SIPRI Yearbook is an annual publication on the current state of armament, disarmament and international security released by the Swedish think tank, Stockholm International Peace Research Institute.
Details on SIPRI report are relevant for IAS exam aspirants from current affairs point of view.
Latest Context on SIPRI Report –
In March 2023, the Swedish Think Tank Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) released data for the arms import-export for 2013-17 and 2018-22.
SIPRI Yearbook [UPSC Notes]:-Download PDF Here
This article will provide information on key findings of the SIPRI Yearbook 2022 which will help candidates prepare for UPSC Prelims and Mains examination.
| Looking for study material to prepare for the Civil Services Exam?
Refer to the links below and complement your UPSC exam preparation: |
SIPRI Yearbook 2022 – Key Findings
- India
- India’s arms imports fell 11% between 2013-17 and 2018-22.
- India (11%) remained the largest arms importer followed by Saudi Arabia (9.6%), Qatar (6.4%), Australia (4.7%) and China (4.7%).
- Russia accounted for 45% of India’s imports followed by France (29%) and the US (11%).
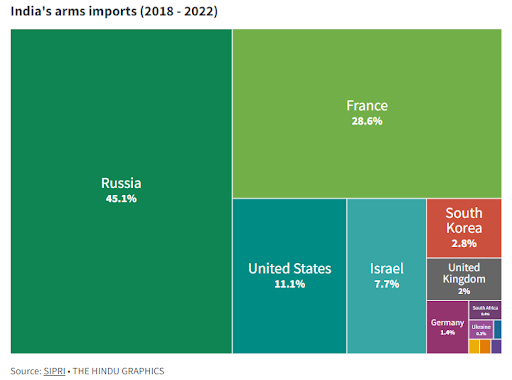
- USA
- The US was the world’s topmost military exporter in the past five years, accounting for 40% of global exports. It is followed by Russia (16%), France (11%), China (5.2%) and Germany (4.2%).
- US arms exports jumped 14% between 2013-17 and 2018-22.
- Russia
- Russia’s fell 31% during the 2013-17 and 2018-22 periods.
- Russia’s imports to India fell 37%.
- Ukraine
- Ukraine was the third biggest importer of major arms in 2022, and the 14th biggest during 2018-22.
- France
- France’s arms exports jumped 44% between 2013-17 and 2018-22.
- France had displaced the US as the second largest supplier of arms to India after Russia.
SIPRI Yearbook 2021 – Key Findings
- There are Nine Nuclear Armed States that include Russia, India, US, UK, China, France, Pakistan, Israel, and North Korea. These together possessed an estimated 13,080 nuclear weapons at the start of 2021. It was 13,400 in 2019.
- India possessed an estimated 156 nuclear warheads at the start of 2021, compared with 150 at the start of 2020, while Pakistan had 165 warheads in 2021, up from 160 in 2020. In 2019, India had 130-140 warheads.
- China’s nuclear arsenal is up from 320 at the start of 2020 to 350 warheads in 2021. The country is in the middle of significant modernisation and expansion of its nuclear weapon inventory.
- China and Pakistan possess more nuclear weapons than India.
- China is developing a nuclear triad for the first time, made up of new land- and sea-based missiles and nuclear-capable aircraft.
- Read more on : India – Pakistan Relations
- India – China Relation
- Russia and the US together possessed over 90% of global nuclear weapons and have extensive and expensive modernisation programmes underway.
- Supplier of Major Arms –
- The five largest suppliers in 2016-2020 accounted for 76% of the total volume of exports of major arms. These major arms suppliers are the United States, Russia, France, Germany and China.
- Major Importers of Arms –
- Between 2016-2020, 164 states are identified by the SIPRI as importers of major arms.
- Largest volume of major arm supplies region-wise in 2016-2020 was received by Asia and Oceania with 42% followed by the Middle East, accounting for 33% of the global total.
- The country-wise data says 36% of the total arms are imported by the five largest arms importers including India, Egypt, China, Saudi Arabia and Australia.
- Largest spenders in Military and Arms –
- The United States and China are 1st and 2nd largest military spenders respectively.
- Their expenditure pattern has largely influenced the growth in total military spending in 2020.
- India is ranked the 3rd highest military spenders in the world. Its spending of USD 72.9 Billion witnessed an increase of 2.1% in 2020 ranked it at 3rd.
- Recent Instances associated with Armed conflicts –
- For the first time in over five decades, in June 2020, the border tensions between India and China in the disputed eastern Ladakh region of Kashmir turned deadly. Know in detail about India – China Conflict – Galwan Valley clash on the given link.
- The territorial conflict between India and Pakistan over Kashmir. Read more on Kashmir-Pakistan Isolated: RSTV – Big Picture. The situation of territorial conflict in 2020 largely reverted to the status quo of relatively low levels of armed violence.
- A new armed conflict broke out between federal government forces and the Tigray People’s Liberation Front in the Tigray region of northern Ethiopia in November 2020, which killed thousands and forced more than 46, 000 refugees to flee into eastern Sudan.
- Even during a pandemic year, the planet’s major military spenders – the United States, China, and India – increased their defence expenditure.
- According to the study, worldwide military spending increased marginally amidst the Pandemic when the global economy shrunk.
Aspirants can check the relevant related links provided below to comprehensively prepare for the upcoming UPSC examination-
Major Concerns
In global military stockpiles the overall number of warheads now appears to be increasing, an alarming sign that the declining trend that has characterised global nuclear arsenals since the end of the Cold War has stalled.
- China’s evolving profile as a nuclear-weapons state was compounding India’s security challenges.
- The main concern is that India and Pakistan are seeking new technologies and capabilities that dangerously undermine each other’s defence under the nuclear threshold.
- India-Pakistan “risks stumbling into using their nuclear weapons through miscalculation or misinterpretation in a future crisis.
- Even though the total number of nuclear warheads decreased in quantity, the number of nuclear warheads put into operation has increased significantly. The United Kingdom has also clarified its stance on operationalising more nuclear warheads.
Status of India in Relation to Nuclear Weapons
- India tested its first nuclear device in May 1974.
- India maintains its commitment to No-first-Use of nuclear weapons and non-use against non-nuclear weapon states.
- It was admitted as a member into the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) in 2016, Wassenaar Arrangement in 2017 and Australia Group in 2018.
- Read in detail about the Wassenaar Arrangement on the given link.
- It remains outside of both the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) and the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty.
- You can read more on Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty – CTBT on the link provided here.
- India has a facility-specific safeguards agreement in place with the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
- It also has a waiver from the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG) allowing it to participate in global civilian nuclear technology commerce.
Stockholm International Peace Research Institute
- SIPRI full form is Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, is an international institute based in Stockholm, Sweden.
- SIPRI was established in 1966 and is dedicated to research into conflict, armaments, arms control and disarmament.
- It provides data, analysis and recommendations, based on open sources, to policymakers, researchers, media and the interested public.
- SIPRI publishes its yearbook annually that provides an overview of developments in international security, weapons and technology, military expenditure, the arms trade and arms production, and armed conflicts, along with efforts to control conventional, nuclear, chemical and biological weapons.
- The first edition of the SIPRI Yearbook was released in 1969.
SIPRI Yearbook [UPSC Notes]:-Download PDF Here
Get the detailed UPSC Syllabus for the prelims and mains examination and start your Civil Services Exam preparation accordingly.
UPSC Preparation:


Comments