What is Absolute Pressure?
When any pressure is detected above the absolute zero of pressure, it is labelled as absolute pressure. It is measured using a barometer, and it is equal to measuring pressure plus the atmospheric pressure.
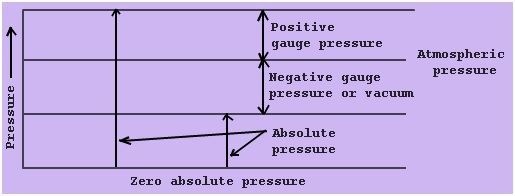
Diagram showing absolute pressure, vacuum and gauge
Absolute pressure formula (pabs) is given by,
Pabs=Patm+Pgauge
where pgauge is the gauge pressure
patm is atmospheric pressure.
The vacuum pressure is articulated as,
Vacuum Pressure = Atmospheric Pressure – Absolute Pressure
At sea level, it is around 14.7 pounds per square inch.
Solved Examples
Let’s see some examples of absolute pressure:
Problem 1: A pressure gauge measures the pgauge reading as 31 psi. If the atmospheric pressure is 14.2 psi. Compute the absolute pressure that corresponds to pgauge reading.
Answer:
Given:
patm (Atmospheric pressure) = 14.2 psi
pgauge (Gauge pressure) = 31 psi
Absolute pressure (pabs) = patm + pgauge
= 14.2 psi + 31 psi
pgauge= 45.2 psi
Problem 2: The psia pressure instrument gives the reading as 35.8 psi. If the atmospheric pressure is 15 psi, calculate the corresponding guage pressure.
Answer:
Given:
Atmospheric pressure patm = 15 psi
Absolute pressure pabs = 35.8 psi
The Gauge pressure is
pgauge = 35.8 psi – 15 psi
gauge = 20.8 psi.
Stay tuned with BYJU’S for more such interesting articles. Also, register to “BYJU’S – The Learning App” for loads of interactive, engaging Physics-related videos and an unlimited academic assist.
Comments