1
Question
What are the four types of cells?
What are the four types of cells?
Open in App
Solution
Types of cells:
- The fundamental structural and operational unit of our body is the cell.
- Every cell in the human body is infinitely many. These cells, which clump together to create tissues that carry out certain bodily duties, share comparable structures and functions.
- The "building blocks of life" are referred to as cells. Based on the tissues they form, the human body contains eight different types of cells.
Connective tissue cells :
- Fibroblasts are the least specialized. They are primarily in charge of secreting the collagen, elastin, or fibronectin fibers that make up the non-rigid extracellular matrix.
- Adipocytes are cells that store fat, and it is considered that they are related to fibroblastic cells.
- Mast cells, plasma cells, and macrophages. All of these are immune cells.
- Tendons and ligaments, bone and cartilage, blood, and adipose tissue are all examples of specialized connective tissue.
- The type of extracellular matrix material (ECM) that makes up bone is secreted by osteoblasts and osteoclasts, which are found in bone.
- The ECM found in cartilage is secreted by chondrocytes and chondroblasts (chondro - cartilage), which are found in cartilage.
- Endothelial cells, the simple squamous endothelium that lines the circulatory system, are discussed in the section on epithelia and are found in blood vessels.
- Additionally, there are perivascular cells known as pericytes, which can divide and serve as a source of new fibroblasts, particularly after tissue injury, right beneath the epithelium of blood capillaries.

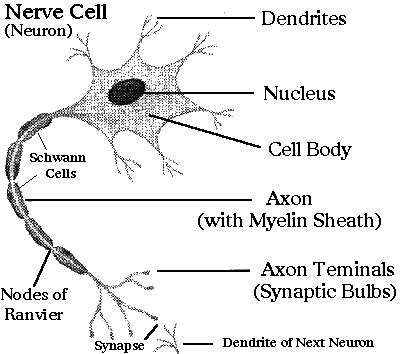
Nerve cells:
- Neurons are nerve cells that assist in the transmission of nerve impulses.
- The tissues' outer layer is formed by epithelial cells, which shield the tissues from abrasion and damage.
- In nerve tissue, there are just two primary cell types.
- The neuron is the real nerve cell. The structural component of the nervous system, the "conducting" cell sends impulses. Neuroglia, often known as glial cells, is the other type of cell.
Muscle cells:
- Since cardiac muscle cells and smooth muscle cells are both small cells, a muscle cell is also referred to as a myocyte.
- Muscle fibers are the long, threadlike cells of skeletal muscle that have several nuclei. Myoblasts, embryonic precursor cells, are the source of muscle cells.
- Muscle cells contribute to muscle contraction, which makes movement easier.

Epithelial cells:
- There are many locations where epithelial tissues are present in the human body.
- They make up the majority of the tissue in glands, line body cavities, and hollow organs, and cover all of the body's surfaces.
- Protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, and sensory reception are just a few of the many tasks they carry out.

Types of cells:
- The fundamental structural and operational unit of our body is the cell.
- Every cell in the human body is infinitely many. These cells, which clump together to create tissues that carry out certain bodily duties, share comparable structures and functions.
- The "building blocks of life" are referred to as cells. Based on the tissues they form, the human body contains eight different types of cells.
Connective tissue cells :
- Fibroblasts are the least specialized. They are primarily in charge of secreting the collagen, elastin, or fibronectin fibers that make up the non-rigid extracellular matrix.
- Adipocytes are cells that store fat, and it is considered that they are related to fibroblastic cells.
- Mast cells, plasma cells, and macrophages. All of these are immune cells.
- Tendons and ligaments, bone and cartilage, blood, and adipose tissue are all examples of specialized connective tissue.
- The type of extracellular matrix material (ECM) that makes up bone is secreted by osteoblasts and osteoclasts, which are found in bone.
- The ECM found in cartilage is secreted by chondrocytes and chondroblasts (chondro - cartilage), which are found in cartilage.
- Endothelial cells, the simple squamous endothelium that lines the circulatory system, are discussed in the section on epithelia and are found in blood vessels.
- Additionally, there are perivascular cells known as pericytes, which can divide and serve as a source of new fibroblasts, particularly after tissue injury, right beneath the epithelium of blood capillaries.

Nerve cells:
- Neurons are nerve cells that assist in the transmission of nerve impulses.
- The tissues' outer layer is formed by epithelial cells, which shield the tissues from abrasion and damage.
- In nerve tissue, there are just two primary cell types.
- The neuron is the real nerve cell. The structural component of the nervous system, the "conducting" cell sends impulses. Neuroglia, often known as glial cells, is the other type of cell.

Muscle cells:
- Since cardiac muscle cells and smooth muscle cells are both small cells, a muscle cell is also referred to as a myocyte.
- Muscle fibers are the long, threadlike cells of skeletal muscle that have several nuclei. Myoblasts, embryonic precursor cells, are the source of muscle cells.
- Muscle cells contribute to muscle contraction, which makes movement easier.

Epithelial cells:
- There are many locations where epithelial tissues are present in the human body.
- They make up the majority of the tissue in glands, line body cavities, and hollow organs, and cover all of the body's surfaces.
- Protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, and sensory reception are just a few of the many tasks they carry out.

Suggest Corrections
1
View More
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
