They are found in growing apices of roots and stems and then migrate to other parts to act.
- Natural: Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), Indole butyric acid (IBA)
- Synthetic: 2,4-D (2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid), NAA (Naphthalene acetic acid)
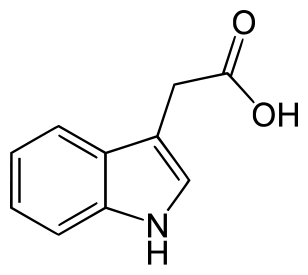
Functions:
- Cell elongation of stems and roots
- Apical dominance, IAA in apical bud suppresses the growth of lateral buds
- Induces parthenocarpy i.e. development of fruit without fertilisation e.g. in tomatoes
- Prevents premature fall of leaves, flowers, fruits
- Useful in stem cuttings and grafting where it initiates rooting
- Promotes flowering e.g. in pineapple
- 2,4-D is widely used as a herbicide to kill undesirable weeds of dicot plants without affecting monocot plants
- Helps in cell division and xylem differentiation
Also Read: MCQs on Plant Hormones
Gibberellins Hormone
- There are more than 100 gibberellins (GA1, GA2, GA3…..) that are known. They are acidic in nature. These are found in higher plants and fungi.
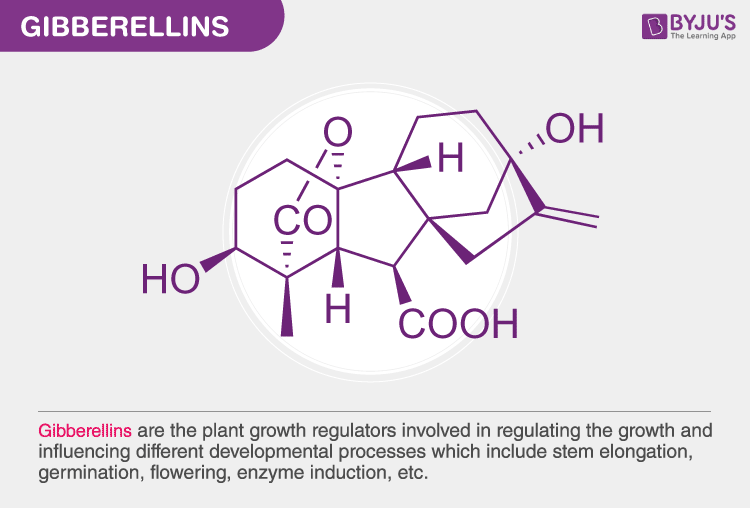
Functions:
- Promotes bolting, i.e. sudden elongation of internodes just before flowering in rosette plants like cabbage, beet
- Delays senescence
- Induces parthenocarpy
- Elongation of the stem and reverses dwarfism
- Induces maleness in certain plants like cannabis
- Induces the formation of hydrolytic enzymes such as lipase, amylase in the endosperm of germinating cereal grains and barley seeds
- Breaks seed dormancy
Cytokinins Hormone
- Cytokinins play an important role in cytokinesis process. Cytokinins are naturally synthesised in the plants where rapid cell division occurs e.g. root apices, shoot buds, young fruits, etc. Movement of cytokinins is basipetal and polar.
- Natural: Zeatin (corn kernels, coconut milk), isopentenyladenine
- Synthetic: Kinetin, benzyladenine, diphenylurea, thidiazuron
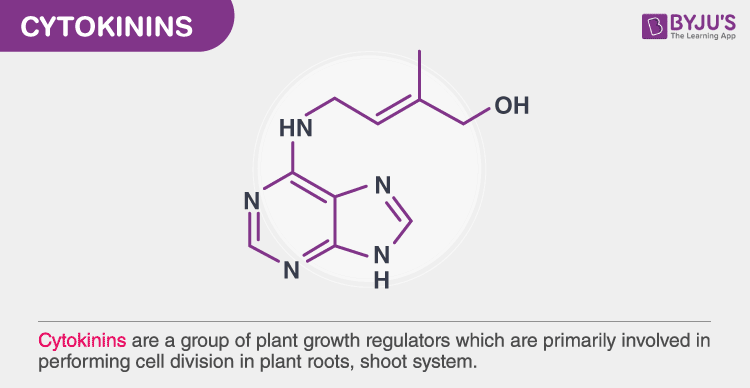
Functions:
- It promotes lateral and adventitious shoot growth and used to initiate shoot growth in culture
- Helps in overcoming apical dominance induced by auxins
- Stimulate the formation of chloroplast in leaves
- Promotes nutrient mobilisation and delay leaf senescence
Abscisic Acid Function
- It is a growth-inhibiting hormone. ABAs act as an antagonist to GAs. It inhibits plant metabolism and regulates abscission and dormancy. It is also called “stress hormone” as it increases the tolerance of plants.
