HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus. It is the virus that leads to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS, if not treated. Unlike some other viruses, the human body can’t get rid of HIV completely, even with treatment. So once a person gets HIV, currently, there is no cure for it.
Since AIDS is a growing issue in the country, it is important for aspirants preparing for the IAS Exam and other Government exams to have knowledge about the topic. HIV is a part of the Science and Technology Section of the general studies paper 3 and Health section of general studies paper 2 of the UPSC Syllabus. The HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act is important in terms of Indian Polity.
What is HIV?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a lentivirus, which is a sub-classification of the retrovirus. It causes the HIV infection which over time leads to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
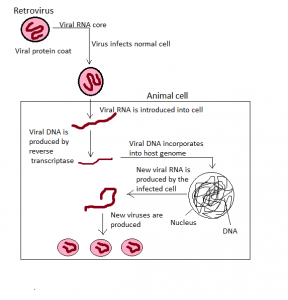
- AIDS is a deadly condition in which the affected person’s immune system fails, leading to the spread of life-threatening infections and cancers in his body.
- HIV demolishes a particular type of WBC (White Blood Cells) and the T-helper cells. This virus also makes copies of itself inside these cells.
- T-helper cells are also known as CD4 cells.
- The average survival period for a person affected with HIV without treatment is nine to eleven years, subject to the subtype of HIV.
- HIV infection can occur by the transference of blood, breast milk, vaginal fluid, semen, or pre-ejaculate.
- HIV occurs as both free virus particles and as a virus inside the infected immune cells within the above-mentioned bodily fluids.
- A weak immune system makes a person prone to opportunistic infections and cancer.
- It becomes difficult for a person infected with this virus to recover from even a minor injury or sickness.
- By receiving treatment, a severe form of HIV can be prevented.
Types of HIV
| Type One | Type Two |
|
|
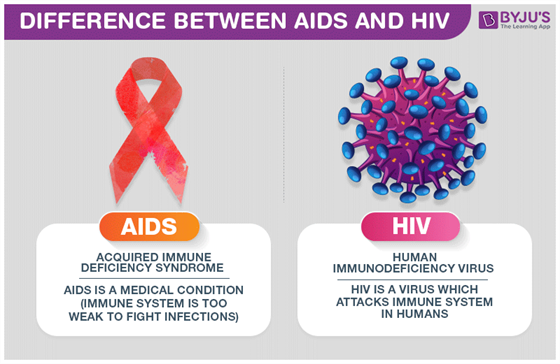
Difference between AIDS and HIV
| AIDS | HIV |
| Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a disease. | Human Immunodeficiency Virus(HIV) is the causal factor (reason) for AIDS |
| Complications and secondary infections from this disease kill the host. | The virus is incapable of killing a host by itself. |
| AIDS is a condition acquired only after the contraction of HIV. | HIV is a virus and like other viruses, can spread from person to person. |
HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act
The Government of India enacted the HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in the year 2017 and was in force in 2018. The State and Central Government are responsible for the following measures:
- Preventing the spread of HIV/AIDS
- Providing ART (Anti-Retroviral Therapy) for infected patients
- Providing awareness about HIV & AIDS
- Conducting educational programmes about AIDS & HIV
- Prohibiting discrimination of infected patients
- Providing HIV treatment and counselling services under the state care facilities
The Act lists various grounds on which discrimination against HIV positive persons and those living with them is prohibited.
HIV and AIDS (Prevention and Control) Act maintain that without the consent of the person, no one can conduct any HIV tests or treatment related to HIV. Also, the person won’t be under any compulsion to disclose his/her HIV status except when required by the Court. Informed consent for an HIV test will not be required in case of screening by any licensed blood bank, a court order, medical research, and epidemiological purposes where the HIV test is anonymous and not meant to determine the HIV status of a person. Establishments keeping records of information of HIV positive persons shall adopt data protection measures. The requirement for HIV testing as a prerequisite for obtaining employment or accessing health care or education is also prohibited.
In the case of violation of the act, the party disclosing information on a person with HIV or advocating hatred against them will be punished with a fine of one lakh rupees or imprisonment ranging from 3 months to 2 years.
Ombudsman Appointment under HIV and AIDS Bill
- An ombudsman will be appointed by each state government to inquire into complaints related to the violation of the Act and the provision of health care services.
- The Ombudsman shall submit a report to the state government every six months stating the number and nature of complaints received, the actions taken and orders passed.
Click the link to read about AIDS and India
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV):- Download PDF Here
Related Links:
| UPSC Books | UPSC 2022 | UPSC Current Affairs |
| National Family Health Survey | NCERT Notes For UPSC | National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) |
Comments