Distinguish between a change in quantity supplied and a change in supply.
Distinguish between a change in quantity supplied and a change in supply.
Supply represents how much the market can offer at different prices. In contrast, quantity supplied represents what amount of commodity producers will supply at a specific price. The supply schedule or supply curve indicates the supply of the commodity.
Movement along the supply curve or change in quanity supplied: When the supply of a good rises due to rise in the price of the good alone, it is termed as an expansion of supply. When supply of a good falls due to fall in its price, it is called contraction of supply. Graphically, it means a movement along the supply curve.

In the given digram, at point OP, the supply is OQ. When price rises to OP1, supply rises to OQ1. In this case, the producer moves from A to B upwards but remains on the same supply curve. When price falls to OP2, supply falls to OQ2. The producer moves from A to C but remains on the same supply curve.
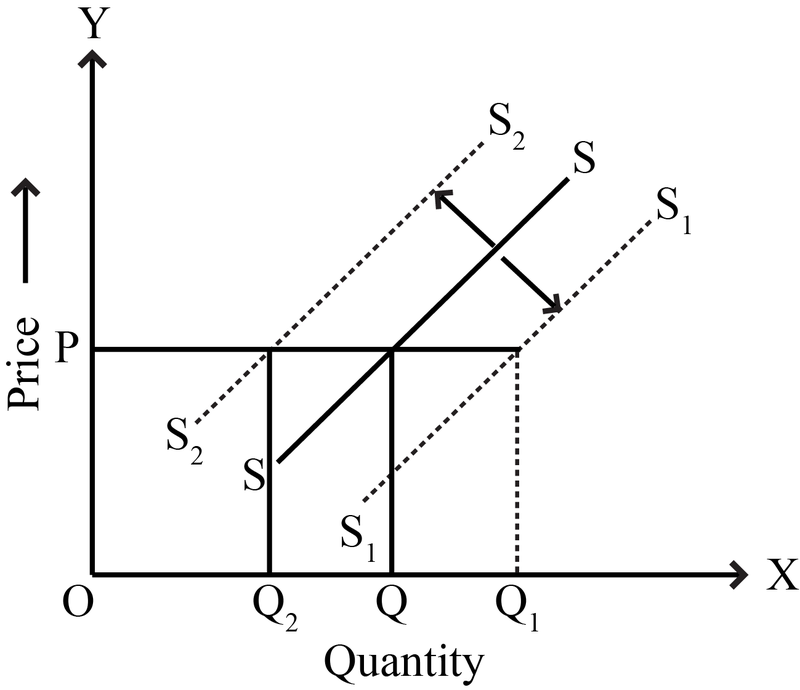
Shifts in supply curve or change in supply. When at the given price, the supply of a good increases, it is called increase in supply. When at the given price, the supply decreases, it is called decrease in supply. Graphically, it means shift of supply curve. In the figure, at price OP, the supply is OQ. When there is increase in supply at the given price, the supply curve shifts to the right, If there is a decrease in supply at the given price, the supply curve shifts to the left.
Thus, movement along the supply curve means expansion and contraction of supply whereas shifts in supply curve means increase and decrease in supply.
Supply represents how much the market can offer at different prices. In contrast, quantity supplied represents what amount of commodity producers will supply at a specific price. The supply schedule or supply curve indicates the supply of the commodity.
Movement along the supply curve or change in quanity supplied: When the supply of a good rises due to rise in the price of the good alone, it is termed as an expansion of supply. When supply of a good falls due to fall in its price, it is called contraction of supply. Graphically, it means a movement along the supply curve.

In the given digram, at point OP, the supply is OQ. When price rises to OP1, supply rises to OQ1. In this case, the producer moves from A to B upwards but remains on the same supply curve. When price falls to OP2, supply falls to OQ2. The producer moves from A to C but remains on the same supply curve.
Shifts in supply curve or change in supply. When at the given price, the supply of a good increases, it is called increase in supply. When at the given price, the supply decreases, it is called decrease in supply. Graphically, it means shift of supply curve. In the figure, at price OP, the supply is OQ. When there is increase in supply at the given price, the supply curve shifts to the right, If there is a decrease in supply at the given price, the supply curve shifts to the left.
Thus, movement along the supply curve means expansion and contraction of supply whereas shifts in supply curve means increase and decrease in supply.

