TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. GS1 Related B. GS2 Related GOVERNANCE 1. Couples in live-in relations cannot adopt, says CARA C. GS3 Related ECONOMY 1. Cess collected for construction workers’ welfare abysmally low ENVIRONMENT 1. India is facing its worst water crisis: NITI Aayog D. GS4 Related E. Editorials POLITY AND GOVERNANCE 1. Major Port Authorities Bill for stronger employee representation F. Tidbits 1. States should protect all strays: AWBI 2. Federal Reserve lifts rates amid stronger inflation in U.S., drops crisis-era guidance 3. WPI inflation at 14-month high in May 4. Will back AI with funds till disinvestment is done: Sinha 5. Ministry takes up Maldives visa row 6. India calls UN report on Kashmir fallacious G. UPSC Prelims Practice Questions H. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
A. GS1 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
B. GS2 Related
1. Couples in live-in relations cannot adopt, says CARA
- The nodal body for adoption in the country has barred partners in live-in relationships from adopting a child on the ground that cohabitation without marriage is not considered a stable family in India.
- The Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA) permits a single woman to adopt a child of any gender, while single men can adopt only boys.
- In case an applicant is married, both spouses must give their consent for adoption and should be in a stable marriage for at least two years.
- Candidates must be physically fit, financially sound, mentally alert and highly motivated to adopt a child, as per the Adoption Regulations 2017.
Central Adoption Resource Authority
- Central Adoption Resource Authority (CARA) is a statutory body of Ministry of Women & Child Development, Government of India.
- It functions as the nodal body for adoption of Indian children and is mandated to monitor and regulate in-country and inter-country adoptions.
- CARA is designated as the Central Authority to deal with inter-country adoptions in accordance with the provisions of the Hague Convention on Inter-country Adoption, 1993, ratified by Government of India in 2003.
- CARA primarily deals with adoption of orphan, abandoned and surrendered children through its associated /recognised adoption agencies.
Foreign agency approval
- It has been decided that the cases of single PAP (prospective adopting parent) in a live-in relationship with a partner will not be considered eligible to adopt a child and their registration through the AFAAs (authorised foreign adoption agencies) will not be considered for approval.
- The rationale behind the decision is that in India, a live-in relationship is not considered a stable family and the best interest of the child is to be ensured.
- But there is no rule yet if a single parent decides to enter into a live-in relationship after adopting a child.
Supreme court
- The Supreme Court has on several occasions said that a live-in relationship is neither a crime or a sin.
- In the month of May, the Supreme Court had said that adult couples have the right to live together even if they were not married.
- It said that even the legislature recognised live-in relationships through the provisions under the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act, 2005.
Domestic violence act
- The Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act 2005 is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted to protect women from domestic violence.
- The Act provides for the first time in Indian law a definition of domestic violence, with this definition being broad and including not only physical violence, but also other forms of violence such as emotional/verbal, sexual, and economic abuse.
- It is a civil law meant primarily for protection orders and not meant to penalize criminally.
- The act does not extend to Jammu and Kashmir.
- Under the Act, women in a live-in relationship have been accorded protection as it allows females living with a male person in a relationship in the nature of marriage to file a complaint of domestic violence.
C. GS3 Related
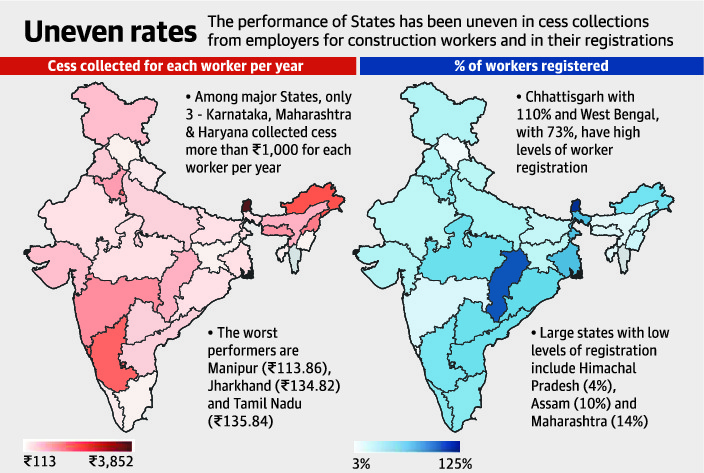
1. Cess collected for construction workers’ welfare abysmally low
- As the government prepares to finalise a model welfare scheme for construction workers, a group fighting for workers’ rights warns that the cess collected from construction companies, which is meant to pay for such workers’ welfare, is abysmally low.
