Explain the construction of a motor with a diagram.
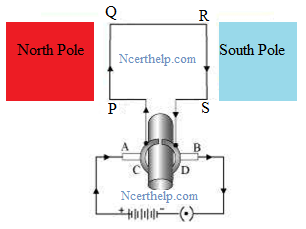
An electric motor is a
device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The principle
behind the electric motor is based on Fleming’s left hand rule.
Working: When a current is
allowed to flow through the coil PQRS the coil starts rotating anti-clockwise.
This happens because a downward force acts on length PQ and at the same time,
an upward force acts on length RS. As a result, the coil rotates anti-clockwise.
Current in the length PQ flows from P to Q and the magnetic
field acts from left to right, normal to length PQ. Therefore, according to
Fleming’s left hand rule, a downward force acts on the length PQ. Similarly at
an upward force acts on the length RS. These two forces cause the coil to rotate
anti-clockwise.
When coil complete half rotation, the position of PQ and RS
interchange. The half-ring D comes in contact with brush A and half-ring C
comes in contact with brush B. therefore the direction of current in the coil
PQRS gets reversed. Now the current flows through the coil in the direction
SRQP. The direction of current through the coil PQRS reverse after every
half rotation. As a result, the coil rotates in same direction. The split rings
help to reverse the direction of current in the circuit. These are called the
commutator.

An electric motor is a device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. The principle behind the electric motor is based on Fleming’s left hand rule.
Working: When a current is
allowed to flow through the coil PQRS the coil starts rotating anti-clockwise.
This happens because a downward force acts on length PQ and at the same time,
an upward force acts on length RS. As a result, the coil rotates anti-clockwise.
Current in the length PQ flows from P to Q and the magnetic
field acts from left to right, normal to length PQ. Therefore, according to
Fleming’s left hand rule, a downward force acts on the length PQ. Similarly at
an upward force acts on the length RS. These two forces cause the coil to rotate
anti-clockwise.
When coil complete half rotation, the position of PQ and RS
interchange. The half-ring D comes in contact with brush A and half-ring C
comes in contact with brush B. therefore the direction of current in the coil
PQRS gets reversed. Now the current flows through the coil in the direction
SRQP. The direction of current through the coil PQRS reverse after every
half rotation. As a result, the coil rotates in same direction. The split rings
help to reverse the direction of current in the circuit. These are called the
commutator.
