Chromosomes are packed, thread-like structures in a cell. They consist of long sequences of DNA packed by histone and non-histone proteins. Centromeres and telomeres are important regions in a chromosome that perform functions related to cell division and chromosomal protection. Below is a table of differentiation between the centromeres and telomeres.
What is Centromere?
Centromeres are structures that are present at the middle of chromosomes. Attachment point of centromeres divides the chromosomes into long and short arms. Centromeres are the structures that have the kinetochores attached. The kinetochores are complex proteins that assemble machinery for cell division.
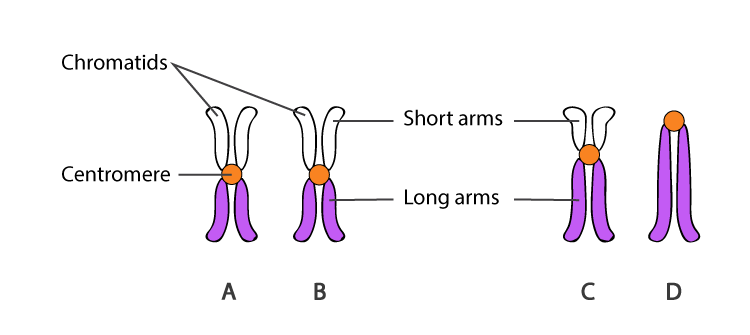
Refer: Function and Types of Centromeres
What is Telomere?
Telomeres are repetitive nucleotide sequences that are present at the end of chromosomes. The telomere determines the age of a cell. As the repetitive sequence of the telomeric region starts to shorten, the cell reaches a point where it cannot divide further and the cell dies. To overcome this problem, a dormant enzyme called telomerase is released, which prevents the shortening of telomeres.
Read about telomeres in detail here.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Centromere is a structure present in the chromosomes that binds the two sister chromatids together. |
Telomeres are repetitive sequences of nucleotides present at the end of chromosomes. |
|
|
|
|
Centromeres are made up of repeated satellite DNA where the sequence in each repeat is similar but not identical. |
Telomeres are made up of repeated sequences of 5′-TTAGGG-3′ in vertebrates. |
|
|
|
|
It is present at the centre of the chromosomes. |
It is present at the chromosomal ends. |
|
|
|
|
It is a structure that holds the kinetochore. The kinetochore assembles the mitotic spindle and microtubules for the division of cells. |
It protects the ends of the chromosomes. As the telomeric region shortens, the cells reach a point where they cannot divide further. This results in the death or ageing of the cells. |
|
|
|
|
Point and regional centromeres. |
No such types. |
Explore BYJU’S Biology for more such differences.
Also Read:
- What Is Telomerase in DNA Replication?
- What is the difference between centromere, centrosome and centriole?
- What is the Difference between Chromosome and Chromatid?
- Who Discovered the Chromosome?
Frequently Asked Questions
How are centromeres and telomeres similar?
Though centromeres and telomeres perform different functions and are present at different locations, they are both made up of repetitive nucleotide sequences and lie in the heterochromatin region of the chromosomes.
What are centromeres and telomeres made of?
Centromeres and telomeres are made up of repetitive nucleotide sequences.
What is the difference between a centromere and chromomere?
Centromeres are structures that are present at the centre of chromosomes, whereas chromomeres are beads or granules that are present throughout the length of the DNA molecule.
How can you differentiate centromeres from telomeres, as per their DNA sequence?
While analysing the DNA sequences of centromeres and telomeres one can notice that the telomeric sequences have highly conserved sequences that hardly vary in comparison to the centromeric sequences.
How many telomeres do we have?
We have a total of 46 chromosomes and each chromosome is supposed to have 4 telomeres in metaphase. Therefore, we are supposed to have a total of 184 telomeres in metaphase.
Comments