The Delta variant of the coronavirus that causes Covid-19 has been identified as a variant of concern. What does a variant of concern mean? Why do viruses mutate and form variants? Get answers to all these questions in this article.
This is an important topic for the UPSC exam especially for the health as well as current affairs sections.
| Candidates can enhance their UPSC exam preparation by attempting UPSC Previous Years Question Papers now!!
To complement your preparation for the upcoming exam, check the following links: |
What are Virus Variants?
Viruses change constantly through mutation and this causes variants of the virus to emerge. Mutation is a natural occurrence and is a part of the evolution of the virus. Many times, mutations emerge and disappear while others persist.
- Covid-19 is caused by the SARS-Cov-2 virus which is a single-stranded RNA virus. Mutations are changes in the genetic sequence of the RNA.
- A virus starts replicating when it enters a host cell or a susceptible body. The rate of replication increases with the spread of the infection increasing.
- A virus that has got a mutation in it is known as a variant.
- Viruses constantly change and become more diverse.
- Scientists and medical experts have to constantly monitor the mutations to identify how they affect the spread of the infection and how severe or not the symptoms can be, and whether current diagnostics, vaccines and medicines will work with the variants or not.
- Variants are concerning because negative effects of the variants in the form of increased severity of the symptoms, lowered immunity to fight the infection, decreased effect of vaccines or treatments, etc. would put more pressure on the already burdened healthcare infrastructure of the country.
Related Links:
| Nipah Virus (NiV) | Avian Influenza |
| Diseases and causing agent | Rare Diseases |
| Zoonotic Diseases | Difference between COVID-19 and SARS |
Why do viruses mutate?
Viruses mutate due to any of the following reasons:
- Random error during replication of the virus.
- Continuous transmission of the virus due to lack of Covid-appropriate behaviour because of which the virus finds good hosts to grow and become more transmissible.
- Immune pressure faced by viruses after treatments such as convalescent plasma, vaccination or monoclonal antibodies.
Read more on the Coronavirus Pandemic in the link.
What is a Variant of Concern?
The terms variant of concern and variant of interest are frequently used in the news in relation to the coronavirus pandemic. These are classifications of the virus variants. In this section, you can read about some of the major classifications of the variants.
- Variant under Investigation: A variant becomes a variant under investigation when the mutations happen and if there is any previous association with any other similar variant which is felt to have an impact on public health.
- Variant of Interest (VOI): This includes variants with specific genetic markers that have been associated with changes to receptor binding, decreased neutralisation by antibodies generated against vaccination/previous infection, lessened efficacy of treatments, potential diagnostic impact, or predicted increase in transmissibility or disease severity. The following are the possible attributes of a VOI.
- Specific genetic markers that are predicted to affect therapeutics, transmission, diagnostics or immune escape.
- Evidence that it is the cause of an increased proportion of cases or unique outbreak clusters.
- Variant of Concern (VOC): When there is evidence for increased transmissions through field and clinical investigations, a variant becomes a VOC. Variants of Concern have one or more of the following characteristics.
- Higher transmissibility
- Change in virulence/disease presentation; evidence of increased disease severity
- Evading diagnostics, drugs and vaccines
- Variant of High Consequence: A variant of high consequence has clear evidence that prevention measures or medical countermeasures (MCMs) have drastically reduced effectiveness relative to previously circulating variants. Possible attributes include:
- Demonstrated diagnostics failure
- Higher severity of the disease and increased hospitalisations
- Reduced susceptibility to treatment
- Evidence for decreased vaccine effectiveness, a very large number of vaccine breakthrough cases, or very low protection from vaccine against severe disease
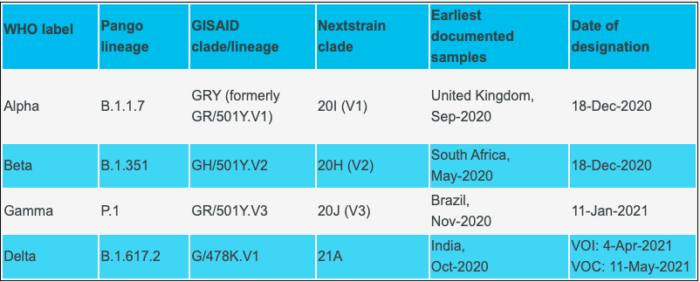
- The first variant of concern was identified in the United Kingdom and it was named the UK variant initially.
