Ti Plasmid
Ti is the tumour-inducing plasmid seen in Agrobacterium tumefaciens (plant pathogenic bacterium). They are responsible for crown gall disease in dicot plants. These tumour-inducing agents are responsible for the overproduction of cytokinins and auxin hormones. Thus, they create swelling/galls/tumours on the crown of the plant. The Ti plasmid DNA (T-DNA or transfer DNA) is also responsible for changes in cell metabolism.
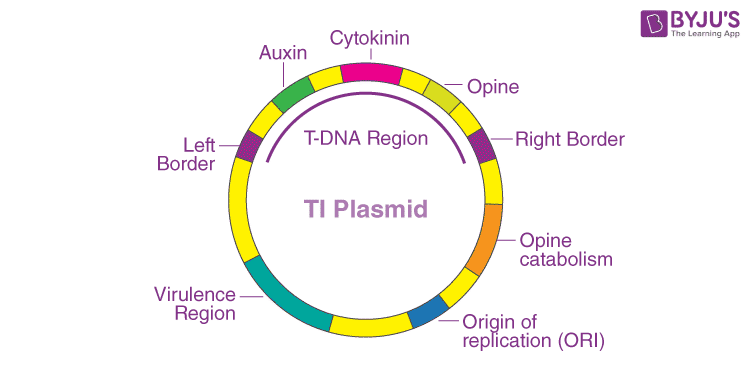
Ti plasmid as a vector
The tumour-inducing genes of the Ti are suppressed and are used as vectors. Recombinant DNA technology is used to insert the gene of interest into the Ti plasmid. Then they are integrated into the genome of the specific plant cell.
Ri Plasmid
Ri is the root-inducing plasmid seen in Agrobacterium rhizogenes. They induce hairy root diseases in dicots. Its virulence plasmid is called pRi (Ri-Plasmid). The T-DNA of the Ri plasmid infects the plants by entering through their wounds. They integrate and express their bacterial genome within the plant. Finally, they alter the plant morphology.
This Ri plasmid can also be used as a vector to transfer the desired genes.
Also Read: What is Plasmid?
Difference between Ti and Ri plasmid
Ti Plasmid |
Ri Plasmid |
| Ti plasmid is found in the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens. | Ri plasmid is found in the bacterium Agrobacterium rhizogenes. |
| They cause crown gall disease in dicots. | They cause hairy root disease in monocots. |
Also see: Plasmids and Vectors
Frequently Asked Questions
What are plasmids?
Plasmids are small, circular extrachromosomal DNA structures that are mostly found in bacteria. Some eukaryotes and archaea also show plasmids. They usually carry vital genes. Also, they are used as a vector in biotechnology due to their self-replicating nature.
What are the similarities between Ti and Ri plasmid?
Ti and Ri are plant pathogenic bacteria that usually affect the dicots. Also, their sizes are almost the same. Both have T-DNA or transfer DNA that is integrated into the host plant. These plasmids are used as vectors in recombinant DNA technology.
What is a hairy root culture?
The Agrobacterium rhizogenes have Ri plasmid that causes hairy root disease. They attack the plant roots and produce opines (bacterial food). Thus, the roots grow abnormally and can also be easily cultured. These root cultures can grow indefinitely without any hormones. Thus, hairy root cultures are used in genetic engineering to study the metabolic processes in plants.
Keep exploring BYJU’S Biology for more exciting topics.
Comments