Hydroponics or hydroponic farming is the technique of cultivating plants in a nutrient medium solution of water without the presence of soil. Yes, it may sound surprising but scientists have successfully developed a method of cultivating various local crops without soil. The word hydroponics has been taken from two root words, ‘hydros’ meaning water and ‘ponos’ meaning working water.
Visual examples of hydroponic farming can be seen at the hanging gardens of Babylon and floating gardens of China.
In this type of farming, the roots of the plant may or may not be supported by inner media. Perlite, gravel, rock wood, coconut coir, vermiculite, sand and pumice are some of the examples that are used as substrates in hydroponic farming.
Tomatoes, strawberries and lettuce are the most common examples of plants grown hydroponically.
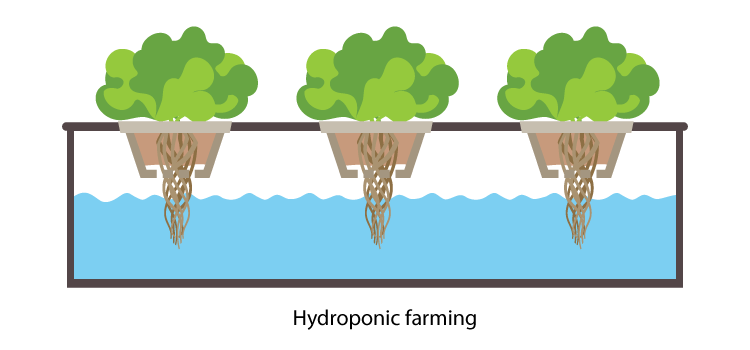
The nutrient solution or the fertiliser solution is composed of macronutrients such as Nitrogen, Potassium and Phosphorus and trace amounts of micronutrients such as Sulphur, Magnesium and Calcium. This solution is prepared in a tank and pumped through the system periodically. Sometimes, the hydroponic farming system also has a recirculating system where the nutrients that are not absorbed in plants are returned to the tank which can be used later.
Sensors and Controllers of Hydroponic Farming
Since hydroponic farming is controlled by humans, there needs to be a way to measure or sense the environmental factors being consumed in the cultivation of plants. Temperature, pH, nutrient concentration, humidity and dissolved oxygen are some of the factors that directly affect the growth of plants.
Electrical conductivity sensors are used to measure the nutrient concentration. Similarly, ultrasonic waves or laser sensors can be used to measure the level of water without touching the system.
Advantages of Hydroponic Farming
- The risk of pathogen contamination is low in hydroponic farming as compared to soil cultures. However, there is a slight chance of contamination through the nutrient tank. To overcome this, a sterilisation or disinfection system of ozone, filters, UV rays or heat is installed in these systems.
- It saves labour because it uses automatic irrigation and fertilising systems.
- It can even be set up indoors in small places which helps to bring greenery in densely populated areas.
- It is also being researched for implementation on spacecraft.
Disadvantages of Hydroponic Farming
- It is costly to install.
- It depends on power and even a few hours of power outage can destroy the crops.
- The nutrient solution needs to be tested frequently.
- It requires expertise.
This sums up in brief about hydroponic farming. Stay tuned to BYJU’S Biology for more interesting topics.
Also Read:
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the disadvantages of hydroponic farming?
Hydroponic farming has the major disadvantage of being costly and requiring learned experts.
What are the types of hydroponics?
The types of hydroponics are:
- Ebb and Flow
- Nutrient Film Technique
- Drip System
- Wick System
- Deep Water Culture
Comments