1
Question
Differentiate between convergent and divergent evolution with an example.
Open in App
Solution
When two or more different species develop similar characteristics due to adaptation to the particular environment, but they do not belong to the same ancestors, are kept under Convergent Evolution. While divergent evolution is the phenomenon in which two species have common ancestors, but develop different characteristics due to changes in the environment which they adapt slowly and hence give rise to new species.The difference between convergent and divergent evolution is :
BASIS FOR COMPARISON CONVERGENT EVOLUTION DIVERGENT EVOLUTION Meaning When one or more different species evolve similarities in their characteristics and functions because of adaptations in an environment. When an ancestral species diverges into multiple different species, ultimately giving rise to new species. Diagram 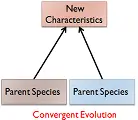
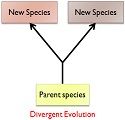
Way of evolution They evolve from different species but develop similar characteristics, like the wings of birds and insects. They evolve from the same species and gradually give rise to new species like Darwin finches which have evolved in around 80 new species. Cause of evolution It is due to change in environmental conditions, or due to the place where they are living. Due to migration or may be due to environmental changes. Way of living They live closely in the same way as other species, of which it has adapted the changes. They live in different ways from their ancestor. Appearance The outer structure of a species may be different, but internally they resemble their ancestors. As this type give rise to totally new species, they can be different from outside as well as inside in appearance. Type of structure Organisms evolve analogous structures (means those structures that are similar in function but different in shapes and origin) despite evolving from different ancestors. These kinds have homologous structures (means structures are same, but functions are different), despite appearing similar to ancestors.
Example 1.Wings of insects, birds, bats.
2.Streamlined body of dolphins and sharks. Darwin finches (kind of birds)
The difference between convergent and divergent evolution is :
| BASIS FOR COMPARISON | CONVERGENT EVOLUTION | DIVERGENT EVOLUTION |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | When one or more different species evolve similarities in their characteristics and functions because of adaptations in an environment. | When an ancestral species diverges into multiple different species, ultimately giving rise to new species. |
| Diagram |  |  |
| Way of evolution | They evolve from different species but develop similar characteristics, like the wings of birds and insects. | They evolve from the same species and gradually give rise to new species like Darwin finches which have evolved in around 80 new species. |
| Cause of evolution | It is due to change in environmental conditions, or due to the place where they are living. | Due to migration or may be due to environmental changes. |
| Way of living | They live closely in the same way as other species, of which it has adapted the changes. | They live in different ways from their ancestor. |
| Appearance | The outer structure of a species may be different, but internally they resemble their ancestors. | As this type give rise to totally new species, they can be different from outside as well as inside in appearance. |
| Type of structure | Organisms evolve analogous structures (means those structures that are similar in function but different in shapes and origin) despite evolving from different ancestors. | These kinds have homologous structures (means structures are same, but functions are different), despite appearing similar to ancestors. |
| Example | 1.Wings of insects, birds, bats. 2.Streamlined body of dolphins and sharks. | Darwin finches (kind of birds) |
Suggest Corrections
2
View More
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
