The government of India is divided into three branches: Executive, Legislative and Judiciary. The Judiciary is independent of the other two branches, i.e. they cannot interfere in the affairs of the judiciary. Thus, the courts play an important role in protecting the constitution.
The Supreme Court of India (SC of India), is at the top of the judicial hierarchy and the final court of appeal set up by the Indian Constitution.
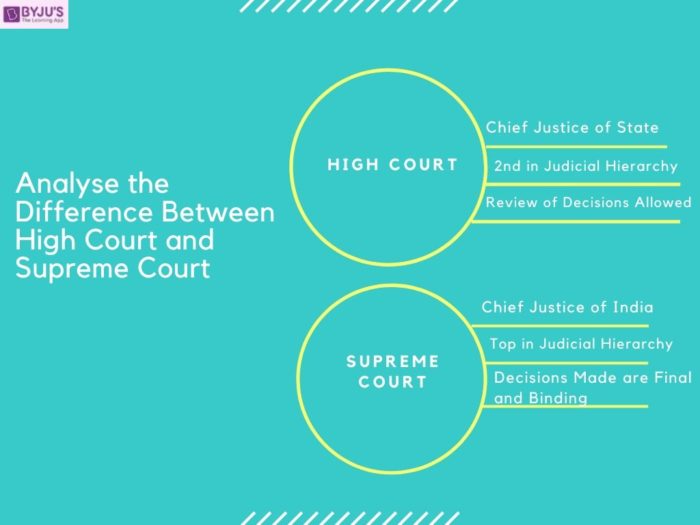
It followed by the High Court (HC), which is the apex judicial forum at the state and union territory level. One of the major differences between High Court and Supreme Court is that the decision made by the HC, can be reviewed in the SC, but the decision of the SC is final and binding and no further appeals are allowed.
You can find the list of the High Courts in India by visiting the linked article
This article will further highlight the differences between the High Court and the Supreme Court
The difference between the High Court and the Supreme Court is given below:
Differences between the High Court and the Supreme Court
| High Court |
Supreme Court |
| The High Court is the apex judiciary body of a State’s administration. It is headed by the Chief Justice of the State | The Supreme Court is the primary court of justice in the country and it is headed by the Chief Justice of India |
| The Judges of the High Court are appointed by the President in consultation with the Chief Justice of India and the Governor of the state in question | According to the Constitution of India, every Judge of the Supreme Court shall be appointed by the President by warrant under his/her hand and seal after consultation with such of the Judges of the Supreme Court and of the High Court in the States. |
| Judges of the High Court retire at the age of 62 years | A Supreme Court judge retires at the age of 65 |
| The High Court has authority over all the other courts under its jurisdiction, which in turn is limited by the boundary of the concerned state | The Supreme Court has jurisdiction over all the courts and tribunals of the country |
| The High Court is headed by the Chief Justice of the State | The Supreme Court is headed by the Chief Justice of India |
| Every High Court there is a Chief Justice and many other judges. The number of judges appointed is defined by the President of India | At Present, the Supreme Court of India consists of 31 judges ( Including the Chief Justice and 30 other judges). The Supreme Court (Number of Judges) has made provisions where four more judges can be appointed. It increased the strength from 31 to 34 including the Chief Justice of India |
Be sure to visit the following links for a thorough revision of the polity segment along
- UPSC Indian Polity
- Difference Between Statutory and Quasi-Judicial Bodies
- Difference Between Procedure Established by Law and Due Process
- Difference between Legislative and Executive
- Polity Syllabus and Strategy for UPSC
Difference Between High Court and Supreme Court – Download PDF Here
Frequently Asked Questions about High Court and Supreme Court
What are the 3 powers of the Supreme Court?
What is the role of High Court in India?
You can find more preparation materials for the IAS Exam by referring to the links given below in the table:
Related Links
Comments