Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Living things
- Non-living things
- Difference between living and non-living things
- Criteria for differentiating living things from non-living things
Introduction
We can find many things around us, from mountains and oceans to plants and animals. The earth in which we live is made up of several things. These “things” can be categorized into two different types – Living and Non-living Things.
- All living things breathe, eat, grow, move, reproduce and have senses.
- Non-living things do not eat, grow, breathe, move and reproduce. They do not have senses.
Living things have “life,” though some might not show its evident signs. For instance, a tree would probably not react the same way a human would. It would not react when we hit it, and it might not be able to walk around. Though the signs of life displayed by them are not very observable, it does not make them non-living.
Let us have a detailed look at the important characteristics of living and non-living things and the difference between the two.
Living things
Living things exist and are alive and are made of microscopic structures called cells. They grow and exhibit movement or locomotion. They experience metabolism, which includes anabolic and catabolic reactions.
Living things are capable of producing a new life which is of their own kind through the process of reproduction. Living things have a particular life span and are not immortal.
Cellular Respiration enables living organisms to acquire energy which is used by cells to perform their functions. They digest food for energy and also excrete waste from the body. Their life cycle can be summarised as follows – birth, growth, reproduction and death.
Examples of living things are animals, birds, insects, and human beings.
Also Read: Living things
Characteristics of Living Things
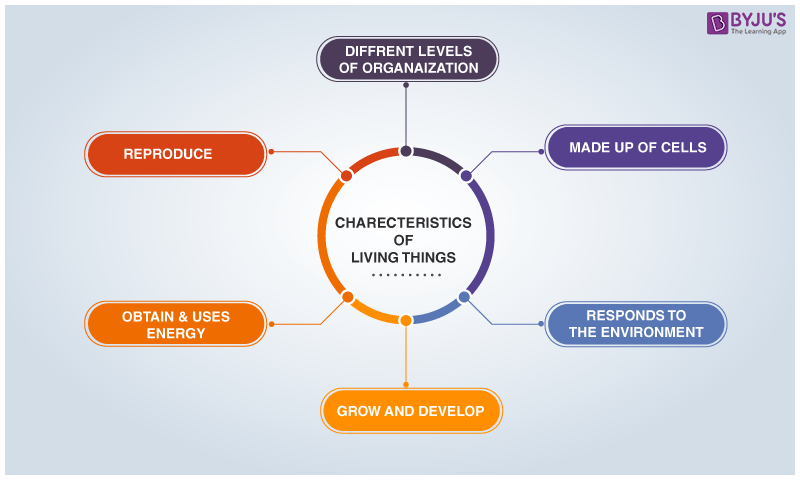
Characteristics of Living Things
Following are the important characteristics of living things:
- Living things exhibit locomotory motion, they move. Animals are able to move as they possess specialized locomotory organs, for example – Earthworms move through the soil surface through longitudinal and circular muscles. Plants move in order to catch sunlight for photosynthesis
- Living things respire. Respiration is a chemical reaction, which occurs inside cells to release energy from the food. Transport of gases takes place. The food that is ingested through the process of digestion is broken down to release energy that is utilized by the body to produce water and carbon dioxide as by-products.
- Living things are sensitive to touch (and other stimuli as well) and have the capability to sense changes in their environment.
- They grow. Living things mature and grow through different stages of development.
- One of the striking features is that living things are capable of producing offspring of their own kind through the process of reproduction, wherein genetic information is passed from the parents to the offspring.
- They acquire and fulfil their nutritional requirements to survive through the process of nutrition and digestion, which involves engulfing and digesting the food. Some living organisms are also autotrophic, which means they can harness the sun’s energy to make their food (also known as autotrophs).
- The digested food is eliminated from the body through the process of excretion.
Also Read: Characteristics Of Organisms
Non-living things
Non-living things are not alive. They do not possess life. They do not have cells and do not grow or show locomotion/movement. They do not undergo metabolism with anabolic and catabolic reactions. They do not reproduce.
Non-living things do not have a life span. They do not respire as they do not require food for energy and hence do not excrete. They do not fall into any cycle of birth, growth or death. They are created and destroyed by external forces.
