CBSE Class 9 Science Notes Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit Of Life
Life, as we know it, took billions of years to evolve. From the very first precursor of life to the multitude of multicellular organisms that we see around us today, the most basic unit of all these is the cell.
For more information on the Fundamental Unit of Life – Cell, watch the below video

All About Cells
Cells are the basic structural and functional unit of life. The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke. A number of cells can work together to form tissues and organs.
For more information on Introduction to the World of Cells, watch the below video

To know more about Cell, visit here.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which food releases energy in the mitochondria. Cells absorb glucose from food and burn it to produce energy.
To know more about Cellular respiration, visit here.
Structural Organization of Cells
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells
Two types of cells – Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are primitive and lack a well-defined nucleus. Eukaryotic cells are more advanced and have a well-defined nucleus.
To know more about Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells, visit here.
Cell Structure in Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells have the most well-defined structure. These cells have cell membranes, membrane-bound cell organelles and a well-defined nucleus. The nucleus has its own membrane called the nuclear membrane.
For more information on Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells, watch the below video

Cell Membrane
- The cell membrane is the outer covering of a cell.
- It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer membrane.
- It is selectively permeable in nature.
- The structure of a cell membrane is best described by the fluid mosaic model.
To know more about Cell Wall and Cell Membrane, visit here.
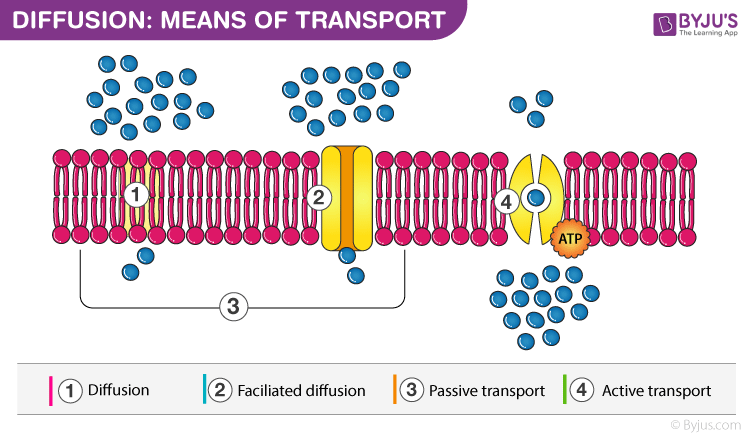
Diffusion
The movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of lower concentration is known as diffusion. E.g. carbon dioxide and oxygen move across the cell membrane by diffusion.
Osmosis in Selectively Permeable Membrane
Osmosis is the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane. Osmosis is a selective process since the membrane does not allow all molecules to pass through it. Water is usually the only free-flowing molecule across this membrane.
To know more about Diffusion and Osmosis, visit here.
Isotonic, Hypotonic, and Hypertonic Solutions
- Isotonic solutions are those which have the same solute and pH concentration as the surrounding body fluid or the cytoplasm.
- Hypotonic solutions contain a lesser amount of solute concentration compared to the surrounding fluid and can force the cell to rupture due to excess input of water into the cell.
- Hypertonic solutions contain a higher concentration of solute compared to the surrounding fluid and thus push water out of the cell, shrinking it.
Cell Walls in Plants
Plant cells are different from animal cells due to the presence of a cell wall. The cell wall is made of cellulose and gives a rigid structure to the plant cell. It provides structural support to plants. Due to cell walls, cells of plants, fungi and bacteria can withstand greater changes in surrounding conditions than animal cells. E.g. Cell wall enables the cells to withstand hypotonic solution without bursting.
Cell Organelles
Eukaryotic cells contain various membrane-bound organelles that carry out various functions in the cell, e.g. Nucleus, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, Lysosomes, etc.
Read more: Cell Organelles – Structure and Functions
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is the invagination of the cell membrane, followed by pinching off, forming a membrane-bound vesicle. This is commonly seen in Amoeba.
Also read: Endocytosis vs Exocytosis
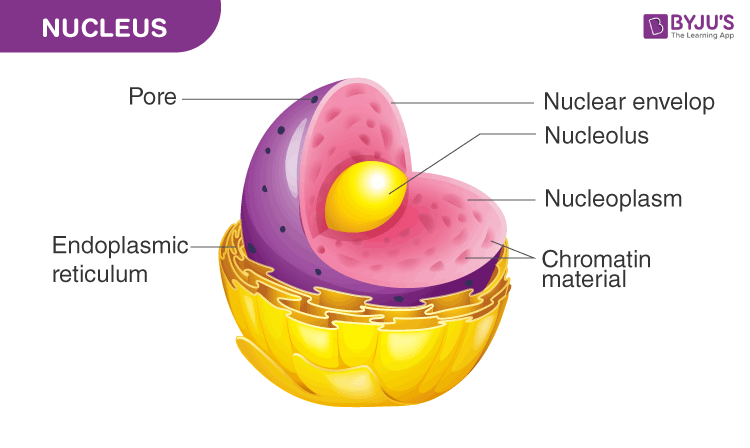
Nucleus in Cells
The nucleus is the processing unit of the cell. It is a double membrane-bound organelle which contains the genetic material for inheritance. The nuclear membrane contains pores that allow the transfer of materials from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. The nucleus is the brain of the cell as it controls various functions such as cell division, reproduction, inheritance, etc. The nucleus contains genetic material, i.e. chromosomes that contain DNA. DNA carries information for inheritance from parents to offspring. Prokaryotes lack a well-defined nucleus, and the genetic material is present in a region known as the nucleoid.
