Cretinism
Cretinism is a disease caused by hypothyroidism. Iodine deficiency in diet during pregnancy is the major cause of cretinism. Hypothyroidism leads to impaired development of the growing fetus and leads to mental retardation and stunted growth.
Download Complete Chapter Notes of Chemical Control and Coordination
Download Now
Table of Contents
- Meaning
- Thyroid Hormone Synthesis and Secretion
- Types
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis
- treatment
- Cretinism and Dwarfism
Cretinism Definition
“Cretinism refers to the congenital hypothyroidism or underactivity of thyroid glands during early childhood leading to stunted growth and mental retardation.”
The term cretin was derived from the French word chrétien, literally meaning “Christian” or “Christ-like” as the diseased were mentally retarded and incapable of doing sin. It is the Iodine deficiency disorder associated with insufficient thyroid hormone activity occurring during fetal, infant or childhood phases.
It is either due to extreme iodine deficiency, i.e. endemic cretinism or due to decreased synthesis of thyroid hormones, i.e. sporadic cretinism. It is typically diagnosed during infancy or childhood, however, the best preventive strategy is the screening of neonates. It is important to diagnose and treat cretinism early, a delay may lead to irreversible damage. Replacement of the hormone will produce an immediate effect.
Thyroid Gland and Thyroid Hormone
- The thyroid gland is one of the important endocrine glands of our body and present in the neck region. It synthesizes and secretes thyroid hormones such as triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (T4). Inside the follicular cells of the gland, these hormones are synthesized by iodinating tyrosine residues at various positions in the glycoprotein called thyroglobulin.
- So, Iodine plays a critical role in the synthesis of thyroid hormones.
- In general, Thyroid hormone plays a vital role in maintaining basal metabolic rate, oxidation of foodstuffs and growth and development at an early stage of life.
Synthesis of Thyroid Hormone
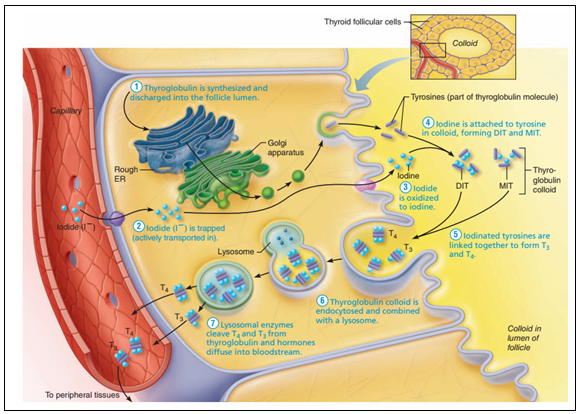
Steps in Thyroid Hormone Synthesis and Secretion
- Step 1: Synthesis of Thyroglobulin in follicular cells and release into the follicular lumen.
- Step 2: Transport of Iodide (anionic form) into the follicular cell by active transport and moves to follicular lumen by facilitated diffusion. This process is called Iodide trap.
- Step 3: Oxidation of Iodide into Iodine takes place in the border of follicular cells.
- Step 4: Attachment of Iodine with Tyrosine, which is catalyzed by the enzyme peroxidase to form (Monoiodotyrosine ) MIT and (Diiodotyrosine) DIT.
- Step 5: Linking of iodinated tyrosines together to form T3 and T4.
- Step 6: Endocytosis of thyroglobulin colloid.
- Step 7: Cleavage of T4 and T3 from thyroglobulin by lysosomal enzymes and release of hormones from the follicular cell into the blood.
Also see: What are the symptoms of Thyroid Abnormalities?
Types of Cretinism
Cretinism is of 2 types:
Congenital Cretinism
- Incidence is 1:3000 to 1:4000 in an iodine-deficient endemic area.
- It can be caused due to a defect in the genes encoding various enzymes involved in thyroid hormone synthesis such as thyroglobulin, iodotyrosine deiodinase and also thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). This type of hypothyroidism is also called congenital hypothyroidism, non-goitrous (CHNG).
- There are at least 5 types of CHNG due to mutation of five different genes namely CHNG1 to CHNG5.
- Non Goitrous congenital hypothyroidism is considered as the most prevalent inborn endocrine disorder.
Endemic Cretinism
- For adults, the normal recommended dietary intake of iodine is 150 μg / day.
- This type of cretinism often occurs in children who live in the geographical settings where iodine is deficient and it is not corrected by either supplementing iodine or thyroid hormone to regain normal thyroid hormone levels during early life.
- Mostly, the mother of endemic cretinism children had been affected with hypothyroidism during pregnancy (Maternal hypothyroidism).
- Exposure to radioactive Iodine during pregnancy may also be the cause in some cases.
- Use of antithyroid drugs or sulfonamides during pregnancy.
- Iodine intake as low as 25 mcg/day during pregnancy would be a potential risk factor for giving birth to cretinism neonates.
Neurological cretinism – It is characterized by the following conditions:
- Retarded growth
- Deaf-mutism
- Motor spasticity
- Severe mental retardation with a squint
Myxedematous cretinism– It is characterized by the following conditions:
- Retarded growth.
- Incomplete maturation of facial expression.
- Thickened and dry skin.
- Small and dry hair, eyelashes and eyebrows.
- Mental retardation of comparatively lesser intensity to neurological cretinism.
- Delayed sexual maturation.
- Other clinical manifestations of hypothyroidism.
Cretinism Causes
There are two main reasons for cretinism:
- Lack of thyroid gland and failure of the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormone (congenital cretinism or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome).