- The National Campaign Committee for Central Legislation on Construction Labour (NCC-CL) which has taken the Centre to the Supreme Court (SC) on the issue, says that the average amount being collected per worker per year is only Rs.477.10.
- Last year, the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Labour had said it was astonished to note that no efforts have been made to compare the collected Cess figure with the total construction activities carried out in respective States.
Model welfare scheme
- In fact, the Labour Ministry released a draft model welfare scheme in the month of May which includes pension, health and maternity benefits, life and disability insurance, education scholarships, skill development and housing benefits.
- Having received feedback from various stakeholders, the Ministry is expected to finalise the scheme this month.
- A report has been submitted to the government, including measures to enhance worker registration and cess collection.
Facts
- According to calculations by the NCC-CL using data from the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) as well as affidavits filed by the Centre and States, only four States have collected more than Rs.2,000 per worker per year.
- In fact, more than 20 States have collected less than Rs.1,000.
- The worst performers are Manipur (Rs.113.86), Jharkhand (Rs.134.82) and Tamil Nadu (Rs.135.84).
- If workers are being paid more than this average amount in the form of incentives for children’s education, marriage assistance, pension or maternity expenses, it is at the cost of other workers who have been deprived of getting registered as beneficiaries due to the insufficient functioning of the Building and Other Construction Workers Welfare Board.
- According to the Building and Other Construction Workers’ Welfare Cess Act, 1996, a 1% cess is to be levied and collected on all types of construction activities, whether by government, PSUs or private players.
- If 25% of the cost of construction except land price, (which is not part of the cess) is wages, the 1% of the total cost would be 4% of the wage bill or approximately 14 days of wages.
- If an average daily wage is Rs.300, then the cess collected should be about Rs.4,000 per worker per year.
- Instead, the national average is less than Rs.500.
- The NCC-CL extrapolated the increase in construction workers as captured by NSSO data to estimate a nationwide total of 7.43 crore for 2016-17.
- States with the largest number of construction workers are: Uttar Pradesh with 1.21 crore, Rajasthan with more than 73 lakh and Tamil Nadu with 59 lakhs.
- However, these numbers are much larger than the number of workers who have been registered with the various State boards, and those eligible for benefits.
- Nationwide, only 2.77 crore workers were registered as of June 2017.
- Welfare benefits are possible now because only registered workers are eligible for the scheme, but if worker registration goes up without cess collection also increasing, it could lead to a collapse of the tripartite board system involving workers, employers and government.
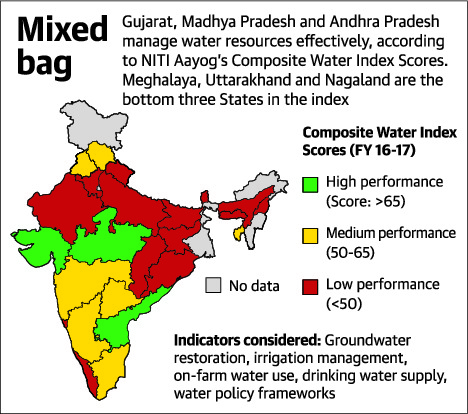
1. India is facing its worst water crisis: NITI Aayog
- The NITI Aayog released the results of a study warning that India is facing its worst water crisis in history and that the demand for potable water will outstrip supply by 2030, if steps are not taken.
Facts
- Nearly 600 million Indians faced high-to-extreme water stress and about 2,00,000 people died every year because of inadequate access to safe water.
- Twenty-one cities, including Delhi, Bengaluru, Chennai and Hyderabad, will run out of groundwater by 2020, affecting 100 million people, the study noted.
- If matters are to continue, there will be a 6% loss in the country’s Gross Domestic Product by 2050, the report says.
- Moreover, critical groundwater resources, which accounted for 40% of the water supply, are being depleted at unsustainable rates and up to 70% of the supply is contaminated.
Report
- The observations are part of a study that ranked 24 States on how well they managed their water.
- Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh took the top three spots, and Jharkhand, Bihar and Haryana came in last in the ‘Non-Himalayan States’ category.
- Himachal Pradesh — which is facing one of its worst water crises this year — led a separate eight-member list of States clubbed together as ‘North-Eastern and Himalayan.’
- These two categories were made to account for different hydrological conditions across the two groups. About 60% of the States were marked as low performers, and this was cause for alarm.
- Many of the States that performed badly — Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, Chhattisgarh — accounted for 20-30% of India’s agricultural output.
- Given the combination of rapidly declining groundwater levels and limited policy action, this is likely to be a significant food security risk for the country.
D. GS4 Related
Nothing here for today!!!
