India has the third-largest AIDS epidemic in the world. The Government of India through NACO has many programs for AIDS control. In this article, we shall focus on the background and statistics of AIDS in India. These facts are also important from the perspective of the IAS Exam.
These UPSC Notes on the AIDS epidemic and related issues in India are aligned with the UPSC Syllabus and aspirants should prepare this topic for General Studies Paper I.
IAS aspirants can also get details about Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) at the linked article.
Given below are other related links that aspirants can refer to while preparing for the upcoming civil services exam:
| United Nations | Diseases and causing agent |
| World Bank | Healthy States, Progressive India Report |
AIDS and India
Context
- India has achieved significant progress in containing the AIDS epidemic.
- The stigma faced by HIV positive patients is a relevant social issue
Background
- As per the latest HIV estimates report (2019) of the Government, India is estimated to have around 23.49 lakh people living with HIV/AIDS in 2019. The HIV epidemic has an overall decreasing trend in the country with estimated annual New HIV infections declining by 37% between 2010 and 2019.
- UNAIDS is working towards ensuring that 30 million people have access to treatment through meeting the 90–90–90 targets, whereby 90% of people living with HIV know their HIV status, 90% of people who know their HIV-positive status are accessing treatment and 90% of people on treatment have suppressed viral loads.
- National AIDS Control Programme (NACP), implemented by the National AIDS Control Organization (NACO) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is the nodal programme for AIDS prevention, treatment and awareness generation. India is committed to achieving the 90-90-90 targets of UNAIDS.
- India has also declared recently its intention to provide free secondary treatment to all patients who require it.
- Even when only 0.27 % national prevalence is reported, vast regional disparities remain.
- The India HIV Estimation 2019 Report suggests:
- Overall AIDS prevalence in adults (15–49 years) has declined in the country
- Three states with the highest adult HIV prevalence are Mizoram, Nagaland, and Manipur
- Nationally, there were an estimated 23.48 lakh PLHIV in 2019
- In India, there were 69.22 thousand estimated new HIV infections in 2019
- 58.96 thousand AIDS-related deaths were estimated in the year 2019
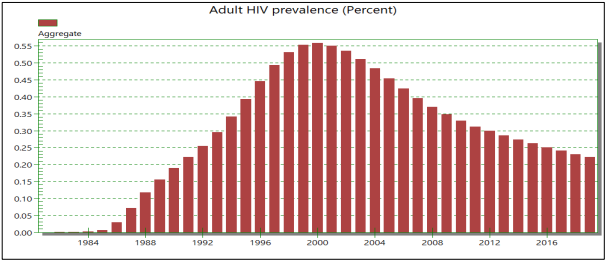
- The image below shows the estimated Adult HIV Prevalence in India during 1983 to 2019, HIV Estimations 2019
Government Initiatives
- After the detection of the first case in India in 1986, the Government of India established a National AIDS Control Program (NACP) which has now become the Department of AIDS under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare
- The National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO) was established in 1992 as a division of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. It provides leadership to HIV/AIDS control programmes in India through 35 Prevention and Control Societies. NACO is the nodal organisation for the formulation of policy and implementation of programs for prevention and control of HIV/AIDS in India
- There are numerous Non‐Governmental and Community Based Organizations (NGOs & CBOs) working on HIV/AIDS issues in India at the local, state, and national levels
- India receives technical assistance and funding from a variety of UN partners and bilateral donors
Aspirants can refer the UPSC Mains Syllabus at the linked article.
| Kickstart your UPSC preparation now and complement it with the links given below: |
Way forward
- Region and state wise plans must be evolved to tackle the spread of new infections.
- New policies for AIDS infected children must be integrated with Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) Anganwadi infrastructure and ASHA workers must be given special training.
- Drug users must be shown compassion by the law enforcement agencies and the Police must coordinate with the medical community to ensure that unsafe use of needles by drug addicts is checked.
- Due to the stigma faced by sex workers they are not able to get access to health counsellors, medical clinics, etc. There must be a comprehensive policy to tackle this.
- National Aids Control Programme (NACP) Phase IV aims to reduce new infections by 50 per cent and also provide comprehensive care, support and treatment to all persons living with HIV/AIDS.
- 2016 United Nations Political Declaration on Ending AIDS sets world on the Fast-Track to end the epidemic by 2030. India must ensure achieving its targets through sustained focused campaign with renewed vigour.
AIDS and India (UPSC Notes – GS 1) – Download PDF Here
Aspirants can check BYJU’S UPSC Notes page for free GS1, GS2, and GS 3 notes.
Frequently Asked Questions on AIDS and India
Q 1. What is India’s rank for HIV cases in the world?
Q 2. When was HIV detected in India?
Related Links:


Comments