1
Question
What is SHM in Physics?
What is SHM in Physics?
Open in App
Solution
- A to-and-fro motion of a particle around a mean position in which the particle moves on either side of the equilibrium (or) mean position is referred to as an oscillatory motion. It's a type of periodic motion with two extreme points.
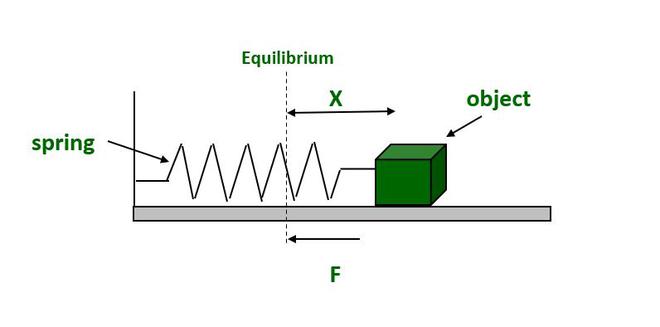
- Simple harmonic motion is an oscillatory motion in which the particle's acceleration and force are directly proportional to its displacement from the mean location at each point. It is a special case of oscillatory motion.
- Mathematical expression for the force acting on the particle
where, is the force, is the acceleration, is the displacement. 
- The maximum displacement of the particle is called the amplitude of motion.
- At the mean position, the energy is entirely kinetic energy. At the extreme position, the energy is entirely potential energy.
- The most common examples of SHM are simple pendulum and spring-mass systems.
- A to-and-fro motion of a particle around a mean position in which the particle moves on either side of the equilibrium (or) mean position is referred to as an oscillatory motion. It's a type of periodic motion with two extreme points.
- Simple harmonic motion is an oscillatory motion in which the particle's acceleration and force are directly proportional to its displacement from the mean location at each point. It is a special case of oscillatory motion.
- Mathematical expression for the force acting on the particle
where, is the force, is the acceleration, is the displacement. - The maximum displacement of the particle is called the amplitude of motion.
- At the mean position, the energy is entirely kinetic energy. At the extreme position, the energy is entirely potential energy.
- The most common examples of SHM are simple pendulum and spring-mass systems.
Suggest Corrections
18
View More
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
Join BYJU'S Learning Program
