Computer fundamentals are a common topic for most Government exams, especially the Bank, Railway and SSC exams conducted in the country.
It must be noted that very basic questions are asked from the computer section for most Government exams as the weightage of marks is not very high for this section.
All Government aspirants can check the Preparation Strategy for Competitive exams at the linked article and start their preparation for the upcoming Government exams accordingly.
| Table of Contents: |
What is a Computer?
An electronic device that accepts data and processes it into useful information is called a Computer. There are two main aspects of the computer:
- Input: The data we enter into the computer is called the input. Input, basically are raw facts for which we want the system to process and give us an outcome
- Output: The answer that the computer provides in return of the raw data entered, is called output
Questions related to networking, the background of computer, Internet and other Computer associated terms are frequently asked in the competitive exams. So, in this article, we bring to the basics of computer and how it has evolved over the years.
To get the detailed syllabus for Computer Knowledge with the competitive exams point of view, candidates can visit the linked article and know the important topics along with a list of exams in which this section is included.
Related links:
| Computer Abbreviations | 10 Important Computer Terms for Government Exams |
| Basics of Cloud Computing | High Level Computer Languages |

There are various terms and programs which may seem similar and candidates tend to get confused with their actual function and uses. Thus, given below are a few computer-based difference between articles which will strengthen an aspirant’s command over the Fundamentals of computer:
- Difference Between Search Engine and Web Browser
- Difference Between RAM and ROM
- Difference Between Hardware and Software
- Difference Between IPV4 and IPV 6
- Difference Between Firewall and Antivirus
- Difference Between WWW and Internet
- Difference Between Virus and Malware
Evolution of Computer
The computer started as a huge electronic device which took a large area for its instalment, and the mechanism was very complication. Still, then with time, those huge machines were converted into smaller versions of the divide, starting with the monitors, then laptop and later on the invention of tablets.
The first fully electronic computer was introduced in the 1930s, and since then, the development of computer and its related devices has been unstoppable.
Computers are nothing but an advanced version of Abacus, which dates back to almost 5000 years. Further below, we have discussed the five generations of computer and how these generations gradually helped in the development of this electronic device.
| Prepare yourself of the upcoming Government exams with the help of links given below: |
Generations of Computer
There are a total of five Generations of Computer, with each Generation something new was discovered to improvise the functioning and the use of the computer systems.
First Generation (Vacuum Tubes) – 1940-1956:
This Generation computers relied on Machine Language (the Language of 0s and 1s) and used Vacuum tubes as components of memory. They were huge in size and occupied almost a room-size area to fit in.
Given below are a few characteristic features of the 1st Generation of computer:
- The price of managing these computers was very high
- They were huge
- They were not capable of multitasking, and only one task could be performed at a time
- There was no use of monitors; the output was directly given in the form of print outs
- The electricity consumption was very high
Examples of computers developed in this generation are ENIAC – Electronic Numeric Integrated and Computer, UNIVAC- Universal Automatic Computer, EDSAC – Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator and EDVAC – Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer
|
Related Links |
|
| Web Browsers | Computer Virus |
| Internet | Microsoft Office |
| Microsoft Windows | Computer Input and Output Devices |
Second Generation (Transistors) – 1956-1963:
The first-ever transistor was invented in 1947 but could never be used in the computer until the 1950s. Given below are a few characteristic features of the 2nd Generation computers:
- The speed of the transistor decided the speed of the computer
- It was less expensive in comparison to the 1st Generation computers
- The electricity consumption had also reduced with the use of transistors
- There was no change in the output as it was still received through a printout
- From machine language, there was a change to usage assembly language in computers. Thus, now computers could understand words
- High-level programming languages were used
Two significant developments during this phase include the development of FORTRAN or Formula Translation and COBOL or Common Business Oriented Language, which was developed for business use.
Aspirants can visit the Computer Networks page to learn more about its types, functions and uses. This will help candidates master another important topic for the Computer Awareness section, from the examination point of view.
Third Generation (Integrated Circuits) – 1964-1971:
The phase when the usage of keyboards and monitors ha started for the input and output. The transistors had been reduced in size and were placed on silicon chips. This increased the speed of the computer.
Given below are the features of the 3rd Generation of computers:
- The Integrated circuits were used where small circuits could work as efficiently as the larger ones
- Multitasking could be done in the computers developed during the 3rd phase
- Functions of the computer were based on the memory of the monitor
A few examples from this Generation of computer are PDP 8, IBM 360, ICL 2900, etc.
Fourth Generation (Microprocessors) – 1972-2010:
The maximum developments were done during this time phase as technology has advanced many folds. By this time, millions of transistors could be placed on the silicon circuits.
The characteristic features of this Generation are given below:
- The first microprocessor, Intel 4004 chip was discovered by Ted Hoff and was made commercially available in 1971. This led to the introduction of personal computers
- This Generation saw revised versions of computers being introduced in the form of laptops and tablets
- GUI – Graphical User Interface was developed during this phase
- Speed, memory and storage had also improved in the computers of this Generation
The computers which were introduced during this Generation include Apple II, the first IBM computer, STAR 1000, and many more.
Fifth Generation (Artificial Intelligence) – 2010-till date:
The current generation of computers which have made our lives easier and more convenient is all a part of the fifth generation of the computer.
Given below is some basic information about the 5th generation of computers:
- Artificial intelligence is being used in devices currently which has enabled millions on tasks to be completed within seconds on a device
- Advancement in the functioning of laptops, palmtops, etc.
