TS Grewal Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 2:
TS Grewal Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 2- Accounting Equation is a fundamental concept to be studied by the students. Here, we have provided in a simplistic and a step by step method, which is useful for the students to score well in the board exams.
Class 11 TS Grewal Solutions Accountancy Chapter 2:-Download PDF Here
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | Class 11 |
| Subject | Accountancy |
| Chapter | Chapter 2 |
| Chapter Name | Accounting Equation |
| Number of questions solved | 28 |
| Category | TS Grewal |
Chapter 1- Accounting Equation defines the below-mentioned concepts:
- Balance Sheet and Income Statement
- Balance in Accounting:
- Fundamental Accounting Equation
- Accounting equation in an Income Statement
- Double-entry bookkeeping system
Ts Grewal Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 2- Accounting Equation
Q.1 What will be effect of the following on the Accounting Equation?
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 45,000
(ii) Opened a Bank Account with a deposit of ₹ 4,500
(iii) Bought goods from M\s. Sun & Co. for ₹ 11,200
The solution for this question is as follows:

Therefore,
Liabilities = 11,200
Capital = 45,000
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
= 45,000 + 11,200 = 56,200
Q.2 Show the Accounting Equation for the following transactions:
| ₹ | ||
| (i) | Gopinath started business with cash | 25,000 |
| (ii) | Purchased goods from Shyam | 10,000 |
| (iii) | Sold goods to Sohan costing ₹ 1,800 | 1,500 |
| (iv) | Gopinath withdrew from business | 5,000 |
The solution for this question is as follows:
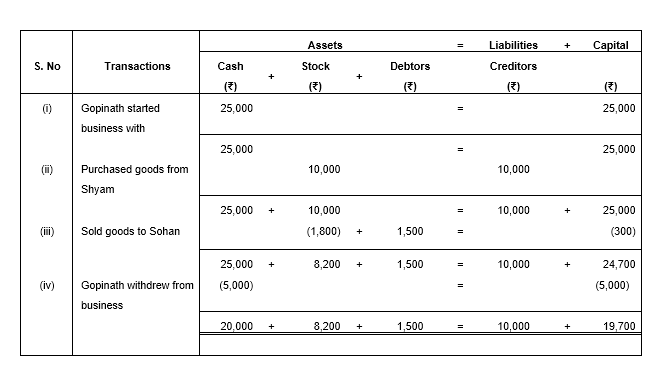
Here,
Liabilities = 10,000
Capital = 19,700
Assets = 10,000 + 19,700 = 29,700
Q.3 Show the effect of the following transactions on the Accounting Equation:
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 50,000.
(ii) Salaries paid ₹ 2,000.
(iii) Wages Outstanding ₹ 200.
(iv) Interest due but not paid ₹ 100.
(v) Rent paid in advance ₹ 150.
The solution for this question is as follows:

Q.4 What will be the effect of the following on the Accounting Equation?
(i) Harish started business with cash ₹ 18,000
(ii) Purchased goods for Cash ₹ 5,000 and on credit ₹ 2,000
(iii) Sold goods for cash ₹ 4,000 (costing ₹ 2,400)
(iv) Rent paid ₹ 1,000 and rent outstanding ₹ 200
The solution for this question is as follows:
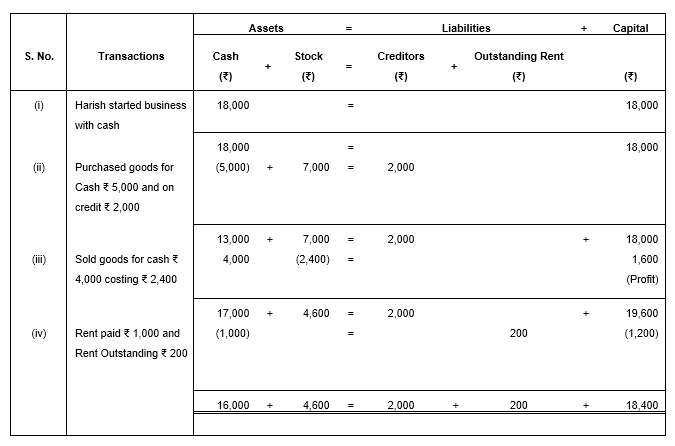
Q.5 Prepare Accounting Equation from the following:
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 1,00,000 and Goods ₹ 20,000.
(ii) Sold goods worth ₹ 10,000 for cash ₹ 12,000.
(iii) Purchased furniture on credit for ₹ 30,000.
The solution for this question is as follows:

