The “Procedure Established by Law” means that a law is duly enacted by the legislature or the concerned body is valid only if the correct procedure has been followed to the letter.
The concept has been enshrined in Article 21 of the Indian Constitution, which states that “No person shall be deprived of his life or personal liberty except according to the procedure established by law.”
“Due Process of Law” is a doctrine that not only checks if there is a law to deprive the life and personal liberty of a person but also ensures that the law is made fair and just.
Both are important concepts in the Indian polity segment of the IAS Exam. Thus, it is important to know how the two are different from each other, which this article will aim to highlight.
Aspirants can find more Difference Between Articles, by visiting the linked page
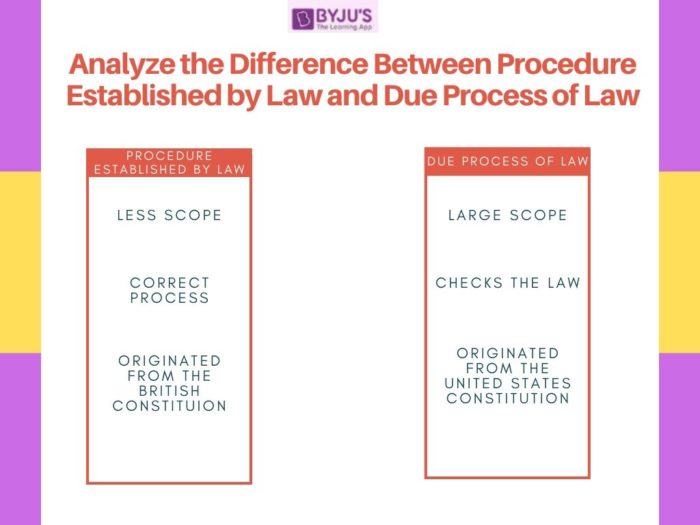
The differences between ‘Procedure Established by Law’ and ‘Due Process of Law’ are given in the table below
Differences between Procedure Established by Law and Due Process of Law

| Procedure Established by Law |
Due Process of Law |
| It means that a law that is duly enacted by the legislature or the body in question is valid if the procedure to establish it has been correctly followed | Due process of law checks whether any law in question is fair and not arbitrary |
| The Judiciary would assess whether the Legislature is competent to frame the law and whether it had followed the procedure laid down to legislate and would not assess the intent of the said law | If the Supreme Court of India that any law as not fair, it will declare it as null and void. This doctrine provides for more fair treatment of individual rights |
| Compared to ‘due process of law” it is narrow in scope as it does not question whether the law concerned is contrary to principles of justice and equity | The due process of law gives wide scope to the Supreme Court to grant protection to the rights of its citizens. |
| The Supreme Court, while determining the constitutionality of the law examines only the substantive question i.e., whether the law is within the powers of the authority concerned or not. | The Supreme Court can declare laws violative of fundamental rights and render them void not only on substantive grounds of being unlawful but also on procedural grounds of being unreasonable. |
| A rigid and inflexible following of the procedure established by law may raise the risk of compromise to life and personal liberty of individuals due to unjust laws made by the law-making authorities. Thus, Procedure established by law protect the individual against the arbitrary action of only the executive. | Under due process, it is the legal requirement that the state must respect all of the legal rights that are owed to a person and laws that states enact must conform to the laws of the land |
The concepts of Procedure Established by Law and Due Process of Law are covered in great detail under the Polity segment of the UPSC Exams. The following links will help in preparing for this segment:
- How a Bill Is Passed in Parliament
- Indian Polity Notes for UPSC Exams
- Public Interest Litigation
- Polity Syllabus and Strategy for UPSC Exams
- Constitution of India
- Indian Penal Code
- Important Amendments In Indian Constitution
- Difference Between Legislative And Executive
- Difference between High Court and Supreme Court
- Difference Between Unwritten and Written Constitution
- 100 Difference Between Articles for UPSC Exams
Difference Between Procedure Established by Law and Due Process of Law- Download PDF Here
FAQs about Procedure Established by Law and Due Process of Law
What do you mean by due process of law?
What is procedure established by law in Article 21?
Candidates can find the general pattern of the UPSC Exams by visiting the UPSC Syllabus page. For more articles and exam-related preparation materials, refer to the links given in the table below:
Related Links

Comments