Table of Content:
| What is Multinodular Goitre ? | Causes Of Multinodular Goitre |
| Multinodular Goitre Types | Multinodular Goitre Symptoms |
All the cellular functions of the body have to be continuously regulated. Hormones perform this function. The endocrine system along with the nervous system coordinate and control the physiological functions of the body.
Hormones are:
- Secreted by endocrine glands directly into the bloodstream, this is why they are called “ductless glands”
- Non-nutrient chemicals, produced in trace amounts
- Act as an inter-cellular messenger and act on target tissues
- As compared to nerve impulses, hormonal responses of the body are much slower
- Long term effects as compared to short-lived effects of the nervous system
- Deficiency or excess production leads to various illnesses
What is Multinodular Goitre ?
Multinodular Goitre (MNG) is defined as the special condition of thyroid glands, where there are multiple lumps (nodules) formed. It appears over a period of time and can be asymptomatic, non-functional, visible or can be associated with serious implications like thyroid cancer.
The Endocrine system comprises many glands located in the different parts of the body and regulating various physiological processes. E.g. Pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, pancreas, adrenal and gonads.
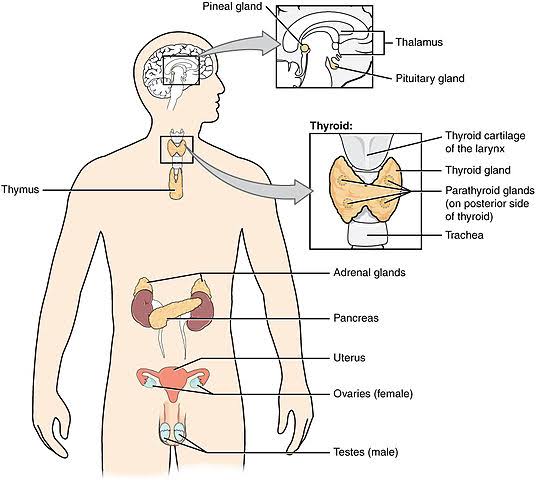
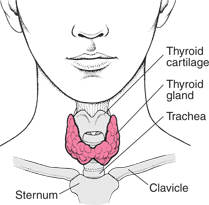
Thyroid gland is present on both sides of the trachea. The two lobes are interconnected with the isthmus. Thyroid gland is composed of follicles and stromal tissues.
Follicular cells synthesise two hormones, Tetraiodothyronine or thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroid gland also produces a protein hormone, thryocalcitonin (TCT).
| Hormone | Function |
| Tetraiodothyronine or thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) |
|
| Thyrocalcitonin (TCT) |
|
Causes Of Multinodular Goitre
Enlargement of the thyroid gland is referred to as a “goitre”. When a person has multiple nodules or bumps on it, it’s called “multinodular goitre”. Nodules are formed when there is a different rate of growth in different parts of the thyroid gland.
Common causes of multinodular goitre are:
- Iodine deficiency
- Biosynthetic defects
- Elevated TSH
- Smoking, stress, certain drugs
- Inherited genes
- Autoimmune disease- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Grave’s disease
- Genetic defects leading to thyroid dysfunction
- Sex- more common in women
- Age- Older people are at higher risk
- Nodular disease
Iodine is essential for the normal rate of synthesis of thyroid hormones. Biosynthetic defects and iodine deficiency reduces the synthesis of thyroid hormone, leading to an increased level of TSH, which stimulates the growth of thyroid gland to compensate for the reduced level of hormone synthesis.
An overactive thyroid can also cause the thyroid to enlarge and become multinodular.
The nodular disease is characterised by disordered growth of thyroid cells often clubbed with the gradual development of fibrosis.
In many cases the causes are unknown.
Multinodular Goitre Types
There are two types of multinodular goitre:
- Non-toxic multinodular goitre: It is not associated with abnormal thyroid function and not too much thyroid hormone is produced
- Toxic multinodular goitre: Excessive production of thyroid hormones leading to “hyperthyroidism”
Multinodular Goitre Symptoms

Multinodular goitre can be asymptomatic. A person can feel the node over their thyroid gland in the neck region. It can be diagnosed in the physical exam, blood test imaging tests or biopsy.
The main symptoms of multinodular goitre are:
- Hoarseness
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Difficulty in breathing
- Difficulty in tolerating heat
- Irritability, nervousness
- Faster heart rate and difficulty in sleeping
- Weight loss
Treatment Of Multinodular Goitre
The main treatment includes:
- Radioiodine therapy, it helps in reducing size of thyroid tissue and controls hormone production
- Thyroid hormone medication
- Thyroidectomy, removal of the thyroid gland
All multinodular goitre don’t require treatment. It depends on the impairment of thyroid function. If it is non-toxic i.e. not producing excessive thyroid hormones, then the treatment depends on the size, symptoms and growth pattern.
There is a high risk (10%-20%) to develop thyroid cancer if a person has multinodular goitre.
Recommended Video:
Chemical Coordination and Integration Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 | NEET 2022 Exam Prep


Comments