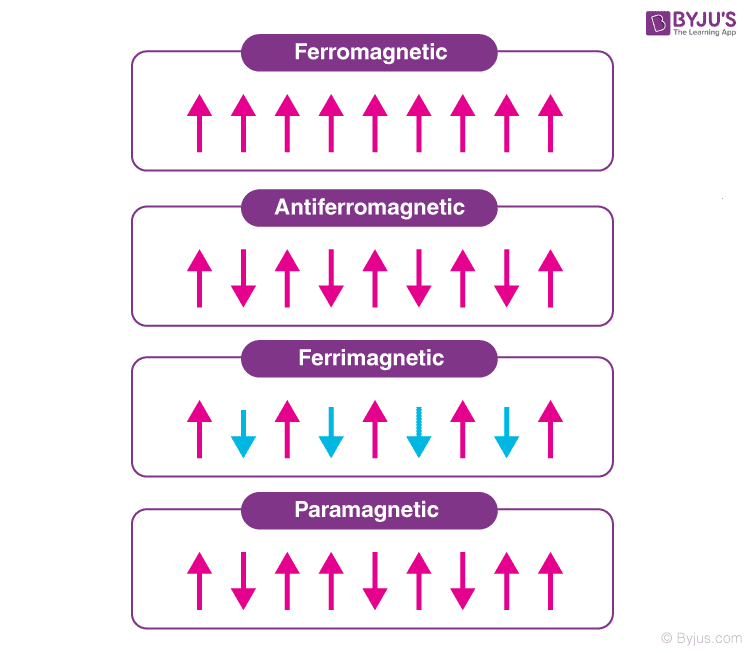
We know that magnetism deals with the interaction of moving charges. The characteristic of the combined electromagnetic force is magnetism. There are five types of magnetism, they are Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism, Ferromagnetism, Anti-ferromagnetism and Ferrimagnetism. In this article let us discuss ferromagnetism in detail.
| Table of Contents: |
What is Ferromagnetism?
Ferromagnetism is a physical phenomenon (long-range ordering), in which certain materials like iron strongly attract each other. Ferromagnets occur in rare earth materials and gadolinium. It is one of the common phenomena that is encountered in life that is responsible for magnetism in magnets.
One of the vital requirements of ferromagnetic material is that ions and atoms should possess permanent magnetic moments. Some ions and atoms consist of the permanent magnetic moment that may be considered as a dipole that comprises a north pole separated from a south pole.
Some degree of dipole alignment can be witnessed if there existed a large atomic magnetic moment. This type of magnetic arrangement can be found in some elements such as iron, cobalt, nickel, and their alloys.
What are Ferromagnetic Materials?
Beneath is a table that states ferromagnetic materials and compounds that exhibit spontaneous magnetization.
| Spontaneous Magnetization (Curie Temperature in K) | Ferromagnetic Materials |
| 69 | EuO |
| 292 | Gd |
| 88 | Dy |
| 1043 | Fe |
| 1400 | Co |
| 587 | MnSb |
| 318 | MnAs |
| 627 | Ni |
Heusler alloy is a ferromagnetic metal alloy wherein its constitutions itself is not ferromagnetic whereas stainless steel is a non-magnetic alloy that is completely comprised of ferromagnetic materials. Non-crystalline ferromagnetic materials are made by expeditious cooling of the liquid. They possess very low hysteresis loss, high electrical resistivity, low coercivity, and high permeability.
What is Antiferromagnetism?
Some antiferromagnetism includes ferrous oxide, nickel oxide, chromium, and manganese fluoride. In antiferromagnetism, the forces between the adjacent atomic dipoles tend to possess signs opposite to that of ferromagnets. Beneath is a table that provides a Neel temperature of the antiferromagnetic substance.
| 116 K | Manganese Oxide |
| 61 K | Manganese Fluoride |
| 311 K | Chromium |
| 198 K | Ferrous Oxide |
What causes Ferromagnetism?
Ferromagnetism is caused in ferromagnets and the ferromagnets need to have net angular momentum which is obtained either through the orbital component of the spin component.
What are the Applications of Ferromagnetism?
- The applications of a ferromagnetic substance are comprehensive. The hysteresis curve plays a vital role and it’s of great importance.
- Ferromagnetism has its applications in transformers, electromagnets, and magnetic tape recording.
To know about magnetism in detail, see the video below.

Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What is magnetism?
What is Ferromagnetism?
Ferromagnetism is a physical phenomenon in which certain materials like iron strongly attract each other.
What are the types of magnetism?
- Diamagnetism
- Paramagnetism
- Ferromagnetism
- Anti-ferromagnetism
- Ferrimagnetism
State true or false: Ferromagnets do not occur in rare earth materials.
Give some applications of ferromagnetism.
Ferromagnetism has its applications in magnetic tape recording, transformers, and electromagnets.


Comments