Table of Contents
Introduction
A seed is an important part of a flowering plant, which gives rise to a new plant on seed germination. The seeds vary in their shapes, colours and sizes. Some seeds are oval in shape, while some are round, wrinkled, hairy, or winged. The main parts of a seed are:
- Embryo
- Seed Coat
- Endosperm
Among all these three parts of a seed, the embryo is the most important part and is developed from the fertilized egg. It is diploid and comprises the embryonic root and embryonic shoot of the plant, which later develops into a new plant. The different parts of an embryo are:
- Radicle
- Epicotyl
- Hypocotyl
- Cotyledons
Let’s learn in detail about Cotyledon.
What is Cotyledon?
Cotyledon refers to the significant part of the embryo found within the seed. It is the first and the tender leaf that emerges when the seed germinates. It is also called the storage unit of a seed, as it provides nutrients to the different parts of an embryo.
Types of Cotyledons
Based on the number of cotyledons in a seed, it is further classified into the following types.
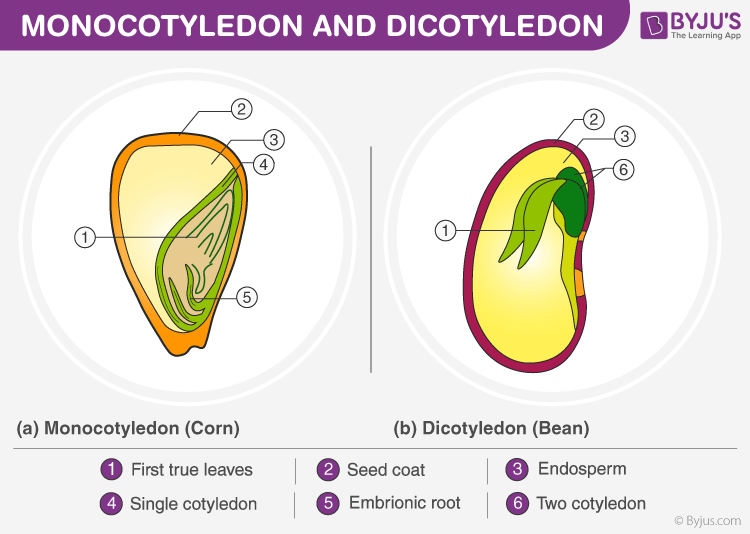
Monocotyledons
It comprises a single cotyledon emerging from the seeds after seed germination. Paddy, wheat, coconut, garlic, and ginger are the best examples of monocotyledons. Monocotyledons are also known as monocots.
Dicotyledonous
It comprises two cotyledons emerging from the seeds after seed germination. Almonds, cashews, tomatoes, and peas are the best examples of dicotyledonous. Dicotyledons are also known as dicots. There are around 200,000 species of dicotyledons
Explore more: Dicotyledonous and Monocotyledonous Seeds
This article concludes with an introduction to cotyledon and its types. To know more about cotyledons, other related topics and important questions, keep visiting our website at BYJU’S Biology.

Comments