E. Editorials
Category: POLITY AND GOVERNANCE
1. Major Port Authorities Bill for stronger employee representation
Why in news?
- On the amendments to the Major Port Authorities Bill
- Amendments approved by the Union Cabinet to the Major Port Authorities Bill, 2016 are meant to make employee representation stronger in a labour-heavy work environment.
- The amendments are based on the recommendations of the department-related Parliamentary Standing Committee.
Proposals in the note?
- The changes include an increase in labour representatives to be appointed in the Port Authority Board, among the serving employees of the port concerned, from one to two.
- The members representing the interests of the employees will hold office for three years and not for more than two consecutive terms.
- The number of independent members in the Port Authority Board will be a minimum of two and a maximum of four.
- Every person who was receiving any retirement benefit from the Board of Trustees under the Major Port Trusts Act, 1963 immediately before such date will continue to receive the same benefit from the Board.
Features
- The Board of each major port will be entitled to create a specific master plan in respect of any development or infrastructure established, or proposed to be established, within the port limits and the land appurtenant thereto.
- Such a master plan will be independent of any local or State government regulations of any authority whatsoever.
- After commencement of the Act, for private-public partnership projects, the concessionaire shall be free to fix the tariff based on market conditions.
Highlights
- The proposed law highlights that amounts received by or on behalf of the Board under its provisions will be credited to a general account or accounts of the Ports which the Board may from time to time open with any nationalised or scheduled bank, according to the guidelines of the Finance Ministry.
- The presiding officer and members of the adjudicatory board have to be appointed by the Centre on the recommendations of the selection committee.
- The government will have the power to remove the presiding officer or any member of the adjudicatory board from office in accordance with procedure.
- A saving clause has been kept under repeal and saving so that the existing benefit enjoyed by Mumbai and Kolkata Ports in respect of municipal assessment of property under the Bombay Port Trust Act, 1879 and the Calcutta Port Act, 1890 can continue.
F. Tidbits
1. States should protect all strays: AWBI
- States will be held responsible for cattle, dogs and cats wandering on streets and officials will be held accountable for inflicting cruelty on them, according to a directive by the Animal Welfare Board of India (AWBI), constituted under the provisions of the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (PCA) Act.
- Directives have been issued to all State departments.
- If animals are wandering on the streets, it is not just the responsibility of cow shelters and animal welfare activists, State departments are also responsible. Else it will be considered as an act of cruelty.
- The AWBI, however, does not have the right to prescribe punishments or fines for violations of the PCA Act but can pursue legal action.
- It has in the past led litigation to disallow the use of bulls in Jallikattu in Tamil Nadu.
- Animal welfare officers for each district will be appointed and they would have a critical role to play in ensuring that strays are not mistreated.
- It is also the responsibility of local bodies to save animals like stray cats, monkeys and stray dogs from cruelty and sufferings.
- Various States — ranging from Uttar Pradesh to Kerala — have had problems with strays.
2. Federal Reserve lifts rates amid stronger inflation in U.S., drops crisis-era guidance
- The Federal Reserve raised interest rates, a move that was widely expected but still marked a milestone in the U.S. central bank’s shift from policies used to battle the 2007-2009 financial crisis and recession.
- In raising its benchmark overnight lending rate a quarter of a percentage point to a range of 1.75% to 2%, the Fed dropped its pledge to keep rates low enough to stimulate the economy for some time and signalled it would tolerate inflation above its 2% target at least through 2020.
Economic expansion
- The ongoing economic expansion coupled with solid job growth has pushed the Fed to raise rates seven times since late 2015, rendering the language of its previous policy statements outdated.
- Policymakers’ fresh economic projections indicated a slightly faster pace of rate increases in the coming months.
India
- Higher interest rates tempt large foreign funds to move their money to the US, hurting emerging markets including India which are already struggling with a stronger dollar and expensive crude oil.
- However, the Fed hiking interest rates this year won’t be a major issue for Indian markets as Indian markets are worried about crude prices and domestic interest rates.
- Generally, rising interest rates suggest pickup in consumption and demand. It is a sign that US economy is getting stronger.
- For emerging markets, it is a short-term negative, but in the long term, a stronger developed market is supportive to emerging markets.
3. WPI inflation at 14-month high in May
- Inflation based on wholesale prices shot up to a 14-month high of 4.43% in May on increasing prices of petrol and diesel, prompting industry to demand action from policymakers to keep fuel prices under check.
- The wholesale price index (WPI)-based inflation stood at 3.18% in April and 2.26% in May last year.
- According to government data, inflation in food articles was at 1.60% in May 2018 against 0.87% in the preceding month.
