Cell Division
Cell division is the interaction by which the cells expand to create new cells. This process is an interaction by which new cells are shaped for development, fixation, and substitution in the body. This interaction incorporates the division of the cytoplasm, along with the cytoplasmic material. The partitioned cell is named the parent cell, and the new cells that are formed are known as offspring or daughter cells.

Also Read – Cell cycle and division
Plant Cell Division
In plants, the growth occurs majorly through cell division. A new cell wall or cell plate is formed in the cytoplasm. This constriction separates the parent cell into two daughter cells.
Animal Cell Division
The animal cell divides to grow as well as repair itself. Here, a ring-like structure helps in the daughter cell formation. This structure contracts inside, forming an indentation. Thus, leading to newer cells.
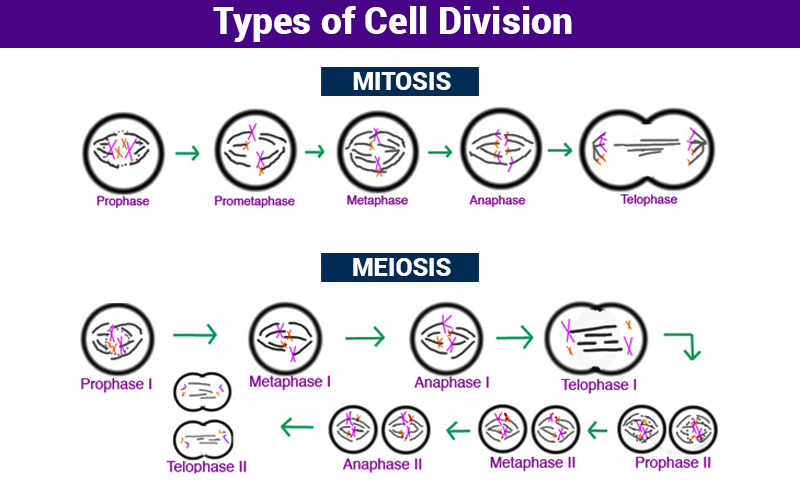
Significant Differences in the Cell Division Process
The cell division process creates a considerable amount of changes in both plants as well as animal cells. For example, the animal cell remains almost circular after cell division. Whereas, the plant cell remains constant due to its rigid cell structure.
The following are the unique differences in the cell division of plants and animals.
Cell Division Process |
Plant Cell |
Animal Cell |
|
Initiation Process |
The cytokine hormone initiates this process. Also, this leads to the formation of a cellular plate that divides the parent cell. |
No hormonal action is involved here. The cell carves an indentation and separates itself. |
|
Spindle Formation |
There is no aster or centrosome involved in the spindle formation. |
Centrosomes play a significant role here. Also, aster is formed on both ends of the spindle. |
|
The plant cell also produces sex gametes through meiosis. But, they are not delivered through direct means. |
The sex gametes (eggs and sperms) are formed this way. Four haploid sex cells are produced directly. |
|
|
Here, mitosis is a necessary asexual process to produce daughter cells. Also, mitosis occurs only in the meristem. |
Similarly, the mitosis here produces genetically identical daughter cells. Here, mitosis occurs everywhere except the sex cells. |
Cytokinesis in plant cells Cytokinesis in animal cells

|

|
See – Importance of Cell Division
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the cytokinesis process differ in plant and animal cells?
Cytokinesis is a process of division of cytoplasm as well as organelles. In plant cells, this process is aided by the cell plates. The Golgi vesicles help in the initiation of these plates. Whereas in animal cells, this process is administered by the constriction ring. Furthermore, this ring is made of actin and myosin proteins.
Are the stages of cell division different in plants and animals?
The stages or steps in cell division are almost identical in plants and animals. In contrast, the formation process of new cells or gametes differs—for example, the spindle formation and the cytokinesis process.
Also Refer – Difference between Karyokinesis and Cytokinesis
Visit BYJU’S Biology for more interesting topics.
Comments