Q.6 Prepare an Accounting Equation and Balance Sheet on the following basis:
(i) Ajeet started business with cash ₹ 20,000.
(ii) He purchased furniture for ₹ 2,000.
(iii) He paid rent of ₹ 200.
(iv) He purchases goods on credit ₹ 3,000.
(v) He sold goods (cost price ₹ 2,000) for ₹ 5,000 on cash.
The solution for this question is as follows:

The balance sheet is prepared as follows

Q.7 Prepare an Accounting Equation from the following:
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 1,00,000.
(ii) Purchased goods for cash ₹ 20,000 and on credit ₹ 30,000.
(iii) Sold goods for cash costing ₹ 10,000 and on credit costing ₹ 15,000 both at a profit of 20%.
The solution for this question is as follows:

Q.8 Develop an Accounting Equation from the following transactions:
| ₹ | ||
| (i) | Mohan commenced business with cash | 50,000 |
| (ii) | Purchased goods for cash | 30,000 |
| (iii) | Purchased goods on credit | 20,000 |
| (iv) | Sold goods (costing ₹ 10,000) for | 12,000 |
| (v) | Bought furniture on credit | 2,000 |
| (vi) (vii) |
Paid cash to a creditor Salary paid |
15,000 1,000 |
The solution for this question is as follows:
Q.9 Prepare an Accounting Equation on the basis of the following transactions:
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 70,000.
(ii) Credit purchase of goods ₹ 18,000.
(iii) Payment made to creditors in full settlement ₹ 17,500.
(iv) Purchase of machinery for cash ₹ 20,000.
(v) Depreciation on machinery ₹ 2,000.
The solution for this question is as follows:

Q.10 Prove that the Accounting Equation is satisfied in all the following transactions of Suresh. Also prepare a Balance Sheet.
(i) Commenced business with cash ₹ 60,000.
(ii) Paid rent in advance ₹ 500.
(iii) Purchased goods for cash ₹ 30,000 and credit ₹ 20,000.
(iv) Sold goods for cash ₹ 30,000 costing ₹ 20,000.
(v) Paid salary ₹ 500 and salary outstanding being ₹ 100.
(vi) Bought motorcycle for personal use ₹ 5,000.
The solution for this question is as follows:

Here,
Liabilities = 20,000 + 100 = 20,100
Capital = 64,400
Assets = 64,400 + 20,100 = 84,500
Balance sheet is prepared as follows

Q.11 Show the effect of the following transactions and also prepare a Balance Sheet:
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 60,000.
(ii) Rent received ₹ 2,000.
(iii) Accrued interest ₹ 500.
(iv) Commission received in advance ₹ 1,000.
(v) Amount withdrawn ₹ 5,000.
The solution for this question is as follows:

