1
Question
If α is the degree of ionization, C the concentration of a weak electrolyte and Ka the acid ionization constant, then the correct relationship between α, C and Ka is
If α is the degree of ionization, C the concentration of a weak electrolyte and Ka the acid ionization constant, then the correct relationship between α, C and Ka is
Open in App
Solution
The correct option is C 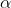 = √(Ka / C).
= √(Ka / C).
According to the Ostwald's dilution formula α2 − Ka(1 − α)C. But for weak
electrolytes α is very small. So that (1 − α) can be taken as 1. So that α = √KaC.
= √(Ka / C).
According to the Ostwald's dilution formula α2 − Ka(1 − α)C. But for weak
electrolytes α is very small. So that (1 − α) can be taken as 1. So that α = √KaC.
Suggest Corrections
2
View More
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
