3291
Question
During cleavages of the mammalian zygote, the resultant blastomeres are smaller and smaller. Comment upon this statement.
Open in App
Solution
In embryology, cleavage is the division of cells in the early embryo. The zygotes formed undergo rapid cell cycles with no significant overall growth, producing a cluster of cells of the same size as the original zygote. The different cells derived from cleavage are called blastomeres and form a compact mass called the morula. Cleavage ends with the formation of the blastula.Depending mostly on the amount of yolk in the egg, the cleavage can be holoblastic (total or entire cleavage) or meroblastic (partial cleavage). The pole of the egg with the highest concentration of yolk is referred to as the vegetal pole while the opposite is referred to as the animal pole.
Cleavage differs from other forms of cell division in that it increases the number of cells and nuclear mass without increasing the cytoplasmic mass. This means that with each successive subdivision, there is roughly half the cytoplasm in each daughter cell than before that division, and thus the ratio of nuclear to cytoplasmic material increases.
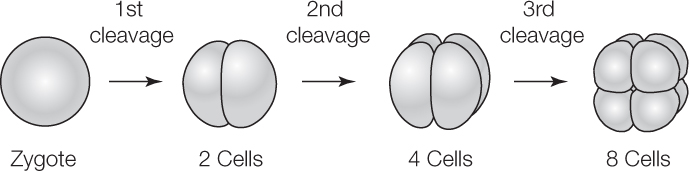
In embryology, cleavage is the division of cells in the early embryo. The zygotes formed undergo rapid cell cycles with no significant overall growth, producing a cluster of cells of the same size as the original zygote. The different cells derived from cleavage are called blastomeres and form a compact mass called the morula. Cleavage ends with the formation of the blastula.
Depending mostly on the amount of yolk in the egg, the cleavage can be holoblastic (total or entire cleavage) or meroblastic (partial cleavage). The pole of the egg with the highest concentration of yolk is referred to as the vegetal pole while the opposite is referred to as the animal pole.
Cleavage differs from other forms of cell division in that it increases the number of cells and nuclear mass without increasing the cytoplasmic mass. This means that with each successive subdivision, there is roughly half the cytoplasm in each daughter cell than before that division, and thus the ratio of nuclear to cytoplasmic material increases.

Suggest Corrections
0
View More
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
