Why TCA Cycle Is Called Common Metabolic Pathway?
Why TCA Cycle Is Called Common Metabolic Pathway?
Kreb's cycle:
The Krebs cycle or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) or Citric acid cycle is a sequence of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that occur in the mitochondrial matrix, in which acetyl-CoA is oxidized to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced, leading to the generation of ATP in the electron transport chain.
The steps involved in the Kreb's cycle are:
Step 1: Condensation of acetyl CoA with 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate leads to the formation of a 6C citrate and coenzyme A is released. The catalyst in the reaction is citrate synthase.
Step 2: Conversion of citrate to its isomer, isocitrate. The catalytic enzyme in this reaction is aconitase.
Step 3: Dehydrogenation and decarboxylation of isocitrate occur, leading to the formation of 5C 𝝰-ketoglutarate. A molecular form of CO2 is also released. Isocitrate dehydrogenase is the catalyst in the reaction. It is an NAD+ dependent enzyme and NAD+ is converted to NADH.
Step 4: Oxidative decarboxylation of 𝝰-ketoglutarate to form succinyl CoA, a 4C compound. Catalyst im the reaction is 𝝰-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. One molecule of CO2 is released and conversion of NAD+ to NADH occurs.
Step 5: Formation of succinate from Succinyl CoA. The catalytic enzyme is succinyl CoA synthetase. This is included with substrate-level phosphorylation of GDP to form GTP. GTP transfers its phosphate to ADP forming ATP.
Step 6: Oxidation of succinate by the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase into fumarate. FAD is converted to FADH2
Step 7: Conversion of fumarate to malate by adding one H2O. The catalyst here is fumarase.
Step 8: Dehydrogenation of malate to form oxaloacetate, which combines with another molecule of acetyl CoA and starts the new cycle. Hydrogen gets removed and transferred to NAD+ leading to the formation of NADH. The catalyst in the reaction is Malate dehydrogenase.
TCA cycle is also termed the common metabolic pathway because:
- It is the common pathway for the complete oxidation of carbohydrates, amino acids and fatty acids.
- The majority of the biomolecules enter the cycle as acetyl CoA.
- Intermediates of the TCA cycle are utilized in a variety of biosynthetic pathways and interconversion of amino acids.
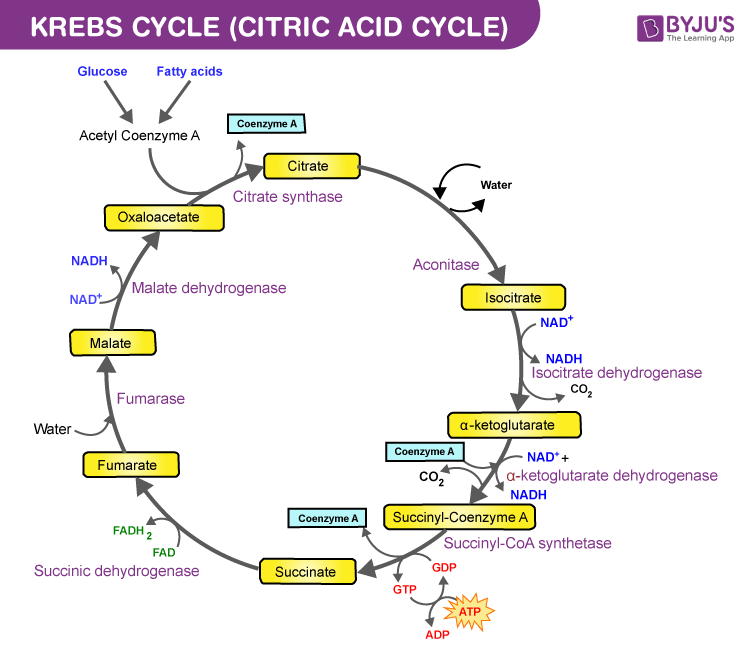
Kreb's cycle:
The Krebs cycle or TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) or Citric acid cycle is a sequence of enzyme-catalyzed reactions that occur in the mitochondrial matrix, in which acetyl-CoA is oxidized to form carbon dioxide and coenzymes are reduced, leading to the generation of ATP in the electron transport chain.
The steps involved in the Kreb's cycle are:
Step 1: Condensation of acetyl CoA with 4-carbon compound oxaloacetate leads to the formation of a 6C citrate and coenzyme A is released. The catalyst in the reaction is citrate synthase.
Step 2: Conversion of citrate to its isomer, isocitrate. The catalytic enzyme in this reaction is aconitase.
Step 3: Dehydrogenation and decarboxylation of isocitrate occur, leading to the formation of 5C 𝝰-ketoglutarate. A molecular form of CO2 is also released. Isocitrate dehydrogenase is the catalyst in the reaction. It is an NAD+ dependent enzyme and NAD+ is converted to NADH.
Step 4: Oxidative decarboxylation of 𝝰-ketoglutarate to form succinyl CoA, a 4C compound. Catalyst im the reaction is 𝝰-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase. One molecule of CO2 is released and conversion of NAD+ to NADH occurs.
Step 5: Formation of succinate from Succinyl CoA. The catalytic enzyme is succinyl CoA synthetase. This is included with substrate-level phosphorylation of GDP to form GTP. GTP transfers its phosphate to ADP forming ATP.
Step 6: Oxidation of succinate by the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase into fumarate. FAD is converted to FADH2
Step 7: Conversion of fumarate to malate by adding one H2O. The catalyst here is fumarase.
Step 8: Dehydrogenation of malate to form oxaloacetate, which combines with another molecule of acetyl CoA and starts the new cycle. Hydrogen gets removed and transferred to NAD+ leading to the formation of NADH. The catalyst in the reaction is Malate dehydrogenase.
TCA cycle is also termed the common metabolic pathway because:
- It is the common pathway for the complete oxidation of carbohydrates, amino acids and fatty acids.
- The majority of the biomolecules enter the cycle as acetyl CoA.
- Intermediates of the TCA cycle are utilized in a variety of biosynthetic pathways and interconversion of amino acids.

