National Disaster Management Plan (NDMP) is the first ever national plan prepared to handle disasters in the country. The NDMP has been aligned broadly with the goals and priorities set out in the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction. This article covers the vision, thematic areas of action, different responses to disasters, and disaster risk governance of NDMP.
Aspirants would find this article very helpful while preparing for the IAS Exam.
| Aspirants should begin their preparation by solving UPSC Previous Year Question Papers now!!
To complement your preparation for the upcoming exam, check the following links:
|
Latest Context related to National Disaster Management Plan –
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has released fresh guidelines for restarting manufacturing and chemical industries after the lockdown period ends.
- It has issued guidelines on Chemical Disasters, 2007, Management of Chemical (Terrorism) Disasters, 2009 and the Strengthening of Safety and Security For Transportation of POL Tankers, 2010.
- Due to several weeks of lockdown and the closure of industrial units, it is possible that some of the operators might not have followed the established SOP. As a result, some of the manufacturing facilities, pipelines, valves, etc. may have residual chemicals, which may pose risk. The same is true for storage facilities with hazardous chemicals and flammable materials.
| What is the National Disaster Management Authority – NDMA?
The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) is the apex body for Disaster Management in India. Prime Minister heads NDMA. It is a statutory body created under the Disaster Management Act 2005. Its primary purpose is to coordinate the response to natural or man-made disasters and for capacity-building in disaster resiliency and crisis response. |
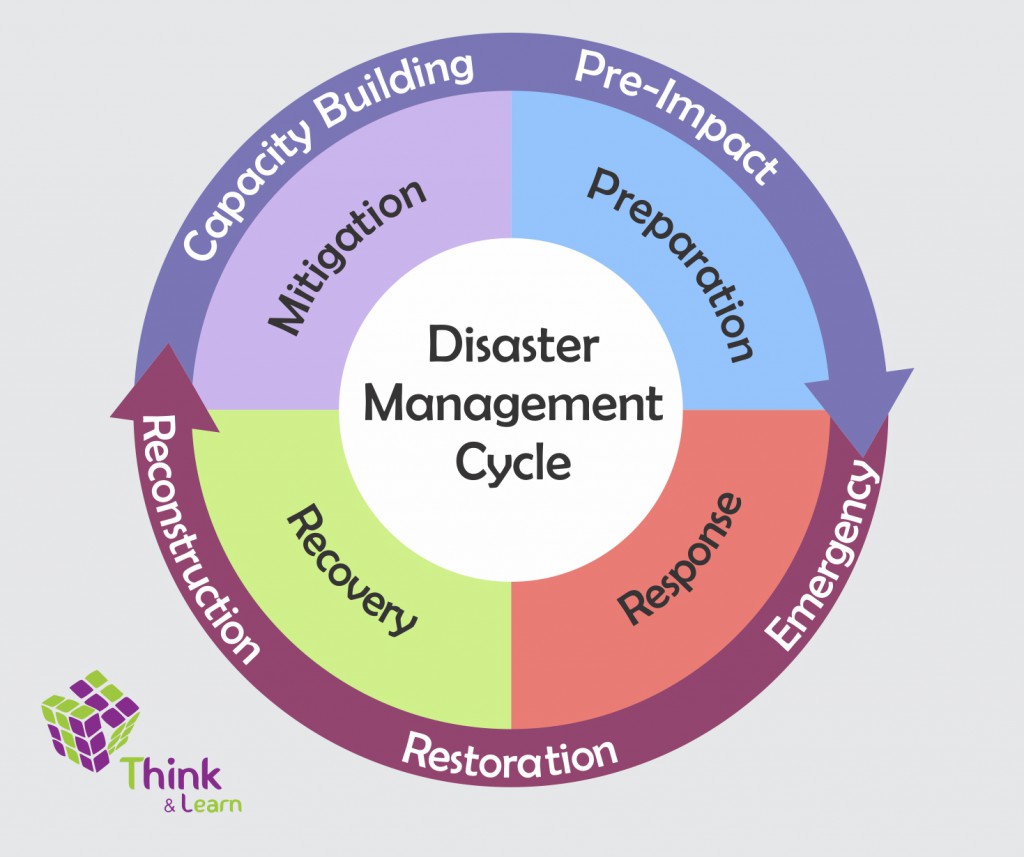
National Disaster Management Plan (NDMP) – Vision
“Make India disaster resilient, achieve substantial disaster risk reduction, and significantly decrease the losses of life, livelihoods, and assets – economic, physical, social, cultural and environmental – by maximizing the ability to cope with disasters at all levels of administration as well as among communities”
NDMP – 5 Thematic Areas of Action
For each hazard, the approach used in this national plan incorporates the four priorities enunciated in the Sendai Framework into the planning framework for Disaster Risk Reduction under the five Thematic Areas for Actions:
- Understanding Risk
- Inter-Agency Coordination
- Investing in DRR – Structural Measures
- Investing in DRR – Non-Structural Measures
- Capacity Development
NDMP – Response to Disaster – 18 Activities
The Response part of the Plan has identified eighteen broad activities which have been arranged into a matrix to be served as a ready reckoner:
- Early Warning, Maps, Satellite inputs, Information Dissemination
- Evacuation of People and Animals
- Search and Rescue of People and Animals
- Medical Care
- Drinking Water/ Dewatering Pumps/ Sanitation Facilities/ Public Health
- Food & Essential Supplies
- Communication
- Housing and Temporary Shelters
- Power
- Fuel
- Transportation
- Relief Logistics and Supply Chain Management
- Disposal of Animal Carcasses
- Fodder for livestock in scarcity-hit areas
- Rehabilitation and Ensuring Safety of Livestock and other Animals, Veterinary Care
- Data Collection and Management
- Relief Employment
- Media Relations
Aspirants can check out the following links to prepare comprehensively for the upcoming Civil Services exam –
NDMP – Disaster Risk Governance – 6 Thematic Areas
The Plan has also incorporated a Chapter on Strengthening Disaster Risk Governance. The generalized responsibility matrix given in this section summarizes the themes for strengthening Disaster Risk Governance and specifies agencies at the Centre and State with their respective roles. The matrix has six thematic areas in which Central and State Governments have to take actions to strengthen disaster risk governance:
- Mainstream and integrate DRR and Institutional Strengthening
- Capacity Development
- Promote Participatory Approaches
- Work with Elected Representatives
- Grievance Redress Mechanism
- Promote Quality Standards, Certifications, and Awards for Disaster Risk Management
Note:
1. Globally, the approach towards post-disaster restoration and rehabilitation has shifted to one of betterment reconstruction.
2. The NDMP provides a generalized framework for recovery since it is not possible to anticipate all the possible elements of betterment reconstruction.
3. The Plan also highlights that the disaster risk reduction will be achieved by mainstreaming the requirements into the developmental plans.
Civil Service Exam aspirants can refer to the list of UPSC Books given in the link, to augment their preparation.
Aspirants can find complete information about upcoming Government Exams through the linked article. UPSC exam-related preparation materials will be found through the links given below.

Comments