- Currently, there are four variants of concern.
Current SARS-Cov-2 virus variants of concern
Currently, there are four variants of concern identified. They have been named Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta by the World Health Organisation (WHO).
In May 2021, WHO announced that it has assigned Greek alphabets for indicating covid-19 virus variants for making it easier for the public to remember the names and also to avoid the stigma that might come when variants are named after the places where they originated or where first identified. Accordingly, the UK variant is now called the Alpha variant.
The Indian Government had objected to the use of the term ‘India variant’ for the Delta variant.
These names do not replace the scientific names of the variants.
Variants of Concern
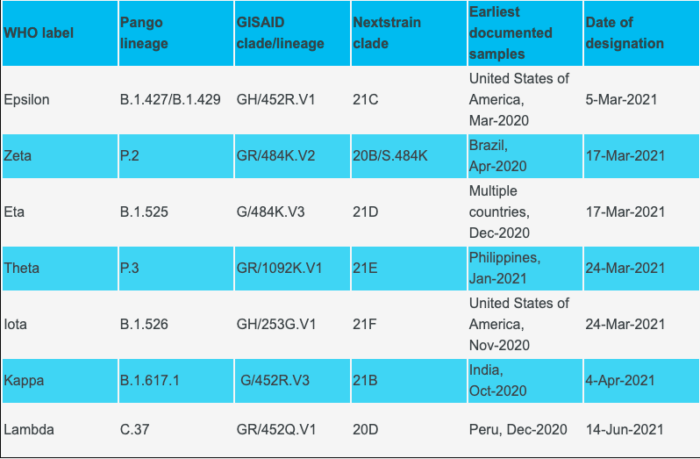
Variants of Interest
 Images source: https://www.who.int/
Images source: https://www.who.int/
Coronavirus Delta Variant
Delta Variant is the name given to the SARS-Cov-2 virus variant first identified in India by Indian scientists.
- It is also called SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617 and has about 15 – 16 mutations.
- It was first reported in October 2020 in India. It is currently the most prevalent variant seen in India.
- It has been reported in at least 80 countries since.
- The Delta variant (B.1.617) has three subtypes:
- 617.1 (variant of interest) – also named Kappa variant
- 1.617.2 (variant of concern)
- 1.617.3 (variant of interest)
- The B.1.617.2 variant has been named Delta Plus.
- An additional mutation to the Delta Plus variant has been named as the K417N mutation.
- The Delta variant has been named a VOC because of:
- Increased transmissibility
- Stronger binding to receptors of lung cells
- Potential reduction in monoclonal antibody response
- Potential post-vaccination immune escape
- The Delta variant has been isolated and is being cultured now at ICMR’s National Institute of Virology, Pune. Tests are being performed to evaluate the effectiveness of the vaccines against this variant.
Omicron Variant
In November 2021, a new variant, now called the ‘Omicron variant’ was first reported from South Africa. Designated a ‘variant of concern’ by WHO, omicron is spreading fast in many countries of the world including India. As of January 2022, 1,892 cases of Omicron have been detected across 23 states and Union Territories so far.
Read more on Omicron in the linked article.
Coronavirus Variants:- Download PDF Here
UPSC Preparation Links
| Topic-wise UPSC Prelims Questions PDF | Science & Technology Questions for UPSC Mains GS 3 |
| Download NCERT Notes PDF | IAS Officer |
| FAQ on UPSC | IAS Preparation |
| IAS Toppers | UPSC Mains Exam |
Comments