The rapid increase in the banking sector particularly after the green revolution, the rural sector had a positive impact on farming and non-farming output, employment, and income. These banking opportunities allowed farmers to take different credit services, facilities and various loans to meet their production requirements.
Here are a few major credit sources of rural credit in India.
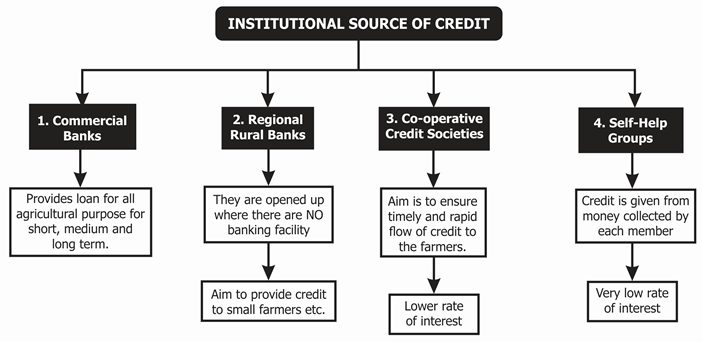
- Co-operative Credit Societies- This source of credit is the most economical and important source of rural credit. It was set up with the aim of facilitating the complete credit needs for small and medium farmers. Co-operative Credit Societies progressed steadily after a few years for inception. They started supporting the farmers in a significant way with short-term loans issued by Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACs), which progressed from ₹305 crores in 1965-66 to ₹5,200 crores in 1999-00. At the same time, the loans granted raised from ₹37 crores to ₹2,100 crores. However, the co-operatives could not meet the credit needs completely, so the moneylenders kept on controlling the rural economic markets.
| You Might Also Like To Read: |
- Land Development Bank- This source of credit is also known as a land mortgage. It essentially gives farmers a long-term loan option upon the mortgage of their land at low-interest rates over a period of 15 to 20 years. These type of loans are usually taken if the farmers have some land developments work or digging of wells, etc, if extra land is to be taken through out-and-out purchase, or if previous dues are to be repaid. Though land development bank has made notable progress still the contribution is insignificant because most of the farmers are not aware of the existence of such land schemes or the importance and use of such banks. However, such a bank set up by the primary banks and the government has increased immensely over the years.
- Commercial Banks- Earlier, these banks were only received deposits from the urban population and issued loans only for trade and industry. They generally neglected agriculture and rural industries because by nature agriculture is a high-risk venture. However, today these banks give both direct and indirect investment to agriculture. Here, direct finance is issued for a small and medium term allowing farmers to conduct agricultural operations easily. Indirect finance is given in advances form to purchase things like grains and fertilisers. Commercial banks also grant finance to the Food Corporation of India, and State food agencies for operations like food procurement. These banks also give credit options for stocking and delivery of agricultural inputs. They have also executed the ‘village adoption scheme’, firstly initiated by the State Bank of India, to examine into credit and additional requirements of the farmers.
- Regional Rural Banks- Government initiated regional rural bank was set up to examine the specific needs of landless workers, small and marginal farmers, rural poor and artesian.
- The Government- The Government provides short and long term goals to farmers if there is an emergency like famine and flood. These type of loans are also known as Taccavo loans.
Quick link: Demographic Condition in Colonial India
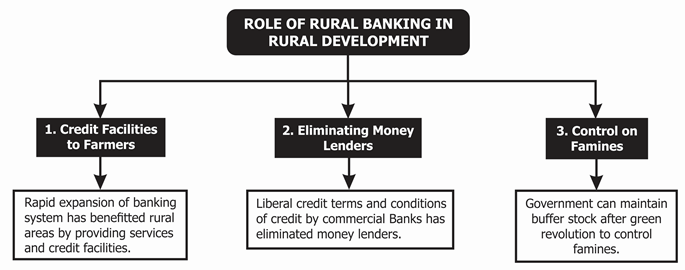
Role of Rural Banking in Rural Development
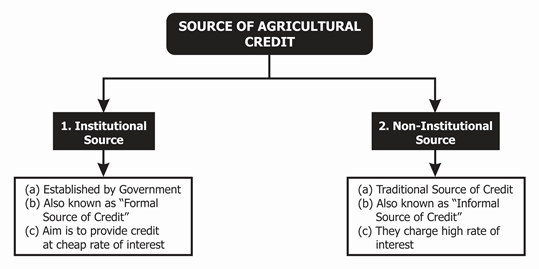
Source of Agricultural Credit
Institutional Source of Credit
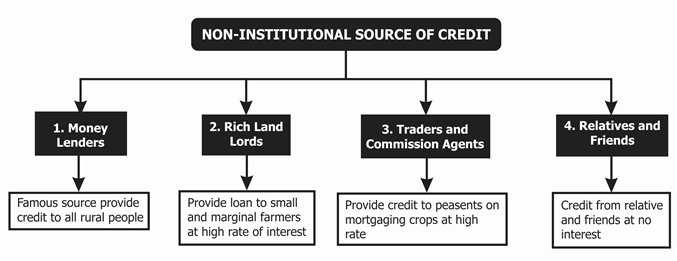
Non- Institutional Source of Credit
| Also, Explore: |
Solved Questions.
| Q1) What is meant by rural credit? |
| ANS: Rural credit means credit for farming families. |
| Q2) What are the micro-credit programmes? |
| ANS: These are the programs which involve developing a credit system of rural areas. |
| Q3) What is microfinance? |
| ANS: Micro Finance is a credit scheme extended to poor through Self Help Groups (SGHs). |
| Q4) What is the apex institution in rural financing? |
| ANS: NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development) is the apex institution. It was set up in July 1982 |
| Q5) Name three institutional sources of agricultural credit? |
| ANS: Three Institutional sources of credit are:
1. Cooperative Credit Society. 2. Commercial Bank. 3. Regional Rural Banks. |
| Q6) Classify rural credit on the base of time |
| ANS: On the basis of time, rural credit can be classified as:
1. Short Term Credit. 2. Medium Term Credit. 3. Long Term Credit. |
| You Might Also Like To Read: |
For more data on Economics Class 11 Syllabus, Commerce notifications and sample papers for Class 11 Commerce, stay tuned to BYJU’S.
Comments