Amoebae are microscopic unicellular organisms that belong to the family Amoebidae. They are freshwater organisms found at the bottom of ponds and streams in the decaying vegetation. They can be identified by their shape changing ability from their cytoplasmic extensions called pseudopodia.
Classification
|
Domain |
Eukaryota |
|
Phylum |
Amoebozoa |
|
Class |
Tubulinea |
|
Order |
Euamoebida |
|
Family |
Amoebidae |
|
Genus |
Amoeba |
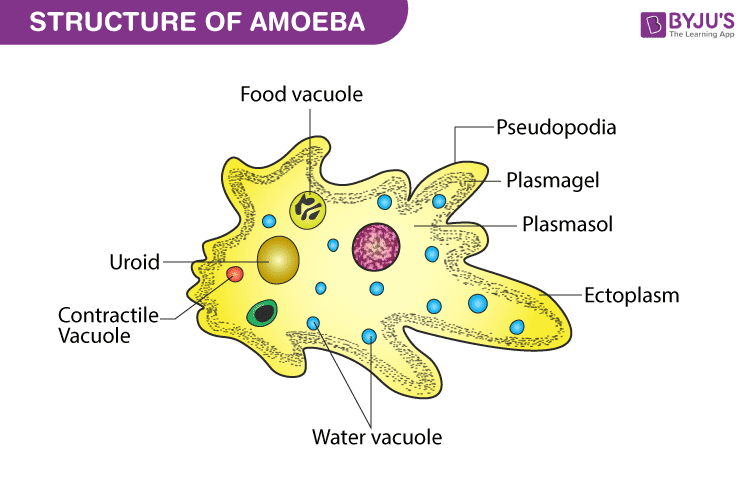
Well-Labelled Diagram of Amoeba
Characteristics
- August Johann Rösel von Rosenhof, a German naturalist was the first person to reference amoebae in 1755.
- The distinguishing feature of the amoeba is its ability to change shapes with the help of cytoplasmic extensions called pseudopodia.
- Pseudopodia, also called false feet, are tubular extensions that are rounded at the end and help in movement of the organism.
- The amoeba is made up of jellylike cytoplasm which differentiates to form a thin outer plasma membrane, a stiff layer of clear ectoplasm just inside the plasma membrane and a central endoplasm that is granular in nature.
- The endoplasm houses a granular nucleus, food vacuoles and a contractile vacuole.
- The amoeba possesses no mouth or anus.
- They feed by surrounding their cytoplasmic extensions around the food particle and then forming a vacuole. Enzymes are then secreted to digest the food particles.
- The contractile vacuole functions to remove excess water from the amoeba and thus maintain the osmotic pressure of the organism.
- The mode of reproduction is asexual and it divides by binary fission.
- The amoebas can survive in extreme environmental conditions by undergoing encystation. It is the phenomenon of secreting a cyst membrane all around by becoming circular and losing all water. The amoebas get back to their original shape once the surroundings improve.
Stay tuned to BYJU’S for more updates on NEET.
Also Read:
Comments