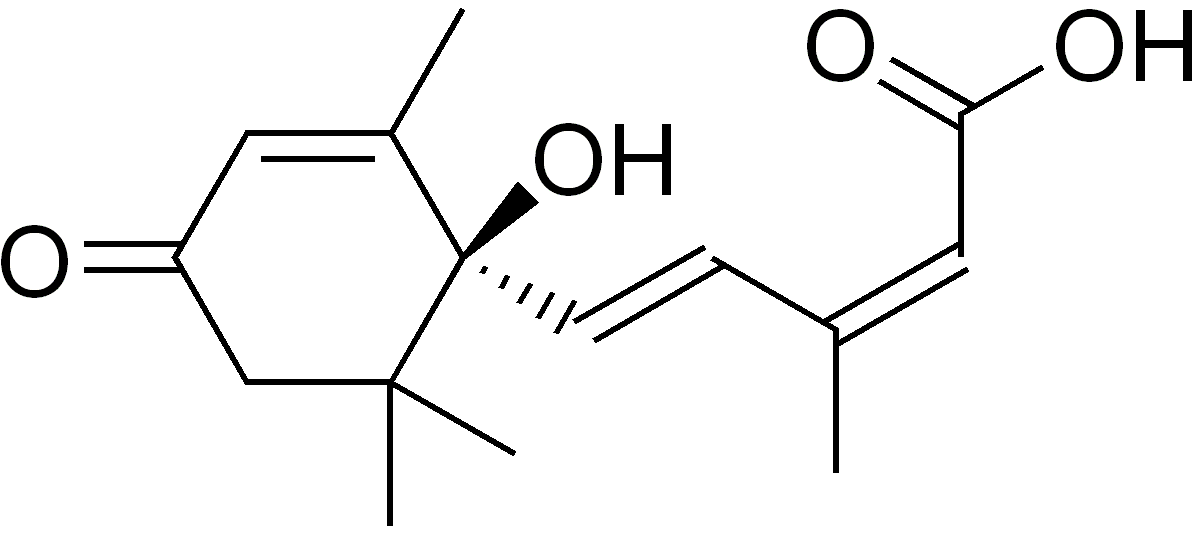
Functions:
- Induces abscission of leaves and fruits
- Inhibits seed germination
- Induces senescence in leaves
- Accelerates dormancy in seeds that is useful for storage purpose
- Stimulates closure of stomata to prevent transpiration under water stress
Ethylene Plant Hormone
- It acts as a growth promoter as well as an inhibitor. Occurs in gaseous form. It is synthesised in the ripening fruits and tissues undergoing senescence. It regulates many physiological processes and one of the most widely used hormones in agriculture.
Functions:
- It hastens the ripening of fruits
- Controls epinasty of leaves
- Breaks seed and bud dormancy
- Stimulates rapid elongation of petioles and internodes
- Promotes senescence and abscission of leaves and flowers
- Induces root growth and root hair formation thereby increasing the absorption surface
- Stimulates femaleness in monoecious plants
- Apical hook formation in dicot seedlings
Other than the main 5 hormones, there are other hormones too that affect the plant’s physiological processes, e.g. brassinosteroids, salicylates, jasmonates, strigolactones, etc.
Also Check:
NEET Flashcards: Transport In Plants
NEET Flashcards: Mineral Nutrition
NEET Flashcards: Photosynthesis In Higher Plants
NEET Flashcards: Respiration In Plants
NEET Flashcards: Plant Growth And Development
Recommended Video:
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the two major categories of phytohormones?
Based on actions, phytohormones can be categorised into two – growth promoters and growth inhibitors. Moreover, phytohormones like ethylene can be both growth promoters as well as inhibitors.
Name a few phytohormones
The five major phytohormones are – auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene and abscisic acid. There are also other phytohormones that affect the plant’s physiological processes like brassinosteroids, salicylates, jasmonates, strigolactones, etc.
What is the main role of cytokinins?
Cytokinins promote lateral and adventitious shoot growth and are used to initiate shoot growth in culture and also help in overcoming apical dominance induced by auxins.


Nice