Chromosomes
Chromosomes are the genetic material present in the nucleus. It contains DNA with associated proteins. They are present as threads called chromatin. During the growth phase of the cell, the chromatin condenses into a much thicker structure called a chromosome. Human cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes (46).
Chromatin
Chromatin is a thread-like structure which serves as the genetic material present inside the nucleus of the cell. It is made up of DNA and protein molecules. DNA contains the hereditary information needed for the structure and function of the organism.
Read more: Chromatin
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the fluid found inside the cell. It gives the structure to the cell and houses different organelles of the cell.
Know more: Cytoplasm Structure and Function
Organelles
Organelles are structures present in the cytoplasm of the cell that helps in several functions of the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound cell organelle that plays an integral role in the interpretation of the genetic information present in the nucleus.
Rough ER
Rough ER is the one that has ribosomes on them. The ribosome is made up of nucleic acids and proteins. They are the site of protein synthesis. The Rough ER is also involved in the modification and folding of proteins.
Smooth ER
Smooth ER does not have ribosomes and thus is not involved in protein synthesis. They are, however, involved in lipid metabolism and detoxifying of poisonous molecules.
Read more: Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus is also called the post office of the cell. They package and transport the proteins across the cytoplasm.
Also read: Golgi Apparatus
Lysosomes
They are referred to as suicide bags of the cell as they contain potent enzymes that can digest a cell. Lysosomes also help in defence by attacking a foreign object.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are also called the powerhouse of a cell. They generate ATP via the electron transport chain. They also have a DNA called mtDNA, which makes them a semi-autonomous organelle. Mitochondria can make their own proteins.
Plastids
There are various types of plastids in different cells based on the pigment they contain. The chloroplast is the plastid where photosynthesis occurs, they contain chlorophyll. Some of the other plastids are leucoplast and chromoplast. Leucoplasts store starch, oil and protein granules. Chloroplasts contain membranes known as thylakoids embedded in the stroma. Plastids also contain their own DNA and ribosomes.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are large vesicles that hold water or air in them and give structural rigidity to the cell. Vacuoles are common in plant cells. In animals, the vacuoles are either very small or absent.
To know more about Cell Organelles, visit here.
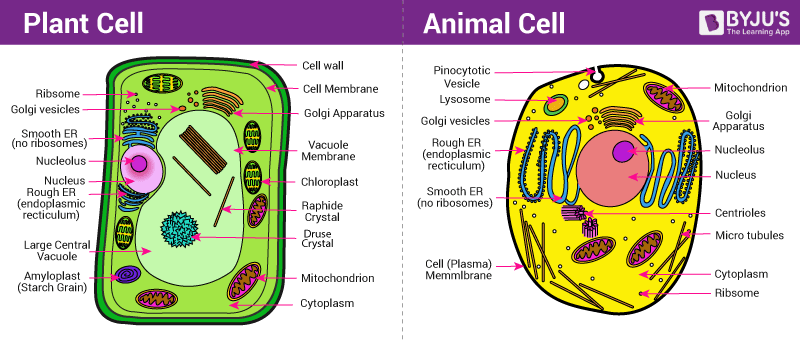
Comparison between Plant and Animal Cells
Plants cells are different from animal cells structurally. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplast which are missing in animal cells. Plants cells also have large vacuoles, which are either very small or missing in animal cells. The nucleus is present at the centre of the cell in animal cells and at the periphery in plant cells.
To know more comparisons between Plant & Animal Cells, visit here.
Questions from The Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9 Notes
- How does a plant cell differ from an animal cell?
- Differentiate between a eukaryotic cell and a prokaryotic cell.
- What would be the outcome in a scenario where a rupture occurs in the plasma membrane?
- Define osmosis.
- How does an amoeba acquire food?
- Growth and repair require which type of cell division?
Further Reading:-
| Difference Between Plant cell and Animal cell | Cells |
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 9 Biology Notes Chapter 5 Fundamental Unit of Life
What is a ‘homogenous’ mixture?
A homogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout the mixture.
What is an ‘isotonic’ medium?
A solution is isotonic when its effective mole concentration is the same as that of another solution.
What is a ‘vacuole’?
A vacuole is a membrane-bound cell organelle. In animal cells, vacuoles are generally small and help sequester waste products. In the plant cells, vacuoles help maintain water balance.
Comments