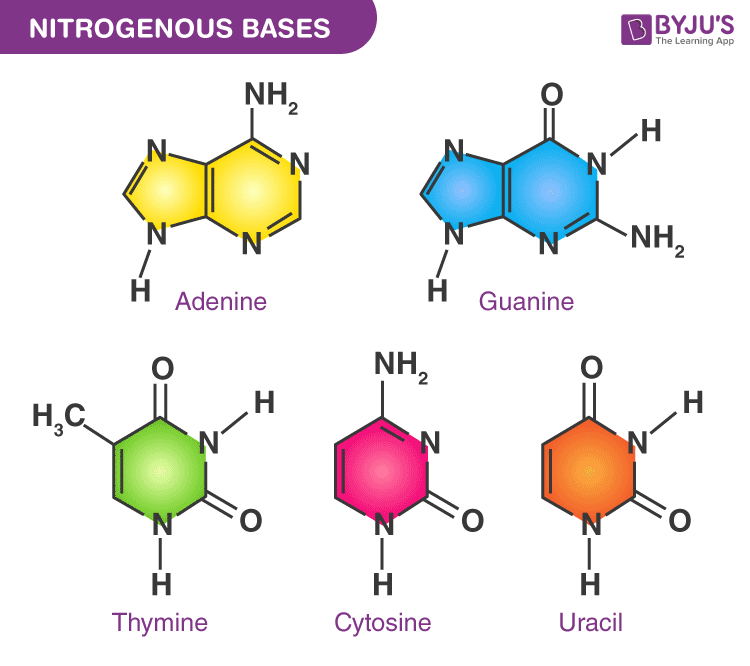
Cytosine
Cytosine is a pyrimidine that has a heterocyclic aromatic ring. In both DNA as well as RNA, it pairs with another base called guanine. This is called complementary base pairing.
It has an amine group at C4 and a keto group at the C2 position.
Thymine
Thymine is a pyrimidine structure found only in DNA. In RNA, a nucleobase called uracil replaces the thymine. Thymidine or deoxythymidine is a nucleoside molecule of thymidine. This nucleoside is created by the combination of thymine and deoxyribose.
It has two keto groups at C4 and C2. Also, it has a methyl group at the C5 position.
Difference between Cytosine and Thymine
Cytosine |
Thymine |
|
Chemical formula – C4H5N3O |
Chemical formula – C5H6N2O2 |
|
It is a nitrogenous base found in both DNA and RNA. |
It is a nitrogenous base found only in DNA. |
|
Guanine is the complementary base pair of cytosine. |
Adenine is the complementary base pair of thymine. |
|
Cytosine and guanine are connected by three hydrogen bonds. |
Thymine and adenine are connected by two hydrogen bonds. |
|
It has an amine group and a keto group. |
It has two keto groups and a methyl group. |
Frequently Asked Questions
What are nitrogenous bases?
What is complementary base pairing?
The lock and key pairing of nucleobases are called base pairing. It is always Adenine that pairs with Thymine or Uracil. Likewise, Cytosine pairs with Guanine. Various functions of the DNA are based on this complementary base pairing.
What are purines and pyrimidines?
The nitrogenous bases can be either purines or pyrimidines. Purines have a pyrimidine ring with an imidazole, whereas pyrimidines have two nitrogen atoms. Adenine and guanine are called purines. Cytosine, thymine and uracil are the pyrimidines.
What is cytidine?
Cytosine with a ribose ring (sugar structure) forms a nucleoside molecule. This nucleoside is called cytidine. Also, if the ribose ring is deoxyribose, it is called deoxycytidine.
Also Read:
- What is Nucleotide?
- Difference between Nucleotide and Nucleoside
- Difference between Purines and Pyrimidines
Keep exploring BYJU’S Biology for more exciting topics.
Comments