Ginkgophyta is one of the four divisions under Gymnosperms. The other three divisions are Pinophyta (or Conipherophyta), Cycadophyta and Gnetophyta. Gymnosperms are a group of seed producing plants such as pines, cypresses, ginkgo, ephedra, etc.
Overview of Ginkgophyta
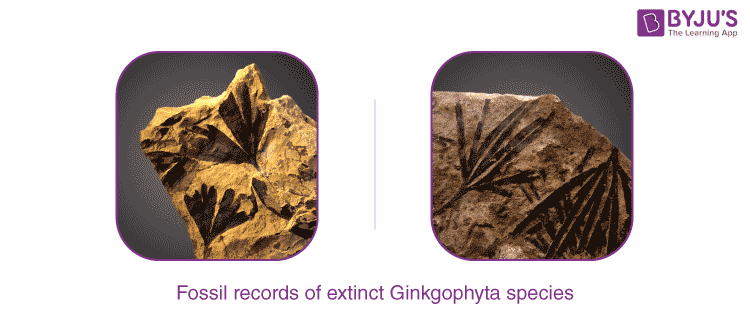
Ginkgophyta is survived by only species Ginkgo biloba under the order Ginkgoales. Fossils indicate that at least 16 genera of Ginkgophyta were known in older mesozoic times but became extinct over the years.
The extant Gingko shows fair similarities to all the fossil records found from the Triassic and Jurassic periods. The classification of Ginkgophyta is as follows:
Kingdom: Plantae
Clade: Tracheophytes
(unranked): Gymnospermae
Division: Ginkgophyta
Characteristics of Ginkgophyta
Characteristics of ginkgophyta can be extracted from the one living species Ginkgo biloba, which are as follows:
- Fan-shaped leaves which are doubly lobed
- Vascular system consists of both xylem and phloem
- Leaves tend to grow in clusters, looking very much like maidenhair fern
- The trees are dioecious
- Taproot system
- Leaves bear stomata only on the lower surface
Conclusion
The division ginkgophyta is barely alive by the species Ginkgo biloba as it is itself one of the endangered species right now, being grown only in certain parts of China.
Stay tuned to BYJU’S biology to read more about the Plant Kingdom.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ginkgophyta used for?
Ginkgo biloba is used as a herbal remedy for reducing anxiety and depression. It is also used to treat diseases like dementia and Alzheimer’s.
Why did ginkgo go extinct?
It is mainly because of man-made reasons that the tree has gone extinct. However, botanists are taking extreme measures to save the dying species.

Comments