- Inflation in ‘fuel and power’ basket rose sharply to 11.22% in May from 7.85% in April as prices of domestic fuel increased in line with rising global crude oil rates.
4. Will back AI with funds till disinvestment is done: Sinha
- Minister of State for Civil Aviation Jayant Sinha said that the Government of India was committed to supporting Air India (AI) with liquidity infusion till the disinvestment process is completed.
- The deadline for submission of Expression of Interest (EoI) ended on May 31, with not a single bidder evincing interest in the airline.
- Since then, salaries of airline staffers were delayed by a fortnight this month.
- The Minister said monetisation of Air India’s assets, now placed under an asset holding company, was happening simultaneously.
- The government has proposed to offload 76% equity share capital of the carrier as well as transfer the management control to private players, as per the preliminary information memorandum.
5. Ministry takes up Maldives visa row
- The government is treating the issue of visa denials to hundreds of Indians, who have been offered work in the Maldives, with utmost importance.
- The Ministry of External Affairs has taken up the matter strongly at various levels and has urged the Maldivian government to abide by the terms of the bilateral visa regime in place since 1979.
- More Indians who were offered work in the Maldives are receiving word that political issues are behind the visa delays.
- According to the normal visa procedures, work permits for Indians to the Maldives, where about 29,000 Indians now work, take about 15 days.
- However, since February this year, there has been a general squeeze on work visas issued to Indians, which has left around 2,000 job-seekers in the lurch, following the downturn in the India-Maldives ties.
- India rejected a report from the UN that called for an international investigation into the alleged incidents of human rights abuse by Indian forces in Kashmir.
- The report covers both Indian territory and Pakistan occupied Kashmir.
India’s response
- A statement from the Ministry of External Affairs said the first-ever UN report on human rights situation was fallacious.
- It is a selective compilation of largely unverified information.
- It is overtly prejudiced and seeks to build a false narrative.
- The report violates India’s sovereignty and integrity.
- The report has chosen to describe internationally designated and UN-proscribed terrorist entities as ‘armed groups’ and terrorists as ‘leaders.’
- This undermines the UN-led consensus on zero tolerance to terrorism.
Opposition’s response
- The Congress supported the government’s stand in dismissing the U.N. report on human rights violations in Jammu and Kashmir, terming it a prejudiced attempt by vested interests to hurt India’s sovereignty and national interests.
- Condemning the United Nations report, the Opposition party said it needed to be junked as it had not taken into account the ground realities in Kashmir and had encouraged terrorists by terming them militant groups.
- The report had been prepared without understanding the ground situation in Jammu and Kashmir.
- The United Nations should overlook state-sponsored terrorism being exported on Indian soil by Pakistan.
G. Practice Questions for UPSC Prelims Exam
Question 1. Consider the following statements with respect to Animal Welfare Board of India:
- The Animal Welfare Board of India is a statutory advisory body on Animal Welfare Laws.
- It was established under the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act.
- The Board consists of 28 members.
Which of the statement/s given above is/are incorrect?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- None of the above
See
Question 2. Which of the following led to the resurgence of revolutionary tendencies in second
and third decades of 20th century?
- Collapse of non-cooperation movement.
- Rise in communal violence.
- Dissatisfaction with Gandhian/ non-violent methods.
- Influence of Marxist ideas and Russian revolution.
Choose the correct option:
- 1, 2 and 3 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 3 only
- All of the above
See
Question 3. Consider the following statements regarding the Home Rule League:
- They opposed the involvement of Indian troops in World War-I.
- They were demanding significant devolution of power after World War-I.
Choose the correct option.
- 1 is correct but 2 is incorrect
- 1 is incorrect but 2 is correct
- Both 1 and 2 are incorrect
- Both 1 and 2 are correct
See
Question 4. Consider the following statements:
- Article 43 deals with Socialist as well as Gandhian philosophy.
- Article 44 deals with intellectual, liberal and Gandhian principles.
Choose the correct answer.
- 1 is correct but 2 is not correct
- 2 is correct but 1 is not correct
- Both 1 and 2 are correct
- Both 1 and 2 are incorrect
See
H. UPSC Mains Practice Questions
- In the light of deteriorating air quality in cities across India, suggest ways to bring down the hazardous levels of air quality.
- Nuclear energy is the saviour for our growing energy needs. Comment.
Also, check previous Daily News Analysis
“Proper Current Affairs preparation is the key to success in the UPSC- Civil Services Examination. We have now launched a comprehensive ‘Current Affairs Webinar’. Limited seats available. Click here to Know More.”
Enroll for India’s Largest All-India Test Series
Comments