Home / United States / Math Classes / 8th Grade Math / Graphing Linear Equations
Graphing Linear Equations
A linear equation is one in which the highest exponent of a variable is 1. A linear equation is represented by a straight line on the coordinate plane. In this article, we will learn about linear equations and the method used to graph them....Read MoreRead Less
Linear Equation
An equation with the highest exponent of 1 is said to be a linear equation. The graph of a linear equation is always a straight line.
We have to note that a linear equation in one variable is known as a one-variable linear equation.
The standard form of a one variable linear equation is \(Ax~+~B=0\), where x is the variable, A is the coefficient of \(x\), and \(B\) is the constant. Here, ‘\(A\)’ can not be zero.
For example: \(3x~+~8=0\)
A linear equation with two variables is a two-variable linear equation.
The standard form of a two variable linear equation is \(Ax~+~By~+~C=0\) where x and y are the variables, \(A\) is the coefficient of \(x,~B\) is the coefficient of, \(y\) and \(C\) is the constant.
For example: \(3x~-~2y~+~5=0\)
What is an Ordered pair?
An ordered pair is made up of the \(x\)(abscissa) and \(y\) (ordinate) coordinates, with two values written in a specific order within parentheses, \((x,~y)\), where x represents the distance from the origin along the \(x\)-axis, and \(y\) states the distance from the origin along the \(y\)-axis.

Graphing Linear Equations
The graph of a two-variable linear equation is a straight line. The graph of a linear equation can be drawn with the help of any two points \((x_1,~y_1)\) and \((x_2,~y_2)\). The following steps are to be followed to draw the graph:
Step 1: Make a table of values by putting values of \(x\) and getting the values of \(y\).
Step 2: Plot all the ordered pairs on the coordinate plane.
Step 3: Draw a line passing through all the ordered pairs.
For example: Plot a graph for \(3x~-~4y=12\).
Here, \(3x~-~4y=12\)

Graphing a Horizontal Line
The standard form of a horizontal line is \(y~=~b\) and the line passes through the point \((0,~b)\). The horizontal line is parallel to the \(x\)–axis.

Graphing a Vertical Line
The standard form of a vertical line is \(x=a\) and the line passes through the point \((a,~0)\). The vertical line is parallel to the \(y\)–axis.

Solved Examples
Example 1: Graph \(y=3x~-~2\).
Solution:
Step 1: Make a table of values.
x | \(y=3x~-~2\) | y | \((x,~y)\) |
|---|---|---|---|
-1 | \(y=3(- 1)~-~2\) | -5 | (-1, -5) |
0 | \(y=3(0)~-~2\) | -2 | (0, -2) |
1 | \(y=3(1)~-~2\) | 1 | (1, 1) |
2 | \(y=3(2)~-~2\) | 4 | (2, 4) |
Step 2: Plot the ordered pairs.
Step 3: Draw the line through the points.

Example 2: Graph \(y=5\)
Solution:
The graph of \(y=5\) is a horizontal line passing through (0, 5). Draw a horizontal line that passes through this point.

Example 3: Graph \(x=-~2\).
Solution:
The graph of\(x=-~2\) is a vertical line passing through (-2, 0). Draw a vertical line that passes through this point.

Example 4: The amount \(y\) (in dollars) of money in Sam’s saving accounts after \(x\) months is represented by the equation \(y=5x~+~200\). Draw the graph for the equation. In how many months Sam will have $300 as a savings in his account?
Solution:
Step 1: Make a table of values.
x | \(y=5x~+~200\) | y | \((x,~y)\) |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | \(y=5(1)~+~200\) | 205 | (1, 205) |
2 | \(y=5(2)~+~200\) | 210 | (2, 210) |
3 | \(y=5(3)~+~200\) | 215 | (3, 215) |
4 | \(y=5(4)~+~200\) | 220 | (4, 220) |
Step 2: Plot the ordered pairs.
Step 3: Draw the line through the points.
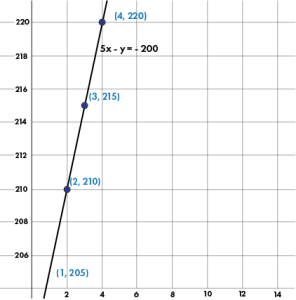
The total amount in the savings account is $300. The number of months in which the account has been saved by solving the equation after putting \(y=300\) .
\(y=5x~+~200\) Writing Equation
\(300=5x~+~200\) Substitute
\(x=20\) Simplify
Sam will take 20 months to save $300.
A linear equation is one in which the highest exponent of a variable is 1. Worksheets allow your child to see their processes and determine where they might be making conceptual or computational mistakes.
The equation whose highest exponent is greater than 1 is known as a non-linear equation.
A linear equation is represented by a straight line on a graph.
A solution is a value or a set of values when substituted for the unknown that makes the equation true.