Examples of non-living things include stones, pens, books, cycles, bottles, etc.
Characteristics Of Non-living Things
The important characteristics of non-living things are mentioned below:
- Non-living things are lifeless. They do not have cells, and there is no protoplasm which forms the basis for life to exist.
- Lack of protoplasm leads means no metabolic activities.
- They do not have a definite and certain size of their own. They take the shape of the substance they are contained in, for example, a liquid takes the shape of its container. Stones, rocks and boulders are moulded by the changing environment and landscape. The change in the state of a non-living thing is due to an external influence.
- Non-living things “grow” by accretion. It occurs through adding materials externally. For example, A snowball may increase in size due to the accumulation of smaller units of its own on its outer surface.
- Non-living things never die as they do not have cells with a definite lifespan. Immortality is a distinguishing factor.
- Fundamental life processes such as reproduction, nutrition, excretion, etc. are absent in non-living things.
Difference between living and non-living things
Here are some of the major differences between living and non-living things:
| Living Things | Non-Living Things |
| They possess life. | They do not possess life. |
| Living things are capable of giving birth to their young ones. | Non-living things do not reproduce. |
| For survival, living things depend on water, air and food. | Non-living things have no such requirements |
| Living things are sensitive and responsive to stimuli. | Non-living things are not sensitive and do not respond to stimuli. |
| Metabolic reactions constantly occur in all living things. | There are no metabolic reactions in Non-living things. |
| Living organisms undergo growth and development. | Non-living things do not grow or develop. |
| They have a lifespan and are not immortal. | They have no lifespan and are immortal. |
| Living things move from one place to another. | Non-living things cannot move by themselves. |
| They respire and the exchange of gases takes place in their cells. | Non-living things do not respire. |
| Example: Humans, animals, plants, insects. | Example: Rock, pen, buildings, gadgets. |
Criteria for differentiating living things from non-living things
For easy differentiation between living things and non-living things, scientists have come up with traits or characteristics that are unique to them.
The criterion for classification is necessary to avoid the wrong grouping. Hence, science developed a basis for classification. Anything that has life is considered a living being.
For example– humans, trees, dogs, etc.
Things which have no life in them are considered non-living.
For example– stone, mountain, watch, etc.
Scientists have discovered a few criteria for differentiating living things from non-living things.
Here are some of them:
- Living beings can grow and develop.
- Living beings obtain and use energy.
- Living beings adapt to their environment.
- All living beings are made of one or more cells.
- Living beings respond to their environment or stimuli.
- All living things excrete to remove waste material from the body.
- Living beings have the ability to give birth to their young ones through the process of reproduction.
- All living beings require energy to perform different metabolic activities, and they gain energy from food/ nutrition.
- All living beings, apart from plants, move from one place to another. This type of movement is called locomotion.
If something obeys a few of the rules, it cannot be categorized as a living thing. It has to follow all the given rules stringently. For example, an icicle, although it grows (increases its mass or length), is still a non-living thing since it cannot reproduce or respond to stimuli.
Non-living things do not have any of the life processes, unlike living beings.
Also Read: What is Living
Learn more about living things, non-living things, characteristics of living and non-living things and the difference between living and non-living things at BYJU’S Biology

Thank you for this good help
Very Very Good
Examples?
Any inanimate objects such as furniture, books, and doors are examples of non-living things. All life on earth – from ants and spiders to humans, plants and blue whales are classified as living organisms.
do both living and nonliving things contain DNA
Living things have DNA and non-living things do not. However, some viruses contain DNA even though they are not technically living organisms. Read more: Virus
It was really helpful. Thank you so much
Thank you for your help
This was helpful.
Thanks for the knowledge
This was very helpful.
Was very helpful, Thank you
Thanks this helped with my school project about growth
Thank you so much
Helpful info thanks
Thanks it helped me so much
Helpful and amazing information
Living things breathe and eat. Non-living things don’t breathe and don’t eat.
Thank you for the information. Really helpful
It is very helpful
Thanks a lot, I really benefited with this article!
I really understand it
Thanks, I really gain a lot with this
This was very very helpful, thank you for so much help
Very helpful, excellent job done
nice job