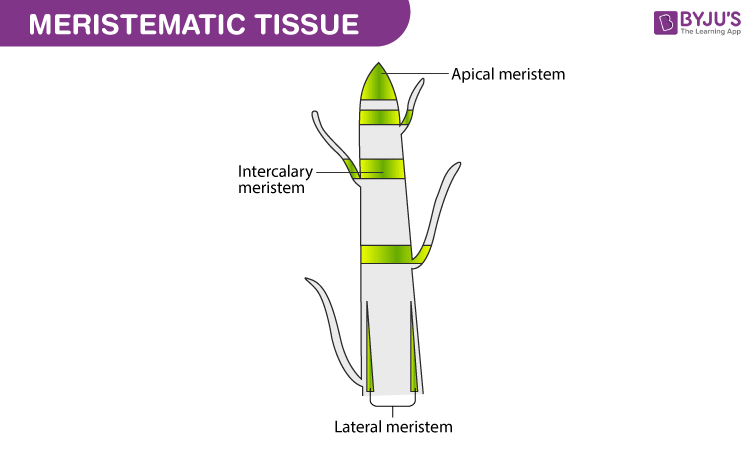
- A group of undifferentiated cells that is capable of continued cell division is referred to as meristematic tissue.
- These cells are totipotent in nature that can divide until the time they finally differentiate and cannot divide further.
- Meristematic cells can give rise to new organs and help in building the basic structure of the plant.
- A meristematic tissue is of three types – apical meristem (found at the tips), intercalary meristem (found in the middle) and lateral meristems (found in the sides).
- Examples of lateral meristems in the plant include vascular cambium and phellogen.
- They are commonly found in gymnosperms and dicot plants and show secondary growth. They are not found in monocots as they do not show secondary growth.
- The meristematic cells are small in size and are packed closely with no intercellular spaces.
- There are small or no vacuoles present in the cells and it is completely filled with protoplasm.
You might also be interested in :
Comments