The Wholesale Price Index (WPI) is an important index necessary for calculating inflation in a country. The Office of the Economic Adviser in the Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion, Ministry of Commerce & Industry is responsible for compiling WPI and releasing it.
In this article, you can understand about Wholesale Price Index and how it is important for the IAS Exam.
This topic is useful for Indian Economy (GS Paper III) segment of the UPSC Syllabus.
The rate of inflation based on WPI Food Index increased from 5.28% in March, 2021 to 7.58% in April, 2021. Final Index for the month of February, 2021-For the month of February, 2021 the final Wholesale Price Index and inflation rate for ‘All Commodities’ (Base: 2011-12=100) stood at 128.1 and 4.83% respectively.
What is Wholesale Price Index (WPI)?
The Wholesale Price Index represents the price of a basket of wholesale goods. WPI focuses on the price of goods that are traded between corporations. It does not concentrate on goods purchased by the consumers.
- The main objective of WPI is monitoring price drifts that reflect demand and supply in manufacturing, construction and industry.
- WPI helps in assessing the macroeconomic as well as microeconomic conditions of an economy.
Importance of WPI
- In a dynamic world, prices do not remain constant.
- The inflation rate calculated on the basis of the movement of the Wholesale Price Index (WPI) is an important measure to monitor the dynamic movement of prices.
- As WPI captures price movements in a most comprehensive way, it is widely used by Government, banks, industry and business circles.
- Significant monetary and fiscal policy changes are often linked to WPI movements.
- Similarly, the movement of WPI serves as an influential determinant, in the formulation of trade, fiscal and other economic policies by the Government of India.
- The WPI indices are also used for the purpose of escalation clauses in the supply of raw materials, machinery and construction work.
- WPI is used as a deflator of various nominal macroeconomic variables, including Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) Latest News
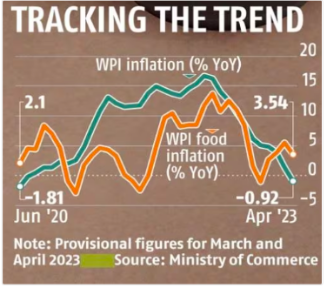
The Wholesale Price Index (WPI)-based inflation in India fell to a 34-month low of -0.92% in April, compared to 1.34% in March 2023.
- The Commerce and Industry Ministry’s data reveals price contractions in multiple sectors, such as beverages, tobacco, apparel, leather, pharmaceuticals, cement, chemicals, textiles, manufactured food products, fats, basic metals and rubber products.
Factors Contributing to WPI Deflation:
- High base effect: The significant decrease in WPI can be partially explained by the higher base effect, as the factory-gate inflation was at 15.38% in April 2022 and -1.81% in June 2020.
- Easing of global commodity prices: The inflation rate is expected to remain low due to the decline in global commodity prices, which has eased the pressure on input costs.
- Continued contraction in prices of manufactured products has also resulted in the decline of WPI.
Impact on Food Inflation:
- Food inflation (excluding manufactured food items) eased to 3.54% in April from 5.48% in March.
- However, certain food items such as cereals, paddy, wheat, milk, and pulses experienced elevated inflation rates.
- The decline in prices of vegetables, onions, potatoes, and fruits compared to the previous year indicates a deflationary trend.
Fuel Inflation and Its Impact
- Fuel inflation significantly eased to 0.93% in April from 8.96% in March ’23.
- The deceleration in the price rise of petrol and high-speed diesel, and the contraction in LPG prices contributed to the decrease in fuel inflation.
Relationship with Consumer Price Index (CPI) Inflation
- The fall in WPI inflation coincides with a decline in the CPI-based retail inflation rate, which reached an 18-month low of 4.7% in April.
- The lower WPI print is expected to have a lagged impact on core CPI inflation, potentially leading to a further decrease in retail inflation.
Monetary Policy Implications
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to keep the policy repo rate unchanged at 6.5%.
- A lower WPI inflation rate and a potential decline in retail inflation could provide leeway for the central bank to consider easing monetary policy in the future.
Future Outlook and Forecasts
- Economists project that the May CPI inflation may track around 4%, undershooting the RBI’s forecast of 5.1% for the April-June quarter.
- Factors such as softer food prices and a significant base effect are expected to contribute to lower inflation numbers.
Aspirants preparing for the upcoming UPSC exam can go through the following links to prepare for economics better-
| For more articles about the Indian economy or about Economics in general, be sure the visit the UPSC Notes on Indian Economy page now!
The following links will help candidates in their preparation of the Economy segment of the UPSC Exams: |
Wholesale Price Index (WPI) in India
Generally, WPI and CPI (Consumer Price Index) are used to calculate the inflation rates. In India, Inflation rates are based on WPI which is released by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
The CPI is a measure that assesses the weighted average of prices of a basket of consumer goods and services, such as transportation, food, and medical care, purchased by households.
India experienced its highest inflation rate of 34.68 per cent in September of 1974. And the lowest rate touched -11.31 per cent in May 1976.
Difference between WPI and CPI
The below table illustrates the differences between Wholesale Price Index and Consumer Price Index:
| Context | WPI | CPI |
| Definition | Amounts to the average change in prices of commodities at the wholesale level. | Indicates the average change in the prices of commodities at the retail level. |
| Publishing office | Office of Economic Advisor (Ministry of Commerce & Industry) | Central Statistics Office (Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation) & Labour Bureau |
| Commodities | Goods only | Goods and Services both |
| Inflation Measurement | First stage of a transaction | Final stage of a transaction |
| Prices paid by | Manufacturers and wholesalers | Consumers |
| Types of Commodities covered | Manufacturing inputs and intermediate goods like minerals, machinery basic metals, etc. | Education, communication, transportation, recreation, apparel, foods and beverages, housing and medical care |
| Base Year | 2011-12 | 2012
Note: Base Year to be revised. |
Wholesale Price Index (WPI):- Download PDF Here
Related Links:

Comments