Dicotyledons are members of flowering plants in the Plant Kingdom that consist of two cotyledons in the embryo of their seed. More than 175,000 species of dicots are known today. The most common examples include roses, magnolias and geraniums.
A dicot plant is well differentiated into roots, stems and leaves. Flowers consist of petals, sepals, pistil and stamen. The leaves have a well-built vascular system for the transport of food and nutrients throughout the plant.
This article focuses on describing the anatomy of a dicot leaf. Find a well-labelled and simple diagram of the transverse section (t.s.) of a dicot leaf below.
T.S. of a Dicot Leaf
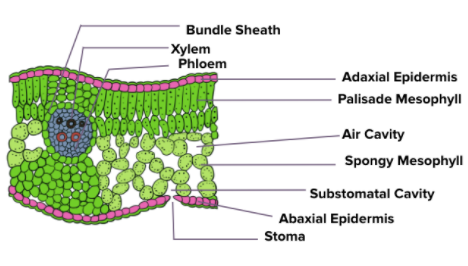
Anatomy of a Dicot Leaf
- A dicot leaf shows a dorsiventral structure, meaning an upper surface called the adaxial surface and a lower surface called the abaxial surface. The two surfaces differ from each other in appearance and structure.
- Broadly, a dorsiventral dicot leaf shows three structures, namely – epidermis, mesophyll and vascular system.
- The epidermis is present on both the upper and lower surfaces of a leaf with thin cuticles which protect the plants against mechanical and physical injury.
- In between the upper and lower epidermis is found a layer called the mesophyll. It is made up of parenchymatous cells and consists of chloroplasts that perform photosynthesis.
- The mesophyll is of two types – spongy parenchyma and palisade parenchyma.
- The palisade parenchyma is present towards the upper surface (adaxial) and is made up of long and elongated cells that are placed in parallel arrangement to each other.
- The spongy parenchyma extends towards the lower epidermis and is made up of round and loosely arranged cells.
- There are a number of spaces and cavities present in between these cells known as air cavities.
- The abaxial surface generally bears more stomata than the adaxial surface.
- The vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) are arranged in vascular bundles and are mainly found in the veins and midrib region.
- The vascular bundles are protected by bundle sheath cells that are composed of one or more layers of parenchyma cells.
This sums up the anatomy of a dicot leaf. Stay tuned to BYJU’S for more such interesting topics related to NEET.
Also Read:
Comments