1
Question
Correlate the hormones produced by the ovary and the pituitary to the events in the menstrual cycle.
Open in App
Solution
At the beginning of menstrual cycle, the brain signals the pituitary gland to produce a hormone called the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which in turn signals the ovaries. As these follicles mature, the level of estrogen in the body rises, indicating that an egg is ready for ovulation. This first half of the menstrual cycle is called the follicular phase.When high estrogen levels signal the pituitary gland, luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the ovary to release the mature egg by the process of ovulation. The ovulation occurs at the 14th day of the cycle, the luteal phase. During the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle the ovaries (the corpus luteum) begin to increase the levels of progesterone in the body. Progesterone is secreted by ovary regulates and maintains the inner lining of the uterus both during menstrual cycle. Progesterone is a hormone that prepares the lining of the uterus for pregnancy. If the egg is fertilized and implanted, the body continues to produce progesterone and if not, then progesterone levels fall, and that month's menstrual period begins.
In simple words, the pituitary secretes FSH and LH, a process which actually begins before the onset of your menses. These hormones in turn stimulate the growth of several ovarian follicles. The increase in estrogen begins to inhibit the secretion of FSH.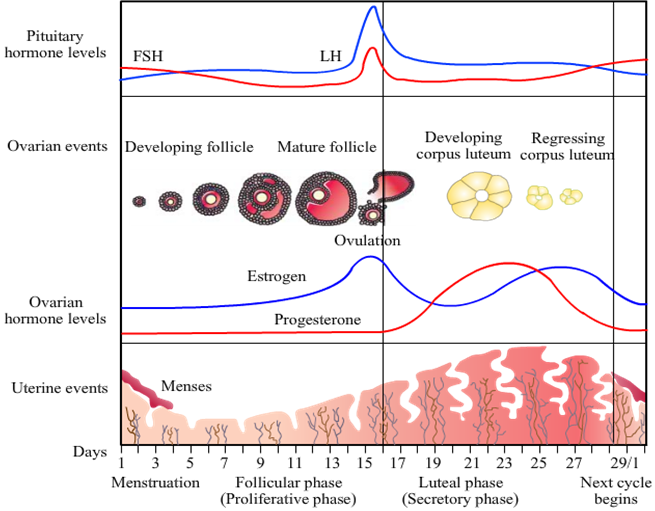
When high estrogen levels signal the pituitary gland, luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers the ovary to release the mature egg by the process of ovulation. The ovulation occurs at the 14th day of the cycle, the luteal phase.
During the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle the ovaries (the corpus luteum) begin to increase the levels of progesterone in the body. Progesterone is secreted by ovary regulates and maintains the inner lining of the uterus both during menstrual cycle. Progesterone is a hormone that prepares the lining of the uterus for pregnancy. If the egg is fertilized and implanted, the body continues to produce progesterone and if not, then progesterone levels fall, and that month's menstrual period begins.
In simple words, the pituitary secretes FSH and LH, a process which actually begins before the onset of your menses. These hormones in turn stimulate the growth of several ovarian follicles. The increase in estrogen begins to inhibit the secretion of FSH.

Suggest Corrections
0
View More
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
