1
Question
Explain in detail the process of development of female gametophyte. Draw diagram.
Open in App
Solution
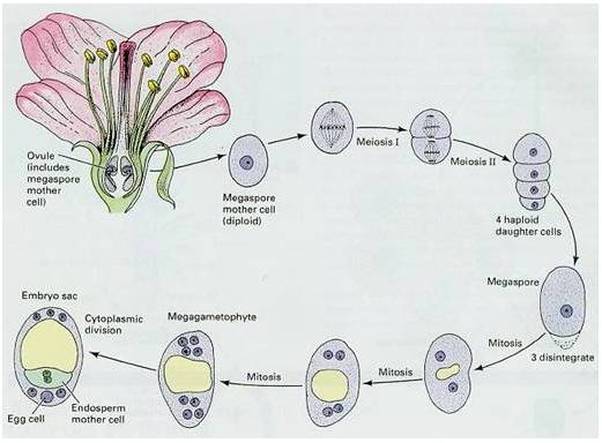
The carpels of an angiosperm is known as megasporophyll. It is differentiated into three regions-ovary, style and stigma. The ovary contains ovules or megasporangium. Megasporogenesis is the process of formation of megaspores from the megaspore mother cell (MMC).Different stages of development of female gametophyte are: 1) In the nucleus of a developing ovule, one diploid cell develops into a diploid megaspore mother cell.2) This megaspore mother cell divides by meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores which are arranged in a linear tetrad.3) One of the megaspores is functional, while the other three degenerate in angiosperms. The lower chalazal megaspore produces the female gametophyte (embryo sac).4) The nucleus of the functional megaspore divides mitotically into two nuclei.These are called primary micropylar and primary chalazal nuclei.5) The second division produces one pair of nuclei at the micropylar end and one pair of nuclei at the chalazal end. The third division results in the formation of 4 nuclei at each pole.6) One nucleus from each pole then migrates towards the centre to become polar nuclei, which fuse together and give rise to the secondary nucleus (2n). Out of these, the central one is the egg cell while the two lateral cells are called synergids.7) The three nuclei towards the chalazal end also get organized into three thin-walled cells called antipodal cells.8) The structure containing egg apparatus, secondary nucleus and antipodals are called female gametophyte or embryo sac.9) Thus, a typical angiosperm embryo sac, at maturity is 8-nucleate and 7-celled.

The carpels of an angiosperm is known as megasporophyll. It is differentiated into three regions-ovary, style and stigma. The ovary contains ovules or megasporangium. Megasporogenesis is the process of formation of megaspores from the megaspore mother cell (MMC).
Different stages of development of female gametophyte are:
1) In the nucleus of a developing ovule, one diploid cell develops into a diploid megaspore mother cell.
2) This megaspore mother cell divides by meiosis to produce four haploid megaspores which are arranged in a linear tetrad.
3) One of the megaspores is functional, while the other three degenerate in angiosperms. The lower chalazal megaspore produces the female gametophyte (embryo sac).
4) The nucleus of the functional megaspore divides mitotically into two nuclei.
These are called primary micropylar and primary chalazal nuclei.
5) The second division produces one pair of nuclei at the micropylar end and one pair of nuclei at the chalazal end. The third division results in the formation of 4 nuclei at each pole.
6) One nucleus from each pole then migrates towards the centre to become polar nuclei, which fuse together and give rise to the secondary nucleus (2n). Out of these, the central one is the egg cell while the two lateral cells are called synergids.
7) The three nuclei towards the chalazal end also get organized into three thin-walled cells called antipodal cells.
8) The structure containing egg apparatus, secondary nucleus and antipodals are called female gametophyte or embryo sac.
9) Thus, a typical angiosperm embryo sac, at maturity is 8-nucleate and 7-celled.
Suggest Corrections
0
View More
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