- Other robotic devices have started being used to reduce human labour
- The devices from this generation are cost-effective, faster, consume lesser electricity and are easily portable and convenient to use
Questions based on the different generations of computer are much likely to be asked in the various competitive exams conducted in the country.
To check the detailed computer syllabus for Government exams and the syllabus for other subjects, candidates can refer to the links mentioned below:
| Bank Exam Syllabus | SSC Syllabus | RRB Syllabus |
| LIC Syllabus | FCI Syllabus | IBPS Syllabus |
Types of Computer
There are majorly 4 types of computers which have been described briefly below. Candidates must know about the different types of computers with respect to the upcoming competitive exams:
- Super Computer – The computers which are used to process a huge amount of data at once are called Supercomputers. They are mostly used in scientific and engineering operations where the processing is complex. They are expensive and complicated to work. For example – The computers used by NASA to launch space shuttles.
- Mainframe Computer – Computers designed to be used in large firms and organisations where a lot of people have to work on the same database are called mainframe computers. They are almost equally as expensive as Supercomputers and are the fastest working computers at present. They are mostly used in Banks.
- Workstation – Usually a single user system is called a work station. The RAM for such systems is more, and the processors are quite fast. They are mostly used by an individual and can be used for multiple purposes.
- Microcomputer – Designed for personal use only. This type of computers can easily be moved from one place to the other. They have a personal storage area, input & output unit and a Central Processing Unit. Examples for microcomputer are desktop, laptop, mobile phone, tablets, etc.
Aspirants can also get the detailed information regarding the Types of Computers, based on its purpose, size and type at the linked article.
Given below are the links to the exams which include Computer Knowledge as a part of their syllabus:
| IBPS Exams | SSC Exams |
| FCI Manager | RRB Exams |
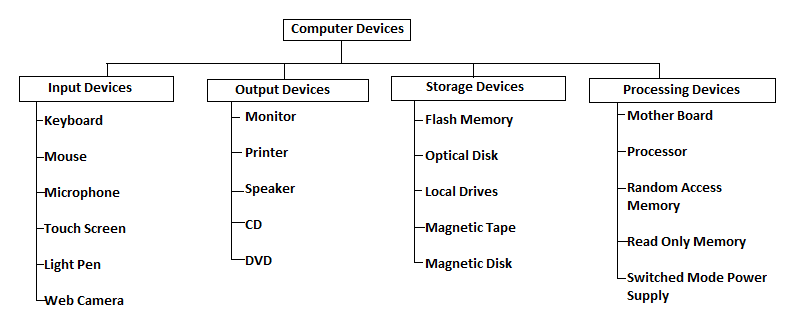
Computer Devices
The image given below shows the different devices which can be connected to a computer:
Functions of Computer
A computer is used in various spheres of life today, and there are multiple advantages that the computer has brought in today.
Given below are the functions of the computer:
- Lengthy calculations which may take hours to be completed manually can now be done within seconds
- Easy to use and cost-effective. People can buy them at reasonable prices
- Reduced manual labour
- Made storing information easier and more convenient
- Years of data can be saved in the form of data in computers without the fear of losing it
- There can be no question over its accuracy if the input has been given correctly
Computer devices can also be classified into categories:
- Hardware
- Software
To know the difference between hardware and software, candidates can visit the linked article.
Given below are a few other links which may help you prepare for the upcoming competitive exams:
| Static GK | Current Affairs | 10 Maths Tricks and Shortcuts |
| Logical Reasoning Syllabus | Banking Awareness | SSC General Awareness |
Sample Questions – Fundamentals of Computer
Given below are a few sample questions based on the upcoming Government exams from the topic of Computer Fundamentals.
Q 1. Which of these is not an example of First Generation computer?
- ENIAC
- Universal Automatic Computer
- PDP-8
- EDSAC
- EDVAC
Answer: (3) PDP-8
Q 2. Who invented the INTEL 4004 chip?
Answer: Ted Hoff, Federico Faggin, and Stan Mazor
Q 3. Which of these is not an example of Microcomputer?
- Personal Computer
- Palm Top
- Laptop
- Tablet
- LAN
Answer: (5) LAN
Q 4. Which of these was introduced in the second generation of computers?
- Microprocessors
- Artificial Intelligence
- Integrated Circuits
- Vacuum Tubes
- Transistors
Answer: (5) Transistors
Q 5. Name the storage device out of the given options
- Monitor
- CPU
- Magnetic Disk
- RAM
- SMPS
Answer: (3) Magnetic Disk
The questions given above will help you analyse the type of questions that may be asked in the final examination from this topic and how they may be framed.
Also, get some sample hardware and software questions at the linked article and thoroughly prepare yourself for the upcoming Government sector exams.
A few other Computer Fundamental links which will help candidates prepare themselves for the upcoming competitive exams are given below:
| MS Word | MS Excel |
| MS PowerPoint | Difference Between Notepad and WordPad |
Candidates must keep themselves thoroughly prepared for indirect questions as the level of the exam is tough and easy direct questions may not be asked.
For aspirants who wish to know more about the different Government exams, their syllabus or get notes or study material, they can turn to BYJU’S for assistance.
What is a bar code reader?
A barcode reader also called barcode scanner is an optical scanner that can read printed barcodes, decode the data contained in the barcode and send the data to a computer.