Balance sheet is prepared as follows

Q.12 Prove that the Accounting Equation is satisfied in all the following transactions of Sameer Goel:
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 10,000.
(ii) Paid rent in advance ₹ 300.
(iii) Purchased goods for cash ₹ 5,000 and credit ₹ 2,000.
(iv) Sold goods for cash ₹ 8,000 costing ₹ 4,000.
(v) Paid salary ₹ 450 and salary outstanding being ₹ 100.
(vi) Bought motorcycle for personal use ₹ 3,000.
The solution for this question is as follows:
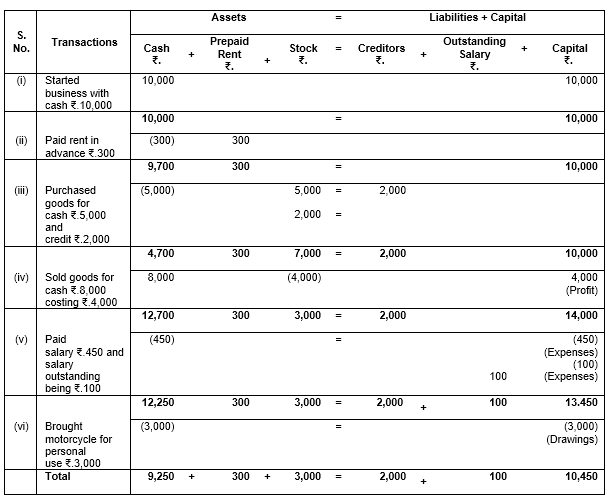
Here,
Liabilities = 2000 + 100 = 2100
Capital = 10,450
Assets = 10,450 + 2100 = 12,550
Q.13 Show the Accounting Equation on the basis of the following transactions and present a Balance Sheet on the last new equation balance:
| ₹ | ||
| (i) | Raj commenced business with cash | 70,000 |
| (ii) | Purchased goods on credit | 14,000 |
| (iii) | Withdrew for Private use | 1,700 |
| (iv) | Goods purchased for cash | 10,000 |
| (v) | Paid wages | 300 |
| (vi) (vii) (viii) (ix) |
Paid to creditors Sold goods on credit for Sold goods for cash (cost price was Purchased motorcycle for cash ₹ 3,000) Purchased furniture for |
10,000 15,000 4,000 500 |
The solution for this question is as follows:

Balance sheet is prepared as follows

Q.14 Raghunath had the following transactions in an accounting year:
(i) Commenced business with cash ₹ 50,000.
(ii) Paid into bank ₹ 10,000.
(iii) Purchased goods for cash ₹ 20,000 and credit ₹ 30,000.
(iv) Sold goods for cash ₹ 40,000 costing ₹ 30,000.
(v) Rent paid ₹ 500.
(vi) Rent outstanding ₹ 100.
(vii) Bought furniture ₹ 5,000 on credit.
(viii) Bought refrigerator for personal use ₹ 5,000.
(ix) Purchased motorcycle for cash ₹ 20,000.
Create an Accounting Equation to show the effect of the above and also show his Balance Sheet.
The solution for this question is as follows:

Balance sheet is prepared as follows

Q.15 Prepare an Accounting Equation from the following:
(i) Started business with cash ₹ 50,000 and goods ₹ 30,000.
(ii) Purchased goods for cash ₹ 30,000 and on credit from Karan ₹ 20,000.
(iii) Goods costing ₹ 40,000 were sold for ₹ 55,000.
(iv) Withdrew cash for personal use ₹ 10,000.
(v) Rent outstanding ₹ 2,000.
The solution for this question is as follows:

Q.16 Show an Accounting Equation for the following transactions:
(i) D. Mahapatra commenced business with cash ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 1,00,000 by cheque; goods ₹ 60,000; machinery ₹ 1,00,000 and furniture ₹ 50,000.
(ii) 1/3rd of above goods sold at a profit of 10% on cost and half of the payment is received in cash.
(iii) Depreciation on machinery provided @ 10%.
(iv) Cash withdrawn for personal use ₹ 10,000.
(v) Interest on drawings charged @ 5%.
(vi) Goods Sold to Gupta for ₹ 10,000 and received a Bill Receivable for the same amount for 3 months.
(vii) Received ₹ 10,000 from Gupta against the Bills Receivable on its maturity.
The solution for this question is as follows:

Q.17 Prepare Accounting Equation from the following:
(a) Started business with cash ₹ 1,00,000.
(b) Purchased goods for cash ₹ 20,000 and on credit ₹ 30,000.
(c) Sold goods for cash costing ₹ 10,000 and on credit costing ₹ 15,000 both at a profit of 20%.
(d) Paid salaries ₹ 8,000.
The solution for this question is as follows:

Q.18 Show the accounting equation on the basis of following transactions:
(a) Ram started business with ₹ 25,000.
(b) Purchased goods from Shyam ₹ 10,000.
(c) Sold goods to Sohan costing ₹ 1,500 for ₹ 1,800.
The solution for this question is as follows:

Q.19 If the capital of a business is ₹ 3,00,000 and liabilities are ₹ 50,000, loss ₹ 70,000, calculate the total assets of the business.