- Iodine deficiency in the diet (Endemic cretinism).
In children, hypothyroidism is the cause of cretinism. Total T4 and T3 level may be normal due to increased TBG (Thyroxine binding globulin). The elevated level of TBG may be due to maternal hyperestrogenism. The lack of feedback mechanisms will also give an elevated TSH level.
Neonatal cretinism may also be caused by maternal hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism may result from the treatment of hyperthyroidism using antithyroid drugs or radioactive iodine.
Explore more: Hyperthyroidism in Females
Pathophysiology
- An optimal level of maternal thyroid status is essential for the normal growth of the fetus. It is the maternal thyroid hormone, the only source for the fetus that crosses placenta for fetal brain development.
- Thyroid hormone is essential for growth, branching and myelination of neuronal cells of CNS at fetal and neonatal stage. So, the absence of thyroid hormone at these stages would severely affect the generalized nervous system development.
- Thyroid hormone also plays a critical role in skeletal muscle development than soft tissue development. During cretinism, this disproportionate rate of growth leads to excessive growth of soft tissue compared to skeletal tissues.
Cretinism Symptoms
- Generally characterized by stunted growth and mental retardation.
- Short stature (dwarfism).
- Mild neurological impairment with reduced muscle tone and coordination.
- Hearing and speech defects.
- Unable to maintain posture and balance with characteristic walking style.
- Myxoedema.
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland (goitre).
- The sparseness of hair and nails.
- Voice will be deep and hoarse.
- Retardation of sexual attributes.
- Thickened skin.
- Enlarged tongue.
- Protruded abdomen.
- Umbilical hernia.
- Delayed tendon reflexes.
- Decreased Intelligent quotient (IQ).
Diagnosis of Cretinism
- Congenital cretinism with severe hypothyroidism can be identified by antenatal screening test in the first month of life.
- Technetium (Tc– 99m pertechnetate) thyroid scan.
- Radioactive Iodine (RAIU) test (to differentiate between the congenital absence and a defect in the organification process).
- Postnatal – Blood spot test such as Guthrie’s test.
- Elevated serum Thyroid binding globulin (TBG) and TSH level.
- Elevated serum T3 and low T4 level.
Cretinism Treatment
- Once diagnosed, treatment should be started within 1-2 weeks of life.
- Treatment should be started before the onset of symptoms, if developmental abnormalities and mental retardation start to appear, it will not reverse even with thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
- The recommended dose is 10 to 15 μg per kg of body weight. The dose should be increased as the age progresses.
- Everyday treatment with thyroxine should be initiated as early as possible as mental retardation that has ensued already is only partially reversible. With early treatment, physical development and growth can be revived and mental retardation can be checked.
Cretinism and Dwarfism
Cretinism and dwarfism are two conditions resulting from deficiency and medical disorder. While Dwarfism is the state of being dwarf, cretinism is the condition of dwarfism showing signs of mental retardation. The causative is the deficiency of thyroid hormone. Cretinism on the other hand is usually a congenital condition.
Dwarfism
Growth retardation is mainly seen in Dwarfism where an uncommon short stature is seen in adults. It could be due to several reasons – metabolic, hereditary disorders etc. At some instances, inadequate amounts of nutrition at the time of critical growth phase and development, and growth-hormone deficiency can also lead to dwarfism.
Difference between Cretinism and Dwarfism – Cretinism vs. Dwarfism
The table below provides important differences between cretinism and dwarfism conditions –
| Cretinism | Dwarfism |
| What it means | |
| It is the condition of severe mental and physical retardation as a result of deficiency of thyroid hormones at the time of early pregnancy. | It is the state of being dwarf as a result of metabolic and hereditary disorders. |
| Cause | |
| Congenital thyroid deficiency | Metabolic and hereditary disorders, growth hormone deficiency |
| Hormone in effect | |
| Thyroid hormone | Growth hormone |
| Signs and symptoms | |
| Short stature, mental retardation | Short stature or stunt growth (youth) |
| Parts of the body | |
| Usually disproportionate – leads to impairment of growth of body affecting mental growth. Skin swells, hair loss, delay in puberty and bone maturation. | Usually proportionate. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the causes of Endemic cretinism?
The main causes of cretinism are the following:
- Dietary iodine deficiency.
- Failure of responding to the iodine of thyroid hormone supplement.
- Maternal hypothyroidism.
- Exposure to radioactive iodine during pregnancy.
- Use of antithyroid drugs or sulfonamides during pregnancy.
What are the main symptoms of cretinism?
The main symptoms of cretinism are the following:
- Stunted growth and mental retardation.
- Short stature (dwarfism).
- Mild neurological impairment with reduced muscle tone and coordination.
- Hearing and speech defects.
- Unable to maintain posture and balance with characteristic walking style.
- Myxoedema.
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland (goitre)
What are the characteristics of cretinism?
The three main characteristic features of neurologic endemic hypothyroidism in its absolutely developed type are very severe moronity alongside squint, deaf-muteness, and motor fitfulness with disorders of the arms and legs.
Can goitre develop into cancer?
Goitre is often the results of thyroid tumours, that are sometimes benign, however generally malignant. Most thyroid tumours occur as separate nodules, however, there are many styles of thyroid cancer which will cause generalized swelling of the secretor.
Stay tuned for more on cretinism and associated conditions. Learn about Multinodular Goitre, only at BYJU’S.
Related Articles:
| Thyroid Problems |
| MCQs of Thyroid Gland |
| NEET Biology Flashcards – Chemical Coordination and Integration |

Comments