In trigonometry, every function such as sine, cosine and tangent has its inverse function. The tangent formula is used to tan of an angle in a right-angled triangle. The inverse tangent formula is used to find the angle when the side opposite to that angle and adjacent side are known to us. The inverse of Tangent is represented by arctan or tan-1.
The trigonometric functions/ratios are:
- Sine
- Cosine
- Tangent
- Secant
- Cosecant
- Cotangent
The inverse of these trigonometric functions are as follows:
- inverse sine
- inverse cosine
- inverse tangent
- inverse secant
- inverse cosecant
- inverse cotangent
Tan Inverse Formula
| Tan (A)= Opposite Side / Adjacent Side
A = Tan-1 (Opposite Side/Adjacent Side) where A is an angle |
For example, if in a triangle, opposite side to angle A is 1 and the adjacent side is √3
So tan-1 (1/√ 3) = A
As we know, tan 30 = 1/√3
Therefore, tan-1 (tan 30) = A
or A = 30 degrees
Solved Examples
Example 1: From the given figure, find the value of x.
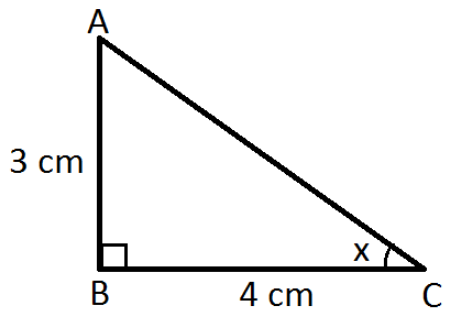
Solution:
From the given,
AB = 3 cm, BC = 4 cm
tan x = AB/BC
tan x = ¾ = 0.75
x = tan-1(0.75)
x = 36.9°
Example 2: If sin x = 0 and cos x = 1, then find the tan-1x.
Solution:
Given,
sin x = 0
x = sin-1(0) = 0
cos x = 1
x = cos-1(1) = 0
Now,
tan-1x = tan-1(0) = 0
Register at BYJU’S to learn more trigonometrical concepts.
Comments