Q.20 If total assets of a business are ₹ 1,30,000 and net worth is ₹ 80,000, calculate the creditors.

Q.21 A commenced his cloth business on 1st April, 2018 with a capital of ₹ 30,000. On 31st March 2019, his assets were worth ₹ 50,000 and liabilities of ₹ 10,000. Find out his closing capital and profits earned during the year.
The solution for this question is as follows:
Here Capital = 30,000
Assets = 50,000
Liabilities = 10,000

Q.22 If capital of a business is ₹ 1,40,000 and liabilities are of ₹ 80,000, calculate the total assets of the business.
The solution for this question is as follows:
Here Capital = 1,40,000
Liabilities = 80,000

Q.23 Calculate the total assets if:
(i) Capital is ₹ 40,000.
(ii) Creditors are ₹ 25,000.
(iii) Revenue during the period is ₹ 50,000.
(iv) Expenses during the period are ₹ 40,000.
The solution for this question is as follows:
Here Capital = 40,000
Creditors = 25,000
Revenue = 50,000
Expenses = 40,000

Q.24 (a) A had a capital of ₹ 75,000 on 1st April, 2018. He had also goods amounting to ₹ 15,000 which he had purchased on credit and the payment had not been made. Find out the value of the total assets of the business.
(b) After a period of one month, he came to know that he had suffered a loss of ₹ 1,700. He withdrew ₹ 800 for his personal use. Find out his capital and assets of the business.


Q.25 (a) Mohan started a business on 1st April, 2018 with a capital of ₹ 10,000 and borrowed ₹ 3,000 from a friend. He earned a profit of ₹ 5,000 during the year ended 31st March, 2019 and withdrew cash ₹ 4,000 for personal use. What is his capital on 31st March, 2019?
(b) Mahesh started a business with a capital of ₹ 15,000 on 1st April, 2018. During the year, he made a profit of ₹ 3,000. He owes ₹ 2,500 to suppliers of goods. What is the total of assets in his business on 31st March, 2019?


Q.26 Mohan started a business on 1st April, 2018 with a capital of ₹ 25,000 and a loan of ₹ 12,500 borrowed from Shyam. During 2018-19 he had introduced additional capital of ₹ 12,500 and had withdrawn ₹ 7,500 for personal use. On 31st March, 2019 his assets were ₹ 75,000. Find out his capital as on 31st March, 2019 and profit made or loss incurred during the year 2018-19.


Q.27 On 31st March, 2019, the total assets and external liabilities were ₹ 2,00,000 and ₹ 6,000 respectively. During the year, the proprietor had introduced capital of ₹ 20,000 and withdrawn ₹ 12,000 for personal use. He made a profit of ₹ 20,000 during the year. Calculate the capital as on 1st April, 2018.


Q.28 Show an Accounting Equation on the basis of the following transactions:
| ₹ | ||
| (i) | Sunil started business with cash | 1,50,000 |
| (ii) | Opened a Bank Account by depositing ₹ 25,000 out of cash | |
| (iii) | He sold his personal car for ₹ 50,000 and deposited the amount in the firm’s Bank Account | |
| (iv) | He purchased a building and furniture for | 1,00,000 |
| (v) | He purchased goods from Ram on credit | 50,000 |
| (vi) | He paid cartage | 500 |
| (vii) | He sold to Shyam on credit goods costing ₹ 6,000 for | 9,000 |
| (viii) | Received rent from tenants | 1,000 |
| (ix) | Received security deposit from tenants | 1,500 |
| (x) | Purchased stationery for cash | 100 |
| (xi) | Invested in shares (personal) | 50,000 |
| (xii) | Received interest in cash | 200 |
| (xiii) | Introduced fresh capital | 25,000 |
| (xiv) | Goods destroyed by fire | 500 |
The solution for this question is as follows:

Thanks Byju’s
I am very thankful to BYJU’s learning program for providing such great study material all the time.