1
Question
Illustrate a glycosidic, peptide and phosphodiester bond.
Open in App
Solution
Glycosidic bonds are the covalent chemical bonds that link ring-shaped sugar molecules to other molecules. They form by a condensation reaction between an alcohol or amine and the anomeric carbon of the sugar.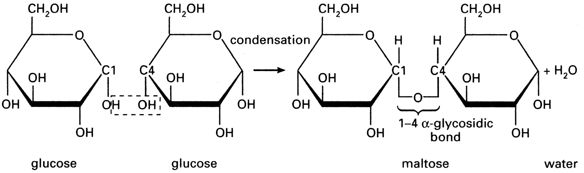
A peptide bond or amide bond is a covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive amino acid monomers along a peptide or protein chain.
The phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the 5' carbon atom of another, deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. It is the strong covalent bonds form between the phosphate group and two 5-carbon ring carbohydrates (pentoses) over two ester bonds.

A peptide bond or amide bond is a covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive amino acid monomers along a peptide or protein chain.

The phosphodiester bond is the linkage between the 3' carbon atom of one sugar molecule and the 5' carbon atom of another, deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. It is the strong covalent bonds form between the phosphate group and two 5-carbon ring carbohydrates (pentoses) over two ester bonds.

Suggest Corrections
2
