The National Security Council (NSC) in India is the executive agency responsible for advising the Prime Minister’s Office on issues of national security and strategic interest. The National Security Council is an important body in India with a powerful responsibility. This topic is important for the IAS exam and is covered in the UPSC Syllabus in the Internal Security segment.
| To complement your preparation for UPSC 2023, check the following links: |
The NSC was established in 1998 by the government of AB Vajpayee. Brajesh Mishra served as the country’s first National Security Advisor (NSA). Before the NSC was formed, these functions were carried out by the Principal Secretary to the Prime Minister.
The NSC is the apex agency in the country handling internal and external security, conventional and non-conventional defence, military affairs, counter-insurgency, space and high technology, economy, counter-terrorism and environment.
The NSC is headed by the Prime Minister and the NSA is its Secretary. The headquarters of NSC is in New Delhi and the current NSA is Ajit Doval.
Mandate – National Security Council
The National Security Council (NSC) is the principal advisory body on the proper coordination and integration of plans and policies affecting national security. The mandates of the NSC are based on presential executive issuance which is as follows-
- Re-Organizing the National Security Council and Defining its Membership, Function, and Authority and Other Purposes
- Directing the National Security Director to Provide Guidance and Direction to the Operations of the National Intelligence Coordinating Council and the Intelligence Community
- Directing the Director-General of the National Security Council to Revitalize the National Security Council and the Intelligence community and to Reorient their Activities Towards Attaining Broader National Goals
- Reconstituting the National Security Council and for Other Purposes
- Directing the Director-General of the National Security Council to revitalize the national intelligence community
- Creating the Presidential Situation Room
- Directing the Formulation of the National Security Policy and National Security Strategy
- Pursuing Our Social Contract with the Filipino People Through the Re-Organization of the Cabinet Clusters
- Operationalizing the Practical Guide for National Crisis Managers and the National Crisis Management Core Manual; Establishing National and Local Crisis Management Organizations; and Providing Funds
National Security Council Members
Apart from the NSA, the other members are:
- Deputy National Security Advisor (DNSA)
- Minister of Defence
- Minister of External Affairs
- Minister of Home Affairs
- Minister of Finance
- Deputy Chairman of the NITI Aayog
Other members can be invited to attend its monthly meetings as and when required.
The NSA is a powerful office and it is to him/her that various intelligence agencies such as RAW, IB, etc. report to rather than directly to the Prime Minister.
Mission and Vision of National Security Council
The mission of NSC is to –
- Advise the President on national security-related matters,
- Provide supervision and guidance over the NICA and general supervision over the intelligence community, and
- Coordinate the national government efforts in the pursuit of the national security goals and strategic objectives.
The vision of NSC –
The National Security Council envisions the national security institution that is responsive to the changing challenges and opportunities, within and outside the country and a policy advisory body that will effectively contribute to the provision of an enabling environment that will enhance socio-economic development and national governance.
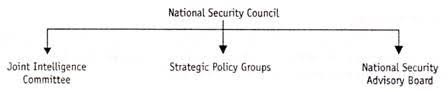
National Security Council Organisational Structure
India’s national security management structure is a three-tiered structure. The three tiers are comprised of:
- Strategic Policy Group
- National Security Advisory Board
- Secretariat represented by the Joint Intelligence Committee
Strategic Policy Group
- It is the first tier in the three-tier system of the NSC.
- It is the core decision-making apparatus of the NSC.
- The Chairman of the SPG now is the NSA. Earlier, it was the Cabinet Secretary.
- The SPG will assist the NSC, and also perform long-term strategic review of the security affairs of the country.
- It is the chief mechanism for coordination among the different ministries and for the integration of inputs for the formulation of security policies.
- SPG meetings will be convened by the NSA and the implementation of the decisions of the SPG by the Ministries and Departments, and the State governments, will be coordinated by the Cabinet Secretary.
National Security Council:- Download PDF Here
Aspirants reading the topic, ‘National Security Council’ can also read similar topics linked in the table below:
UPSC Preparation:
| Time Table for UPSC Preparation | UPSC 2021 Calendar |
| Documents Required for UPSC Exam | Language Papers in UPSC – Tips to Study |
| UPSC Admit Card | IAS Eligibility Criteria |
Comments