What is Transfection?
It is a process of introducing naked DNA or RNA into the eukaryotic cells. Here, the eukaryotic cells involve the opening of pores in their cell membrane (transient pores) through which the uptake of nucleic acid occurs. This can also be carried out using the electroporation technique or by using a cationic lipid and usually mixing with the nucleic acid material to form liposomes. These liposomes can fuse the target cell membrane and deposit their materials inside the cell.
Thus, this process produces abnormalities in the target cells.
Transfection can be done using-
- Physical methods – Microinjection, Electroporation, Gene gun, etc.
- Chemical methods – Lipofection
- Biological method – Virus-vectors
What is Transduction?
Transduction is also similar to transfection. This term is solely used for the transfer of genetic material into a target cell using viral vectors.
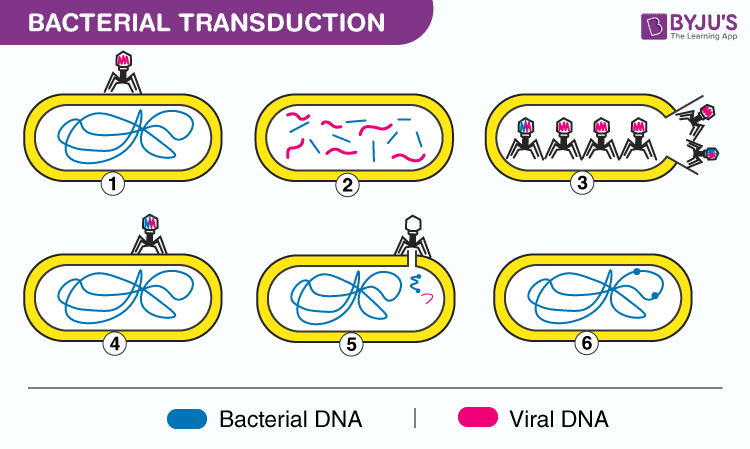
It is typically used to introduce genetic material in a stable way. The ways in which they can be introduced are –
Generalised Transduction
Here, random pieces of genetic material are packed into a bacteriophage and delivered to the target cell.
Specialised Transduction
Here, only a restricted portion of the genetic material is transferred. Example – Lambda phage infecting the bacterial species E.Coli.
Lateral Transduction
When compared to generalised and specialised, this can transfer more genes at high-frequency rates. It usually involves the transfer of long DNA fragments.
Also see : Bacterial Transduction
Difference between Transfection and Transduction
Transfection |
Transduction |
|
It is a gene transfer method that can be done by chemical or non-chemical methods. |
It is a gene transfer method that solely involves viral vectors (biological method). |
|
Uses gene gun, electroporation and lipofection techniques. |
Uses viral vectors such as bacteriophages. |
|
The transient pores open in the target cell membranes through which the genetic material is transferred. |
The viral vector infects the target cell and inserts the given genetic material. |
Also Refer: Bacteriophage
Frequently Asked Questions
What is transformation?
Transformation is also a gene transfer method. Here, direct uptake of the nucleic acids takes place. This alteration occurs through an intervening medium. Also, the uptake of genetic material is solely dependent on the target/recipient cell.
What is horizontal gene transfer?
Horizontal gene transfer is nothing but the movement of nucleic acid between the cells. It can happen between multicellular and/or unicellular organisms. The transfer of the genetic material from parents to offspring is called vertical transfer.
What is a phage?
A Phage is a virus that typically infects and replicates within a bacterial cell. They are used in antibacterial therapy. Also, they can be used as a tool (vector) in recombinant DNA technology. Some commonly known phages are – Lambda phage, M13 phage, P1 phage, phi X 174 phage, etc.
Extended Reading: Bacterial Genetics
Keep exploring BYJU’S Biology for more exciting topics.
Comments